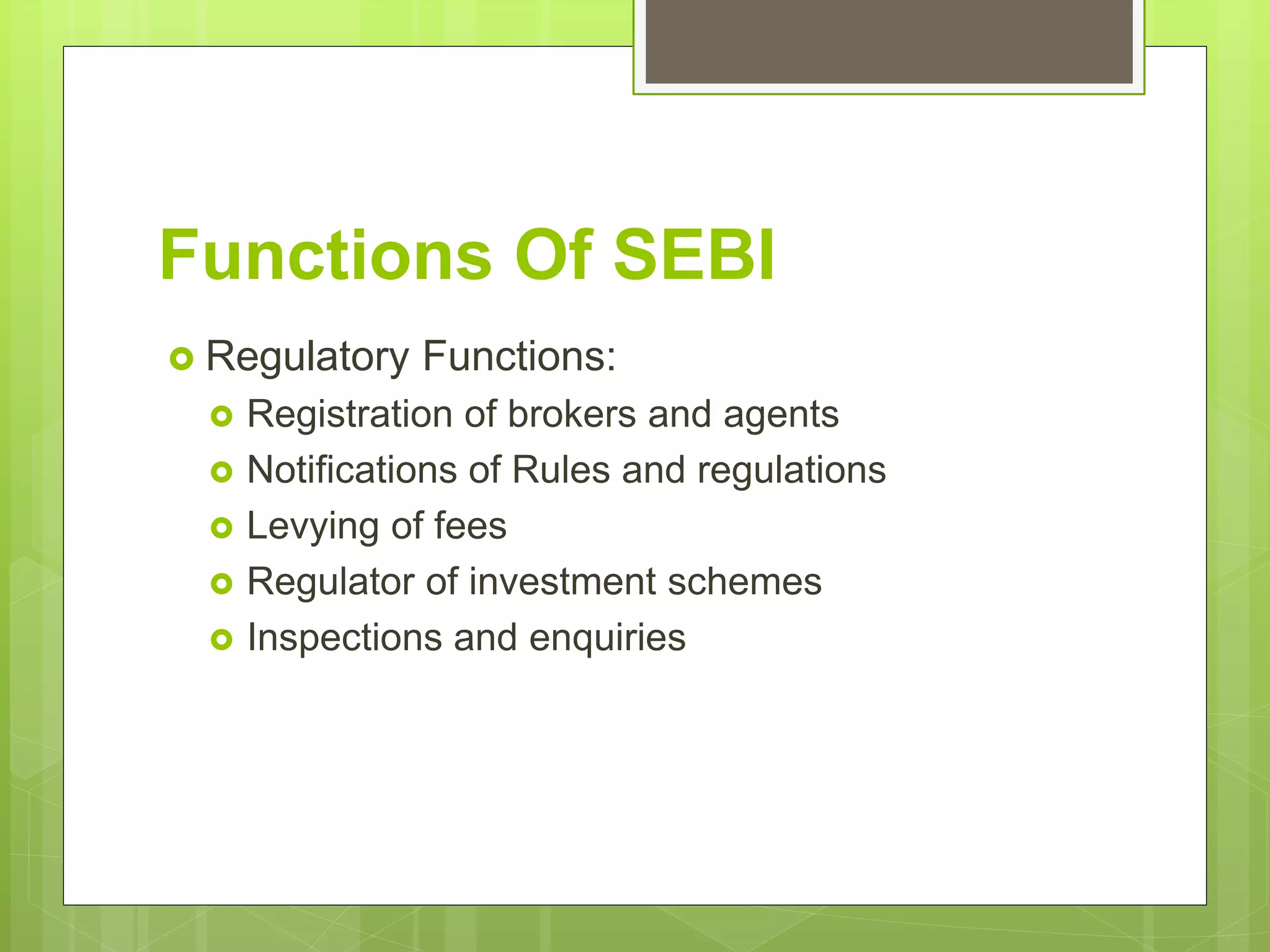
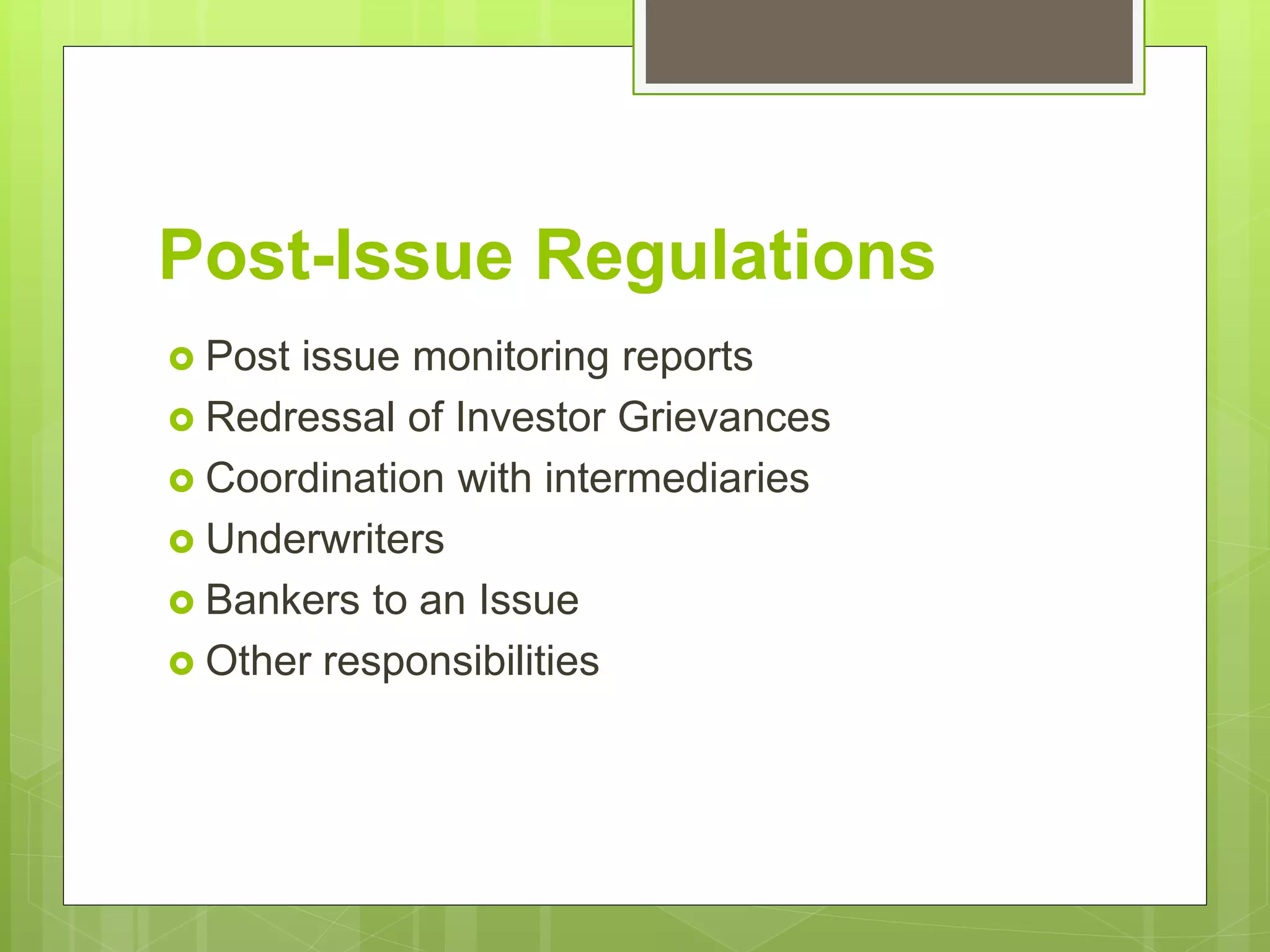
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the apex regulatory body for the securities market in India. It was established to protect investors, maintain fair practices, and promote the development of the securities market. SEBI regulates stock exchanges, trading of securities, registration of market intermediaries, and issues guidelines for companies regarding public offers. It aims to educate investors and enforce regulations regarding insider trading, disclosure requirements, and corporate governance.