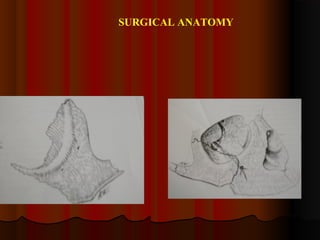
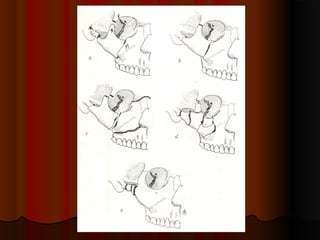
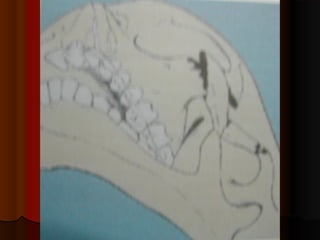
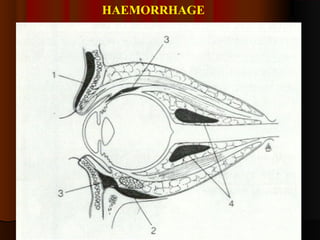
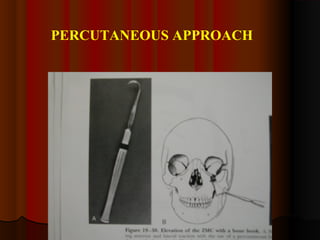
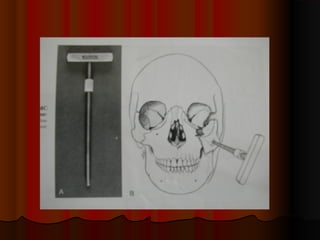
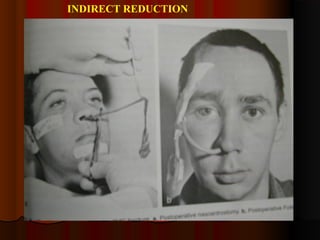
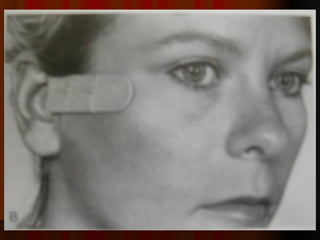
This document discusses fractures of the zygomatic complex, which is part of the cheek bone. It begins with the surgical anatomy and classifications of fractures. Common signs and symptoms are outlined, including flattening of the cheek, swelling, bruising around the eye. Causes of complications like double vision and sunken eyes are explained. Techniques for reduction and fixation of fractures are described, including both closed and open reduction approaches as well as different surgical incisions.