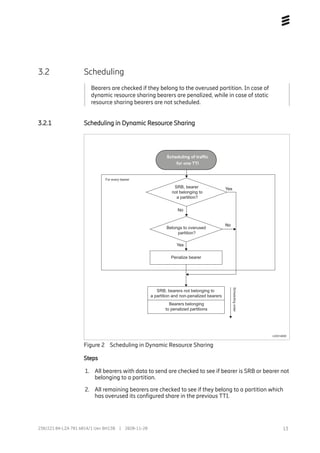
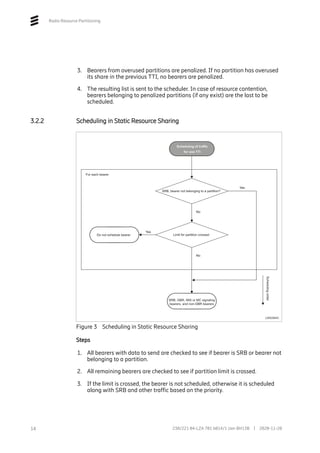
The Radio Resource Partitioning feature enables the configuration of predefined shares of radio resources in a network where resources are shared between user categories. Up to six partitions can be configured per cell based on PLMN or SPID, with each partition assigned a specific resource share. In dynamic sharing, partitions using more than their share are de-prioritized, while in static sharing partitions are limited based on their share. Priority bearers like SRB and signaling are excluded from partitioning.













![3.3 Configuration
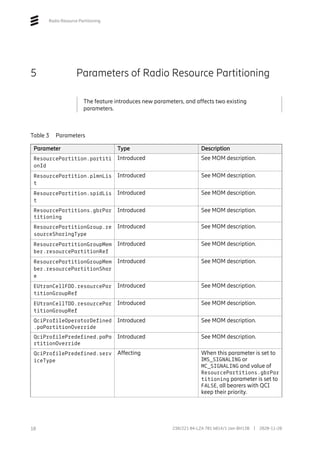
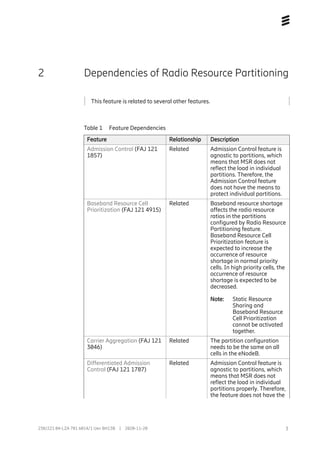
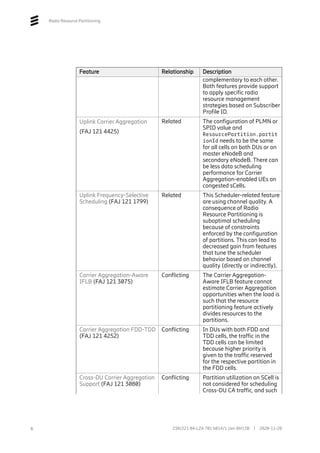
The configuration is done by creating ResourcePartition and
ResourcePartitionGroup MOs, which define the share of radio resources.
0..24
ENodeBFunction
ResourcePartitionGroup
resourceSharingType
EUtranCellFDD/TDD
resourcePartitionGroupRef
PmEventService
cellTracePartitionMcsResolution
ResourcePartitions
gbrPartitioning
ResourcePartition
partitionId: [0, 1..24]
plmnList: [0..6]
spidList: [0..20]
ResourcePartitionGroupMember
resourcePartitionRef:
resourcePartitionShare: [0..100]
0..6
0..24
1
L0001470D
Figure 4 New MO Structure for Radio Resource Partitioning
Configuration of the Radio Resource Partitioning feature is done in the following
way:
1. A set of ResourcePartition MOs is created. The
ResourcePartition.plmnList attribute is used if partitioning is done
based on PLMN, and ResourcePartition.spidList attribute is used if
partitioning is done based on SPID.
Note: The SPID value of 0 can exist in the ResourcePartition.spidList
to include UEs with no SPID value set by the core network. A
partition can be configured using an empty
ResourcePartition.spidList which will include all UEs with any
SPID value.
2. The ResourcecPartitions.gbrPartitioning attribute can be set to TRUE
(by default FALSE) to enable partitioning of GBR traffic.
3. A ResourcePartitionGroup MO is created. The group contains up to six
ResourcePartitionGroupMember MOs. Each MO references an existing
ResourcePartition MO and defines the share (in percentage) of radio
resources the partition can be granted in the cell.
DYNAMIC (by default) or STATIC resource sharing type can be configured for
each cell.
238/221 04-LZA 701 6014/1 Uen BH13B | 2020-11-20 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/radioresourcepartitioning-230717190225-19193f23/85/Radio-Resource-Partitioning-pdf-19-320.jpg)