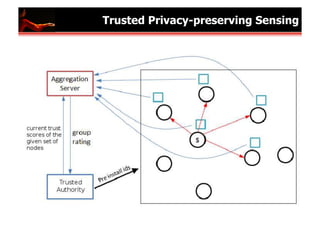
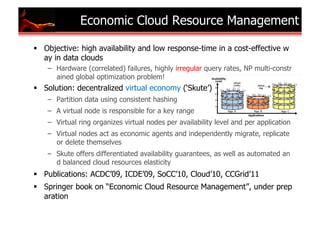
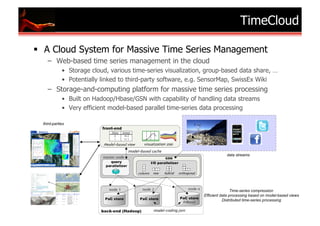
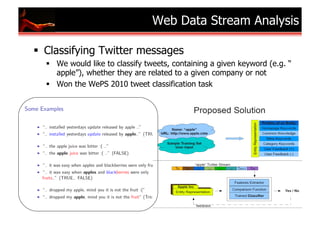
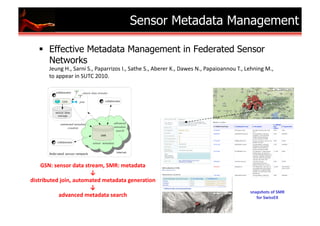
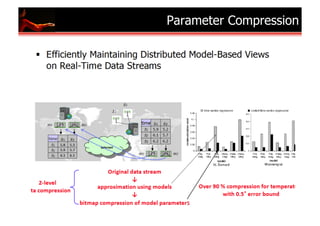
The document outlines research and developments in sensor data management and web data management at EPFL, focusing on global sensor networks, time series compression, and resource allocation in distributed cloud systems. It discusses various methodologies for sensor metadata management, economic cloud resource strategies, and innovations in data integration and analysis, including semantic annotation and probabilistic reasoning techniques. Several key publications and frameworks, such as SEMITRI and the economic resource management system 'skute,' are mentioned in relation to improving efficiency and collaboration in data processing.



![Data Compression
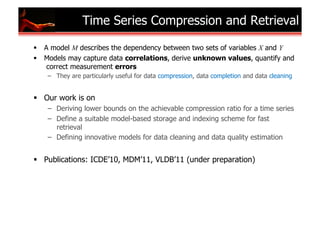
Towards Multi-Model Approximation of Time-Series
Thanasis Papaioannou, Mehdi Riahi, Karl Aberer [MDM 2011] (under review)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sensordatamanagement-110810104902-phpapp02/85/Sensor-Data-Management-9-320.jpg)
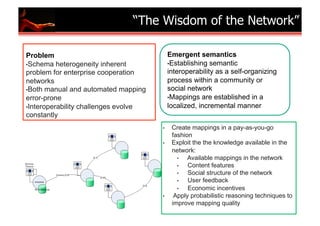
![Sensor Context Extraction
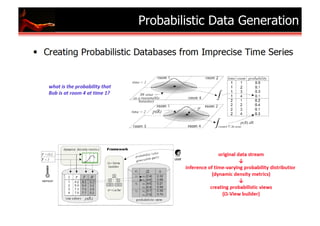
SeMiTri: A Framework for Semantic Annotation of Heterogeneous Trajectories
Z. Yan, D. Chakraborty, C. Parent, S. Spaccapietra, K. Aberer [EDBT 2011]
Objec&ve:
A
Middleware
for
automa&cally
annota&ng
trajectories
of
different
types
of
moving
objects
(cars,
people)
Spa&al
join
(region)
bus metro walking
Semantic
trajectory home office market home
Semantic Annotation Middleware
Map-‐matching
(road
network)
Hidden
Spatial Map
Markov
Join Matching
Model
HMM
(point
of
Interest)
region road network point of interest
e1 e2 e3 e4 e5 e6 e7
GPS
episodes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sensordatamanagement-110810104902-phpapp02/85/Sensor-Data-Management-11-320.jpg)