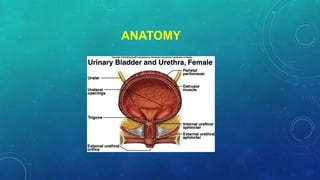
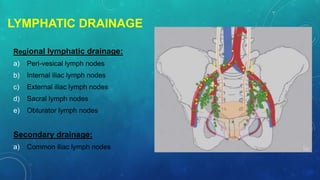
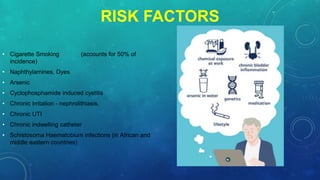
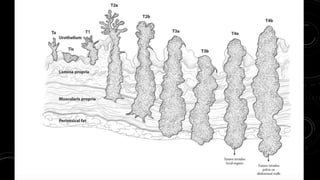
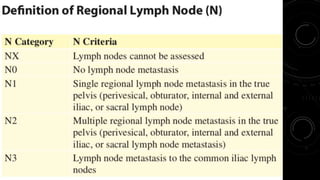
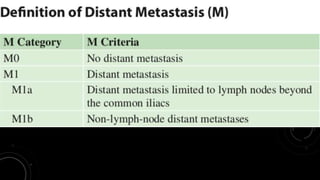
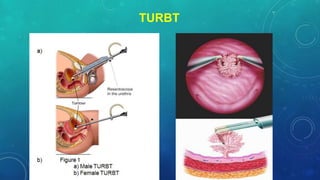
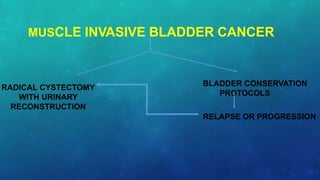
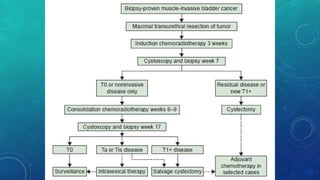
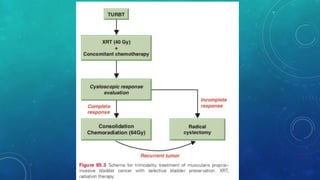
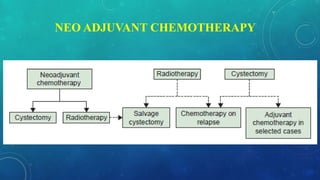
This document discusses radiotherapy planning for carcinoma of the urinary bladder. It begins with epidemiology of bladder cancer, noting it is the 11th most common cancer worldwide and more common in men than women. Risk factors include smoking, chemicals, and chronic irritation. Symptoms include blood in the urine and pain. Diagnostic workup involves tests like cystoscopy and imaging. Treatment depends on tumor stage and grade as well as patient factors. For early stage cancers, options include transurethral resection of the bladder tumor followed by immunotherapy with bacillus Calmette-Guerin or intravesical chemotherapy. For muscle invasive cancers, options are neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy or bladder preservation protocols with chem

















![RADIOTHERAPY DOSE
T1 high-risk [ CTRT
• PTV - 45 Gy,
• boost up to 61.2 Gy
Bladder preservation.
• PTV - 40–45 Gy, then cone down
• PTV bladder - 54 Gy, then cone down
• PTV tumor bed - 64.8 Gy [with concurrent chemo]
Post-op - pT3-4 pN0-2:
• Pelvic nodes (and cystectomy bed if +margins) to 50.4 Gy.
• Local recurrence after cystectomy
• 45–50 Gy to pelvic nodes,
• 60–65 Gy to gross local recurrence with cisplatin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/radiotherapyplanningincarcinomaurinarybladder-210707145920/85/Radiotherapy-planning-in-carcinoma-urinary-bladder-33-320.jpg)

