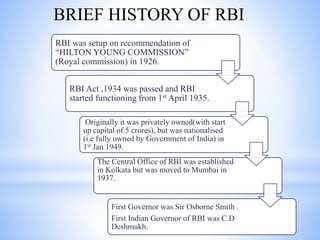
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India's central bank. It was established in 1935 under the Reserve Bank of India Act and is headquartered in Mumbai. RBI was set up on the recommendations of the Hilton Young Commission in 1926. Some key points about RBI:
- It regulates the country's banking and monetary system and oversees functions like issuing currency, controlling credit and foreign exchange.
- RBI has four zonal offices and 31 other local offices across India. It has two training colleges for its officers in Chennai and Pune.
- As a central bank, RBI cannot directly participate in business or trade activities. It is prohibited from purchasing immovable property or