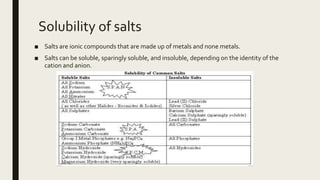
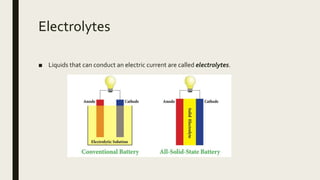
This document discusses chemical changes that occur in aqueous solutions. It explains that water is a polar solvent that is able to dissolve many ionic and polar compounds. When ionic salts dissolve in water, their ions dissociate from each other. Acids also ionize when dissolving in water, representing a chemical change. The solubility of different compounds, such as salts, in water depends on factors like the identity of the ions and whether they form strong ionic bonds. Precipitation reactions can occur when two soluble salts are mixed and one of the resulting salts is insoluble.