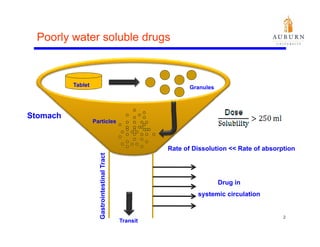
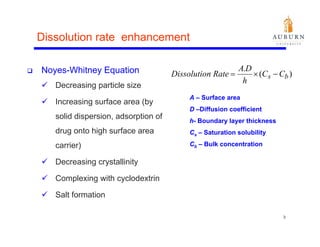
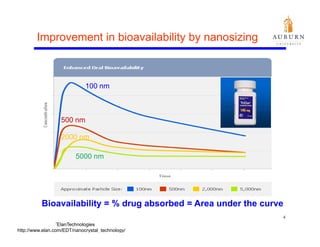
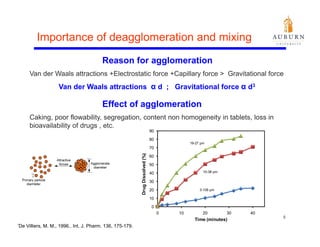
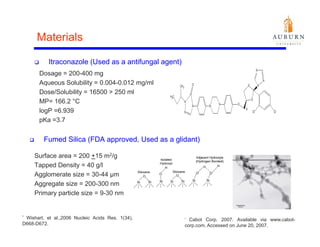
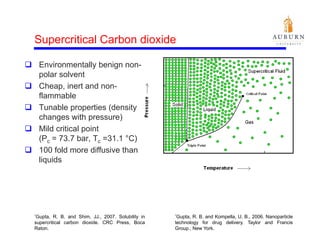
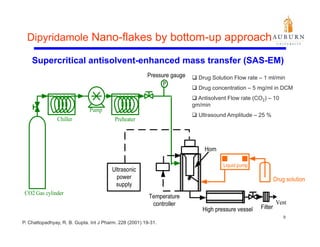
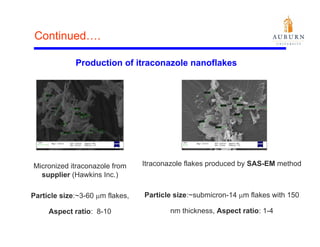
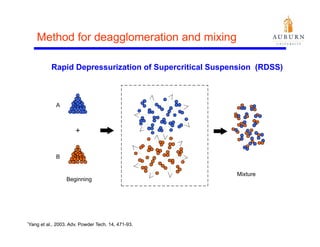
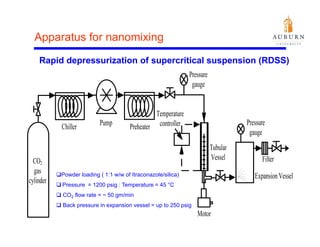
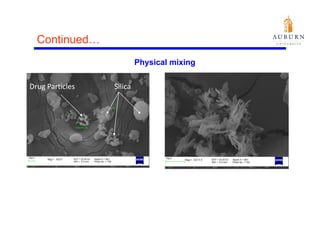
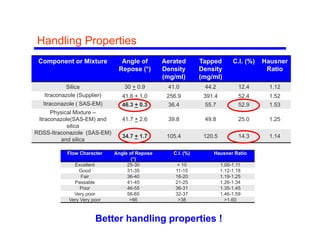
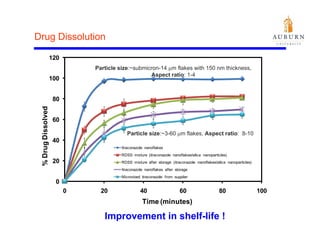
This document summarizes a study on enhancing the shelf-life and handling properties of itraconazole drug nanoparticles by mixing them with silica at the nanoscale using rapid depressurization of supercritical suspensions (RDSS). Poorly soluble itraconazole drug flakes produced by a bottom-up approach were deagglomerated and uniformly mixed with fumed silica nanoparticles using RDSS. This resulted in improved flowability, physical stability over time, and constant drug dissolution rate compared to pure drug flakes. The presence of silica particles between itraconazole nanoflakes improved stability by preventing reaggregation.