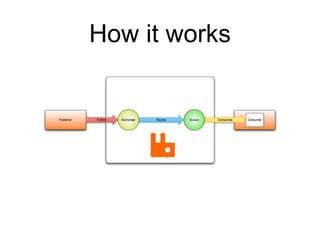
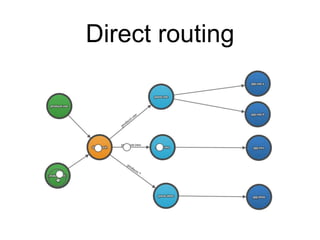
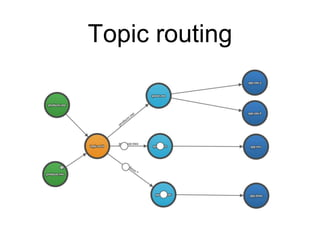
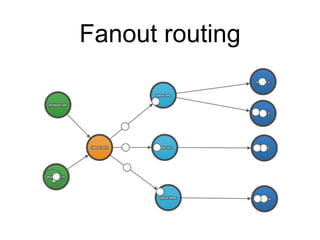
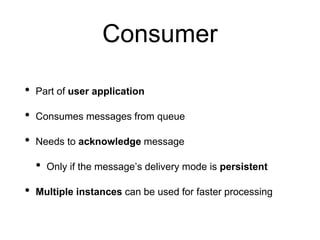
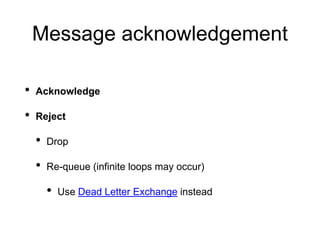
This document summarizes RabbitMQ, an open source message broker. It discusses the key components - producers, exchanges, bindings, queues, and consumers. Producers publish messages to exchanges. Exchanges route messages to queues based on routing keys and exchange type (direct, topic, fanout). Consumers consume messages from queues. It also covers topics like dead letter exchanges, acknowledgements, and remote procedure calls.