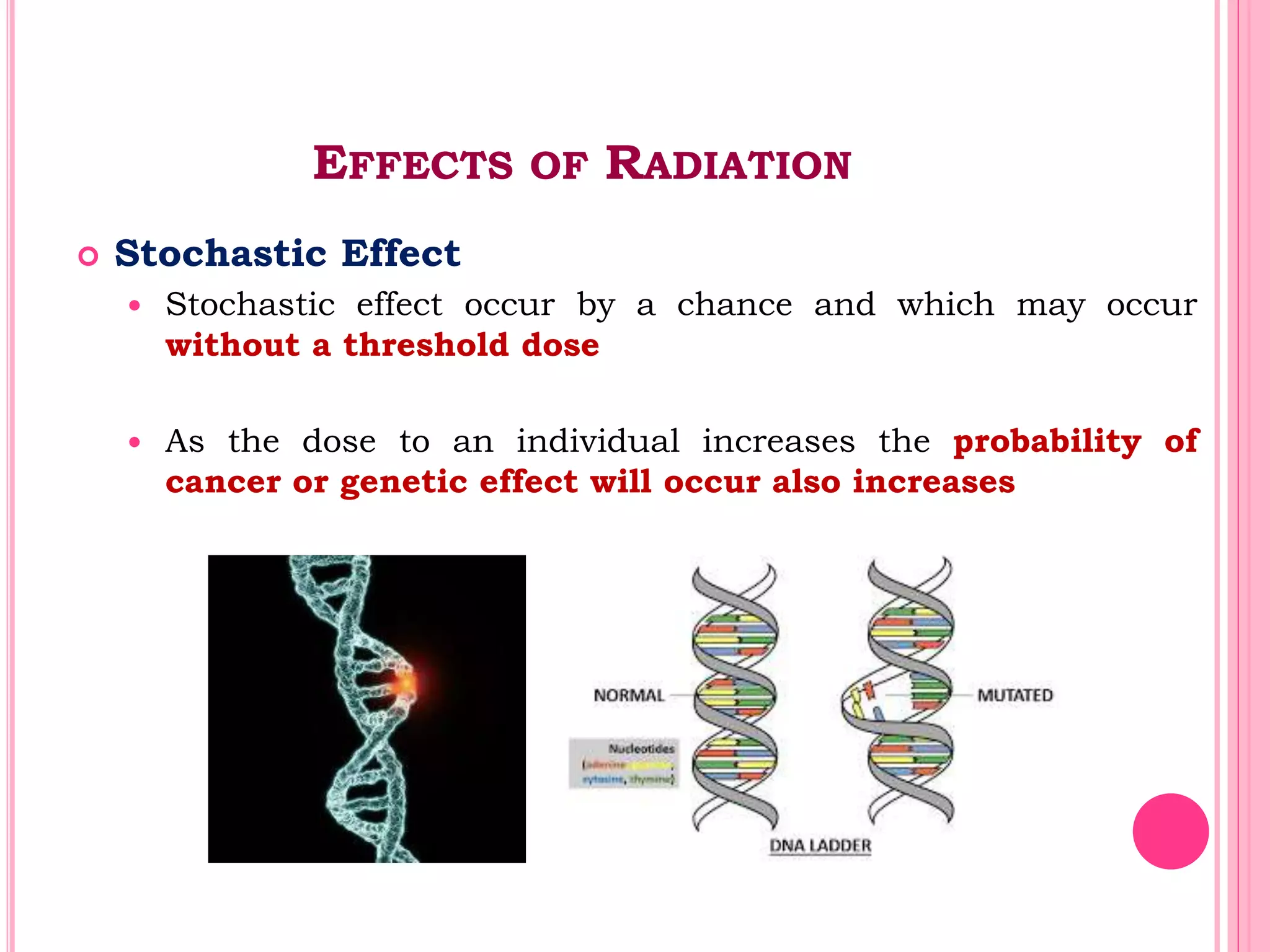
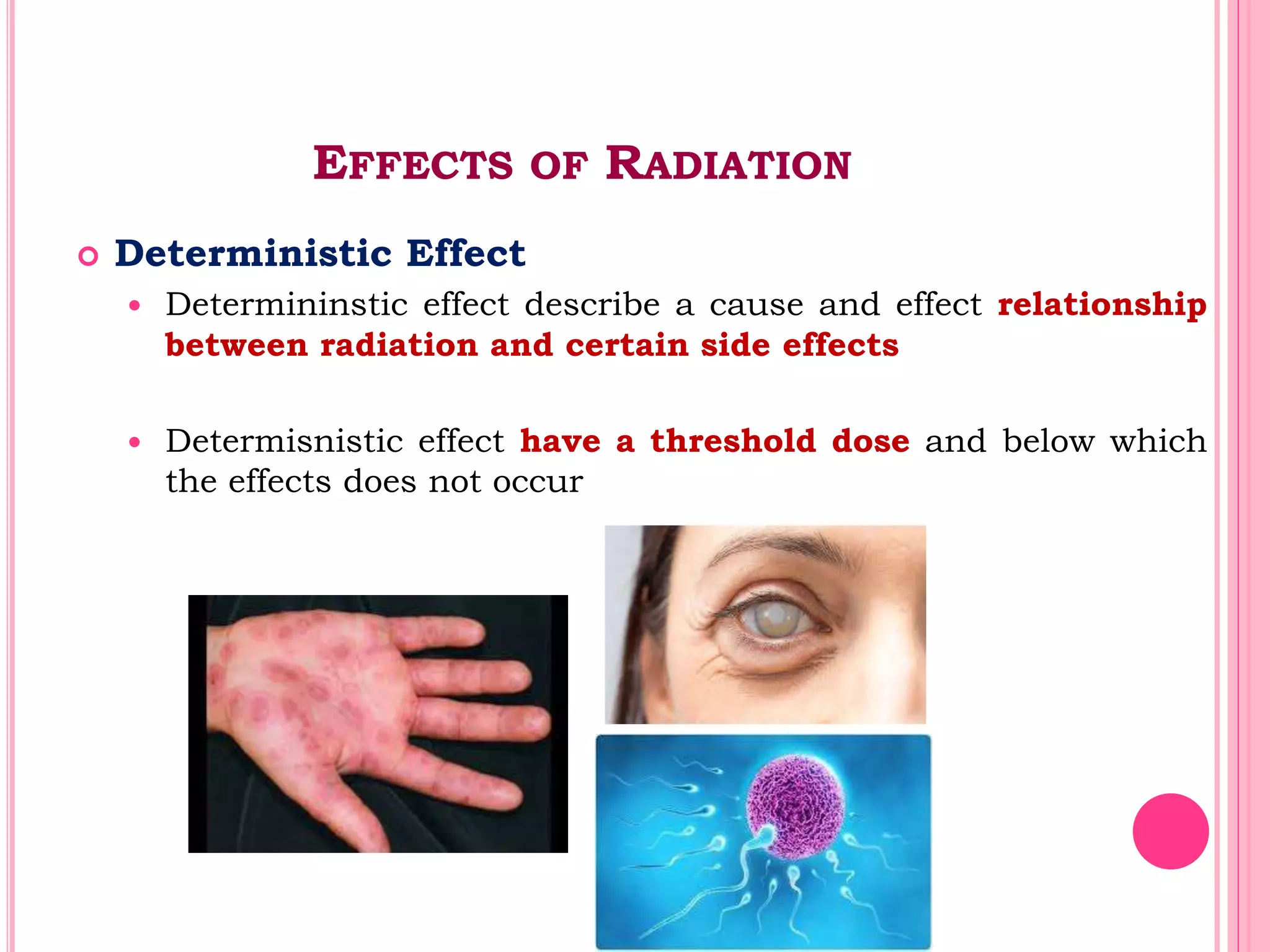
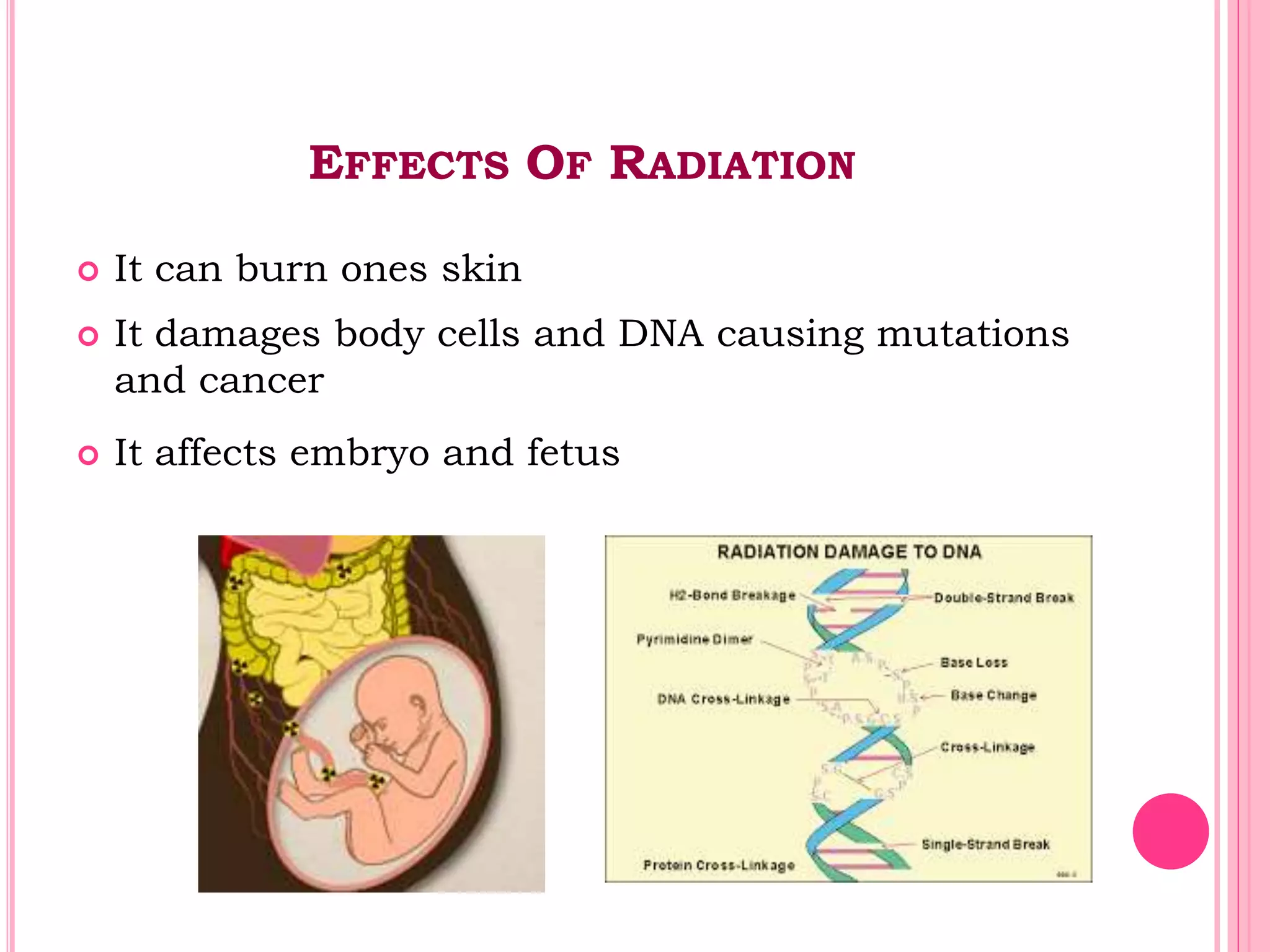
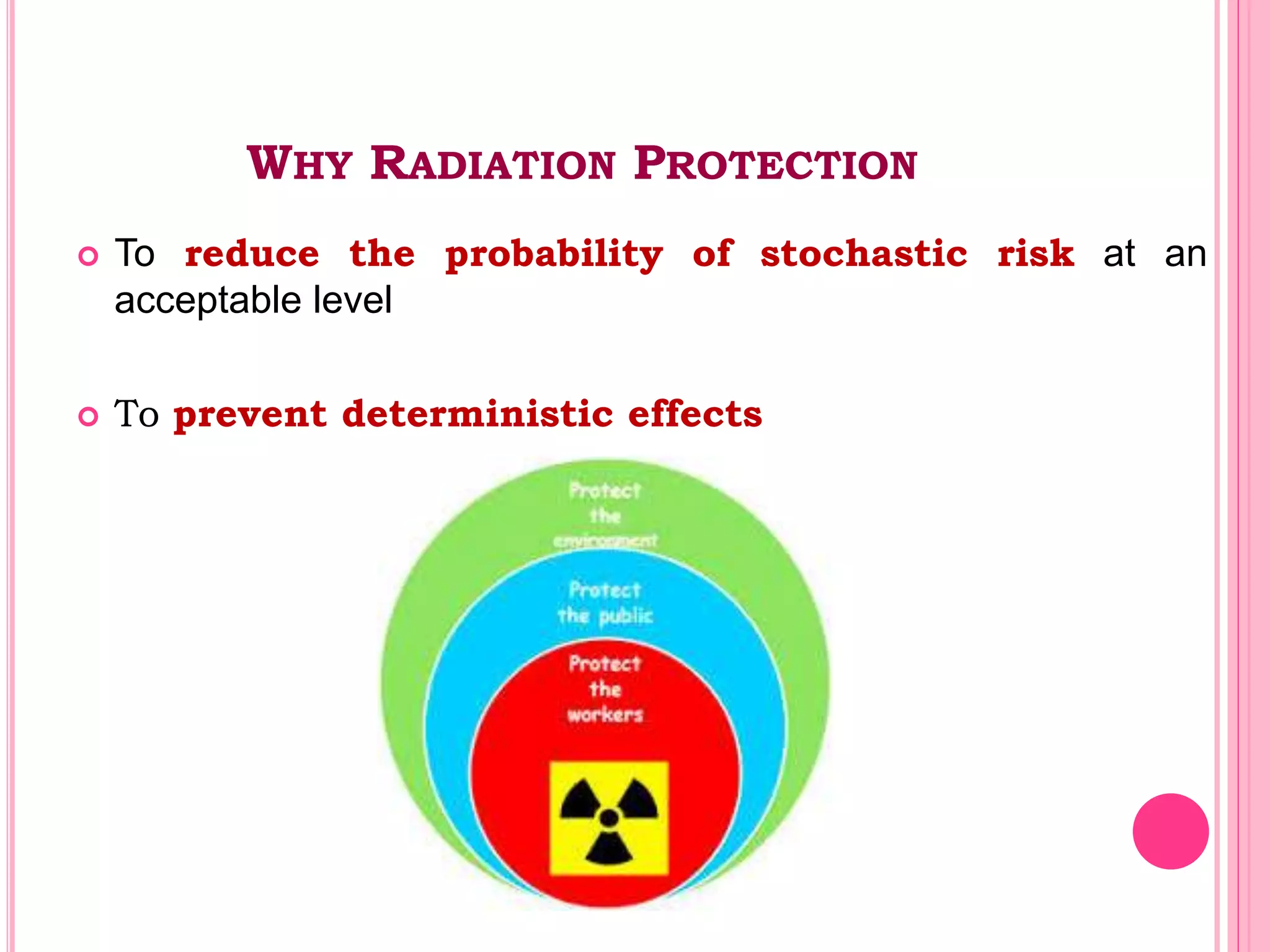
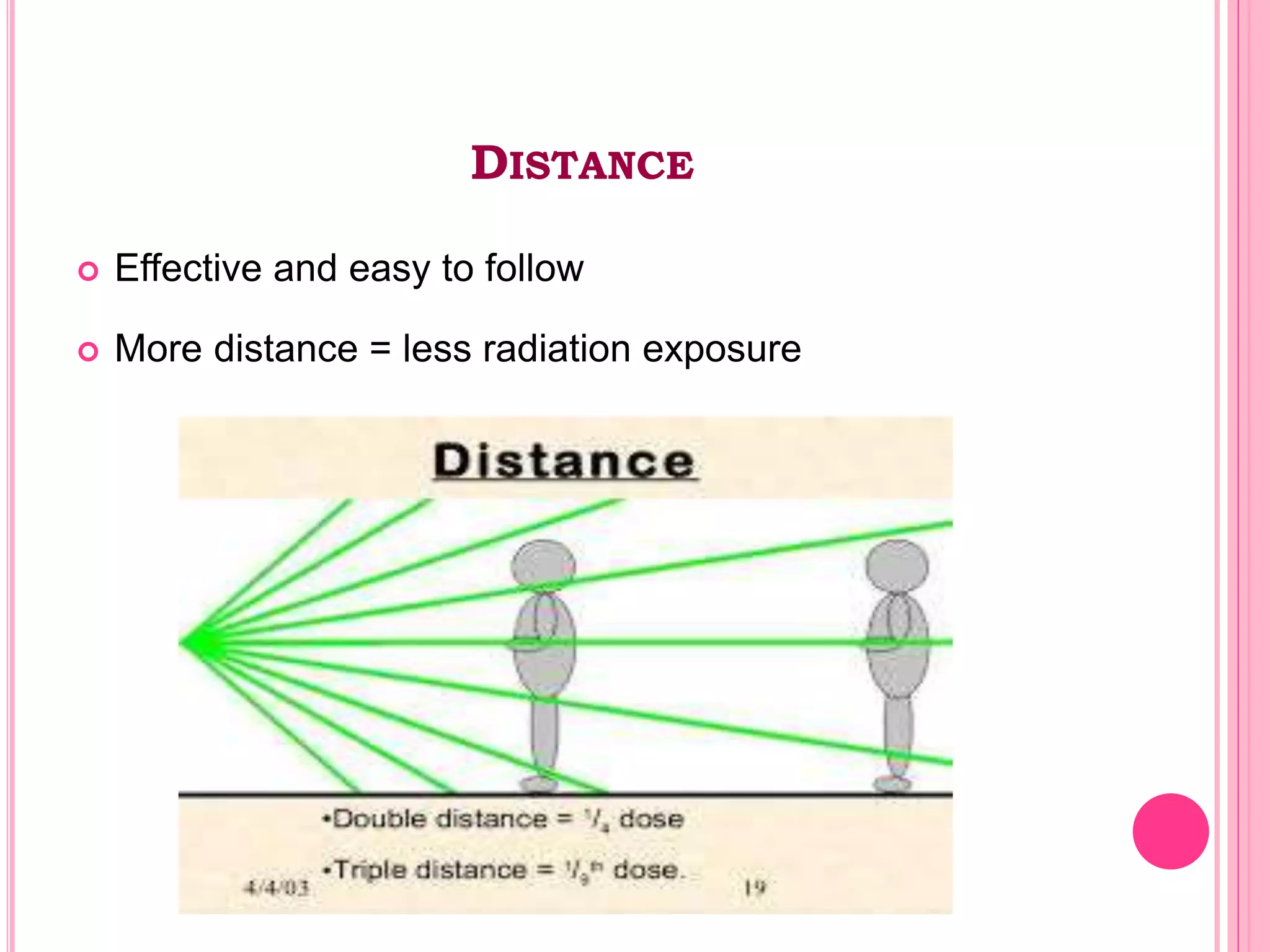
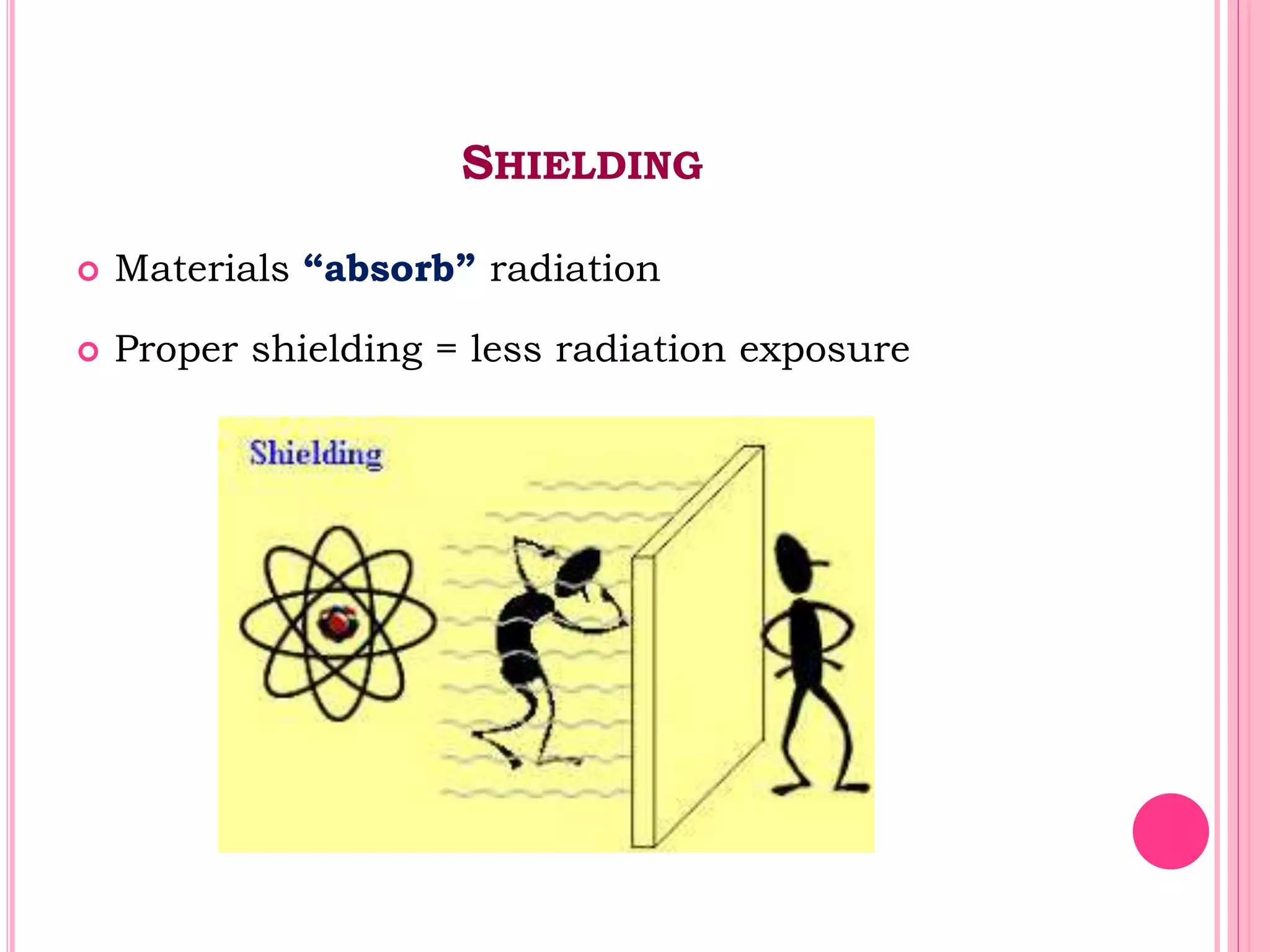
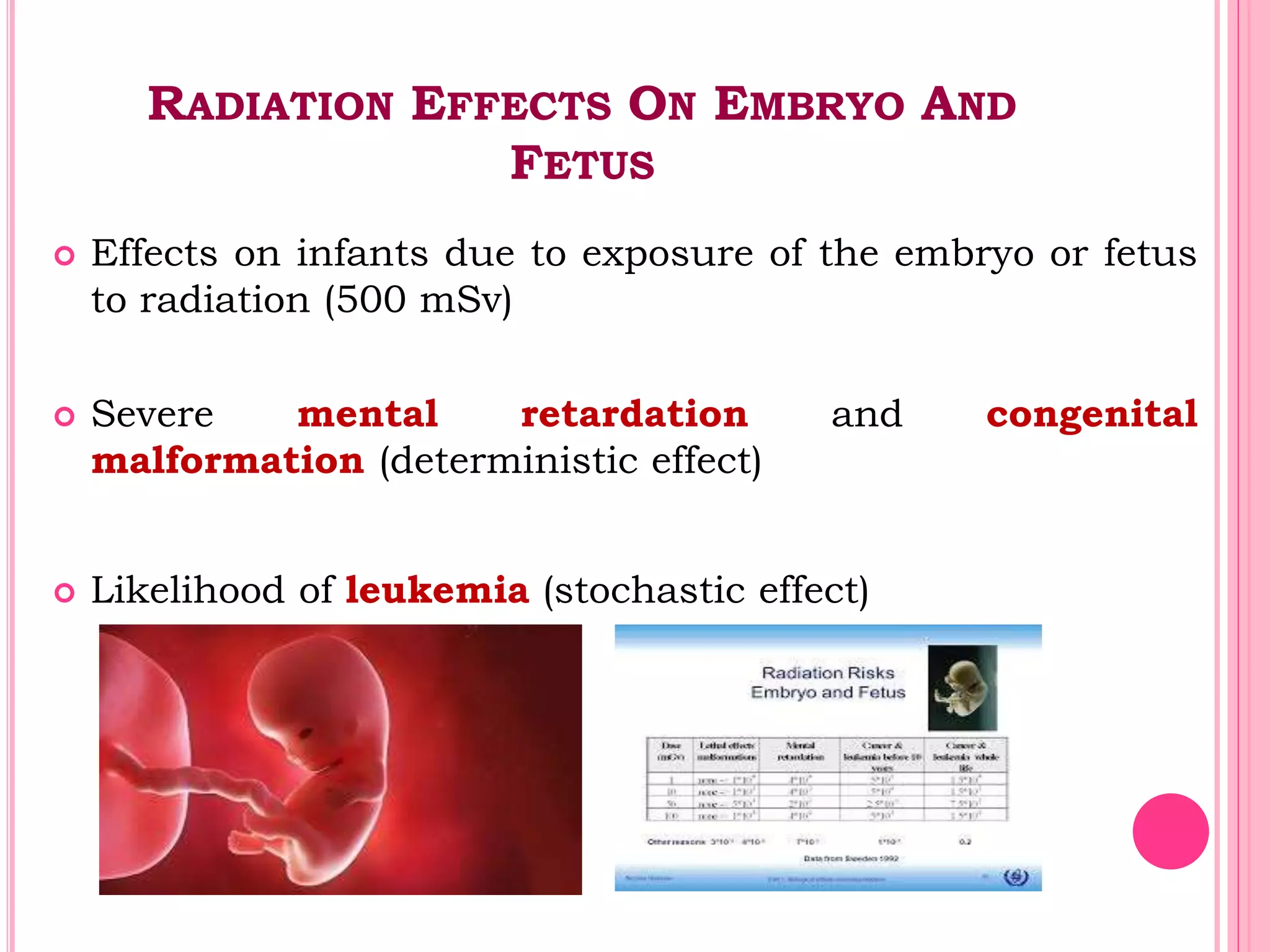
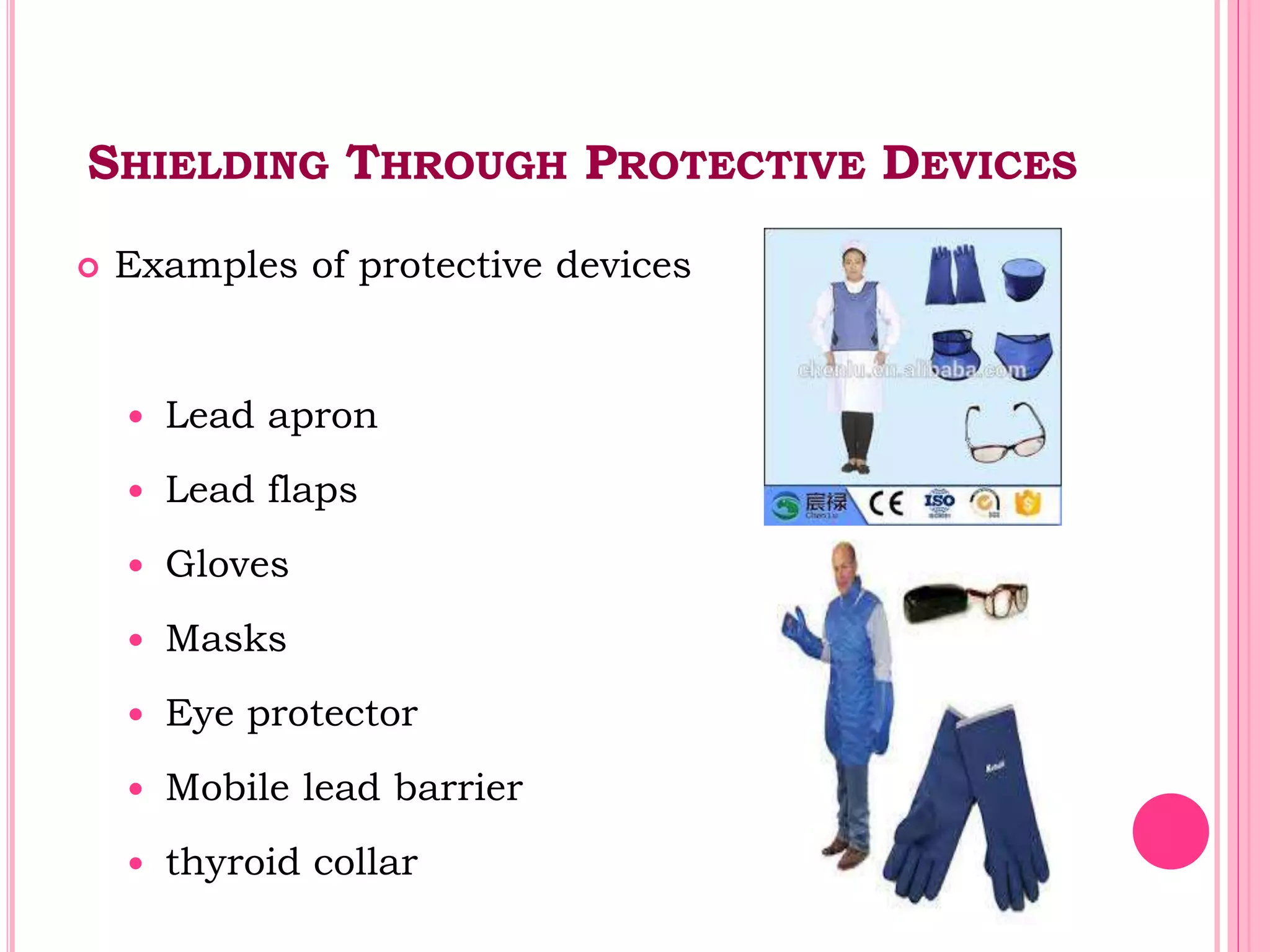
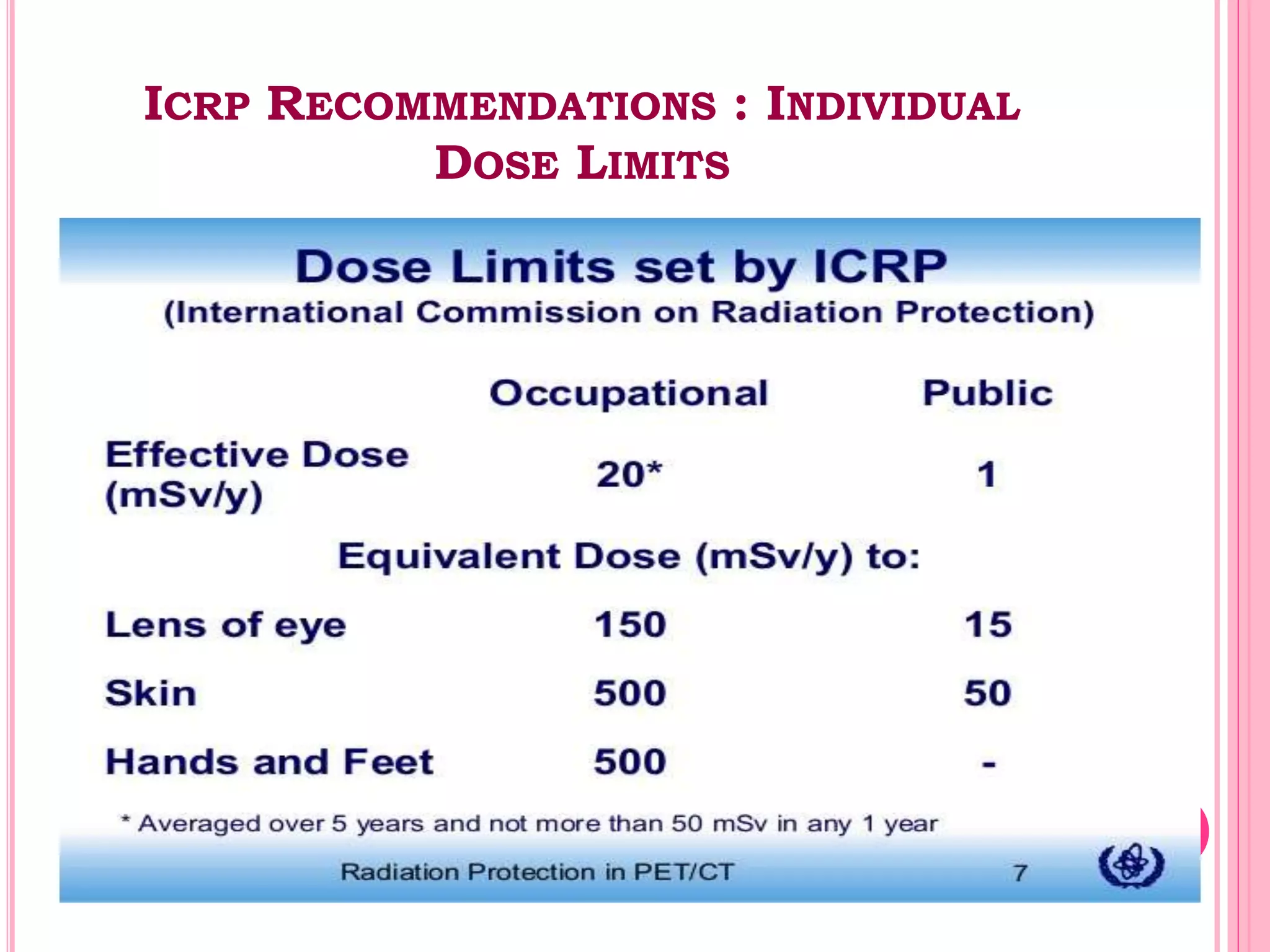
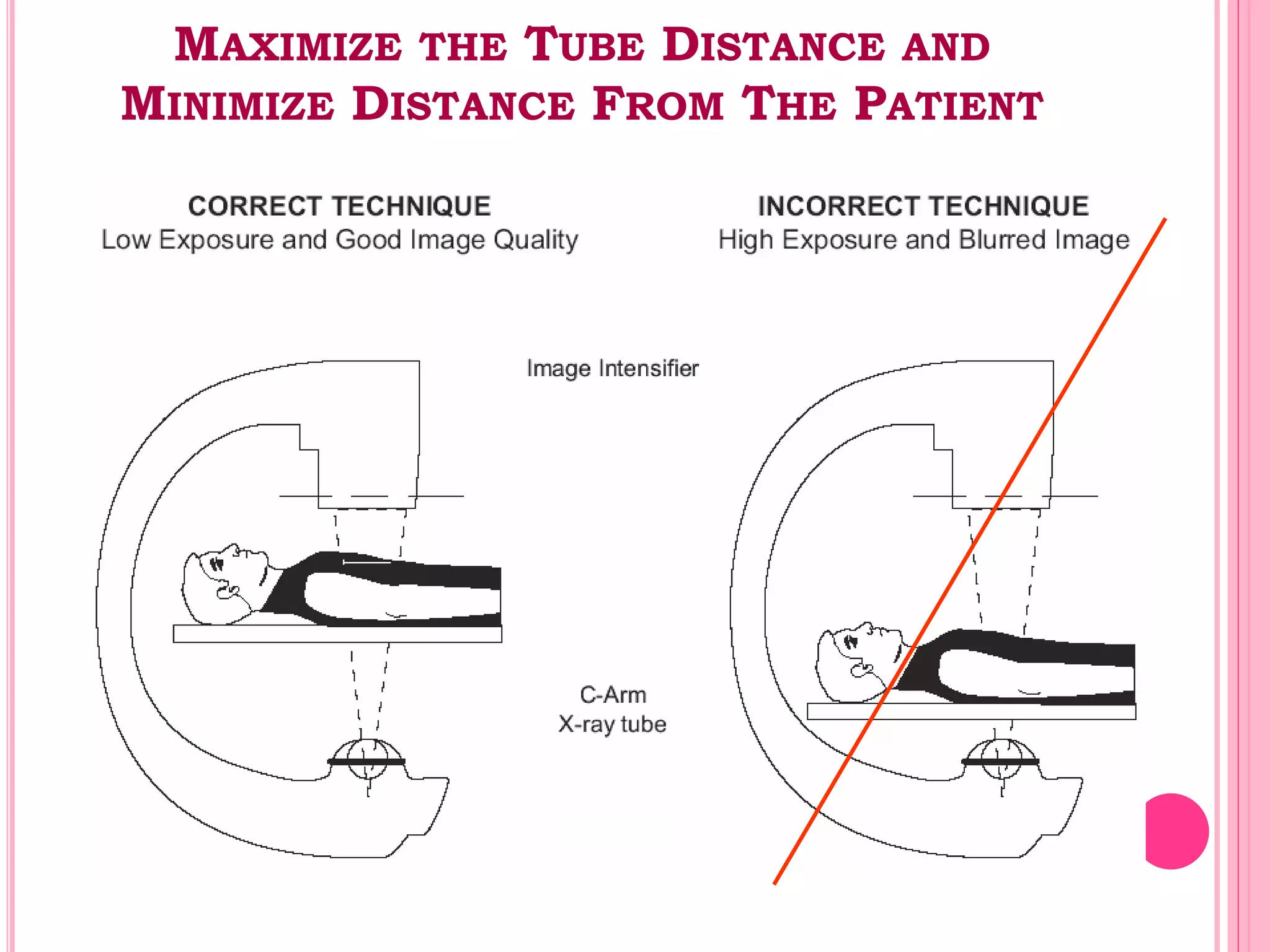
This document provides an overview of basic radiation safety. It discusses the effects of radiation, including stochastic effects like cancer and genetic effects, as well as deterministic effects that have a threshold dose. It outlines principles for protecting radiation workers, patients, and the public, including minimizing time, distance and shielding exposure. Specific protections like lead aprons, signs, and dosimeters are also reviewed. Proper handling and storage of protective equipment is emphasized.