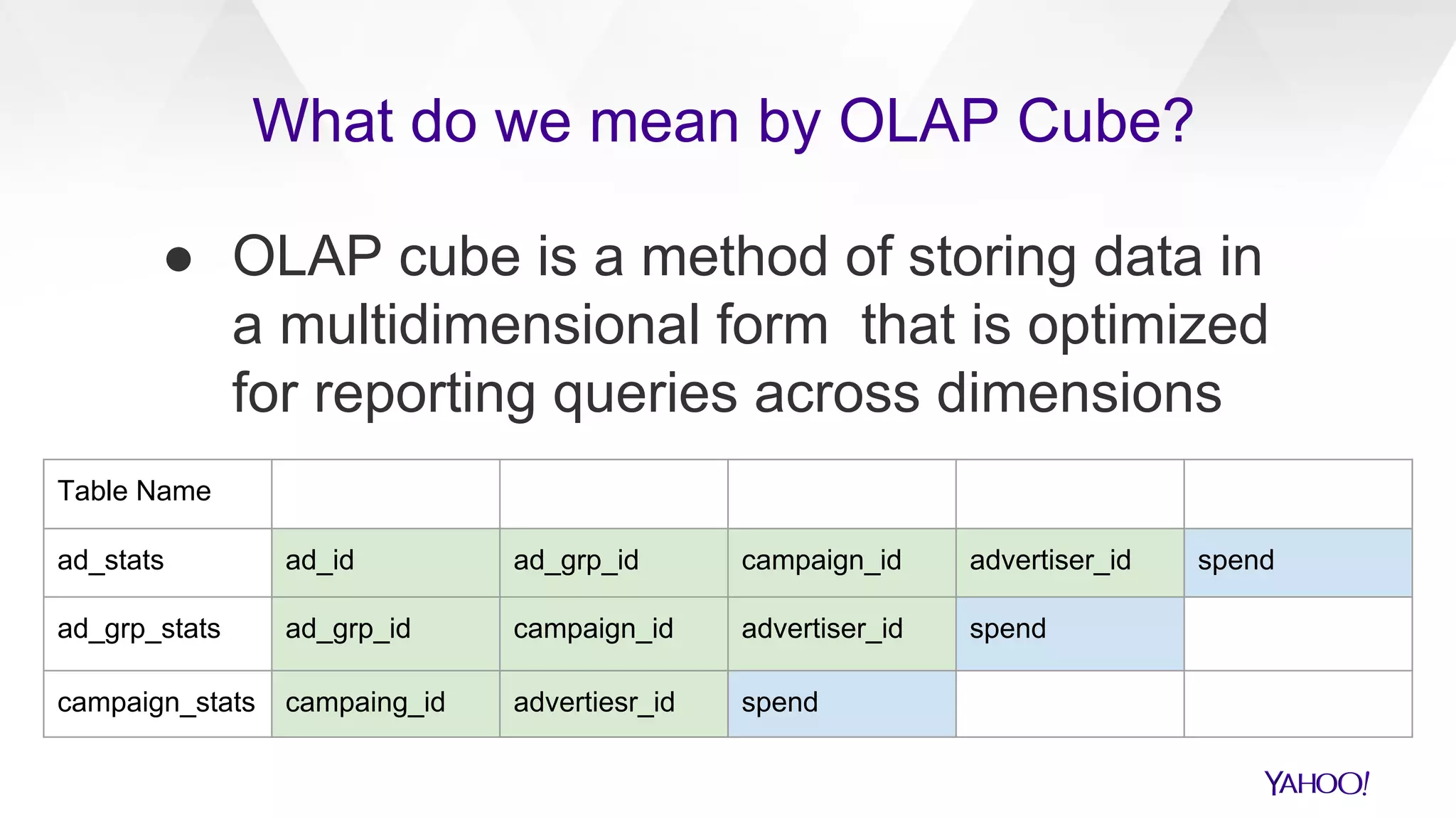
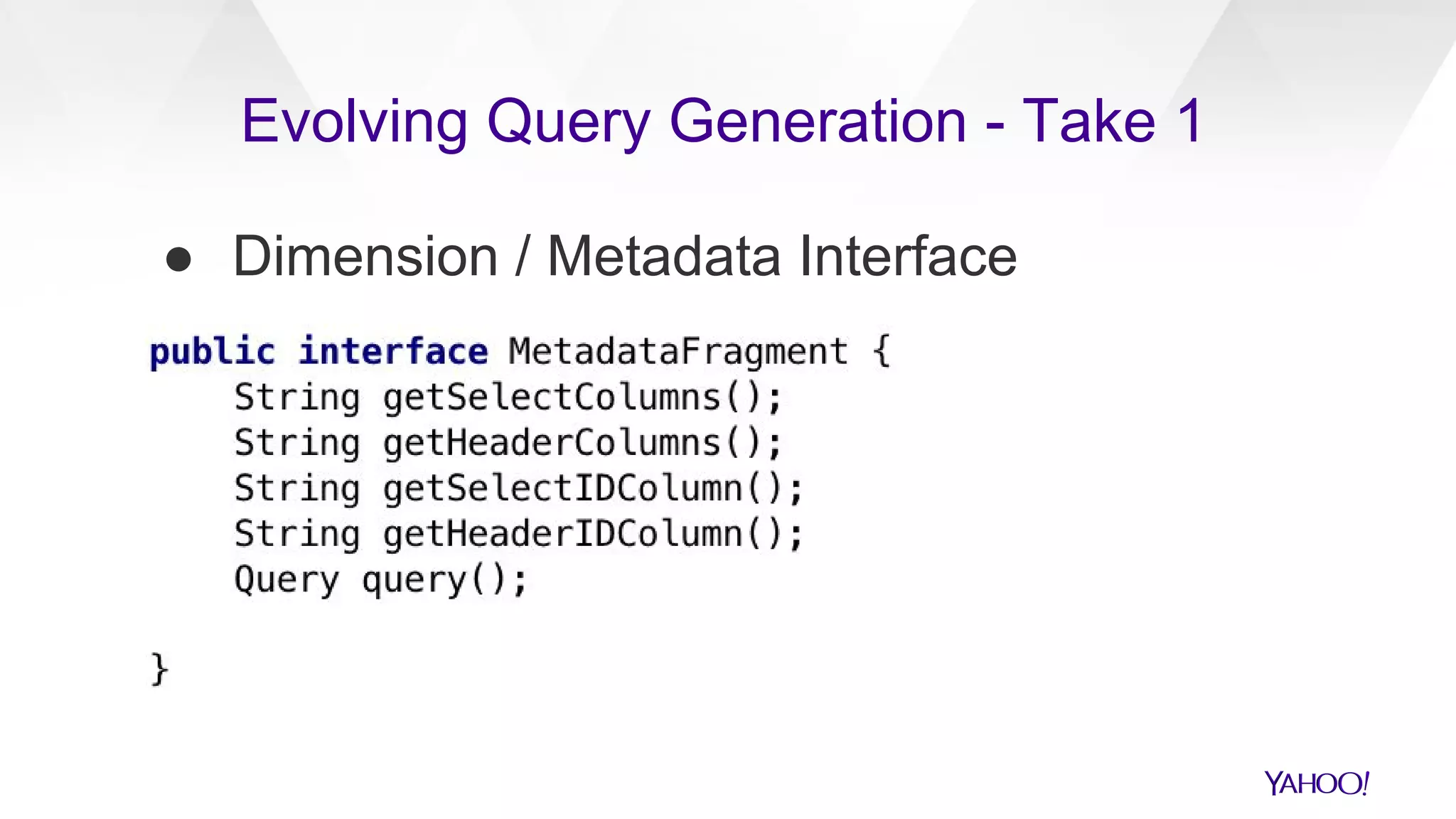
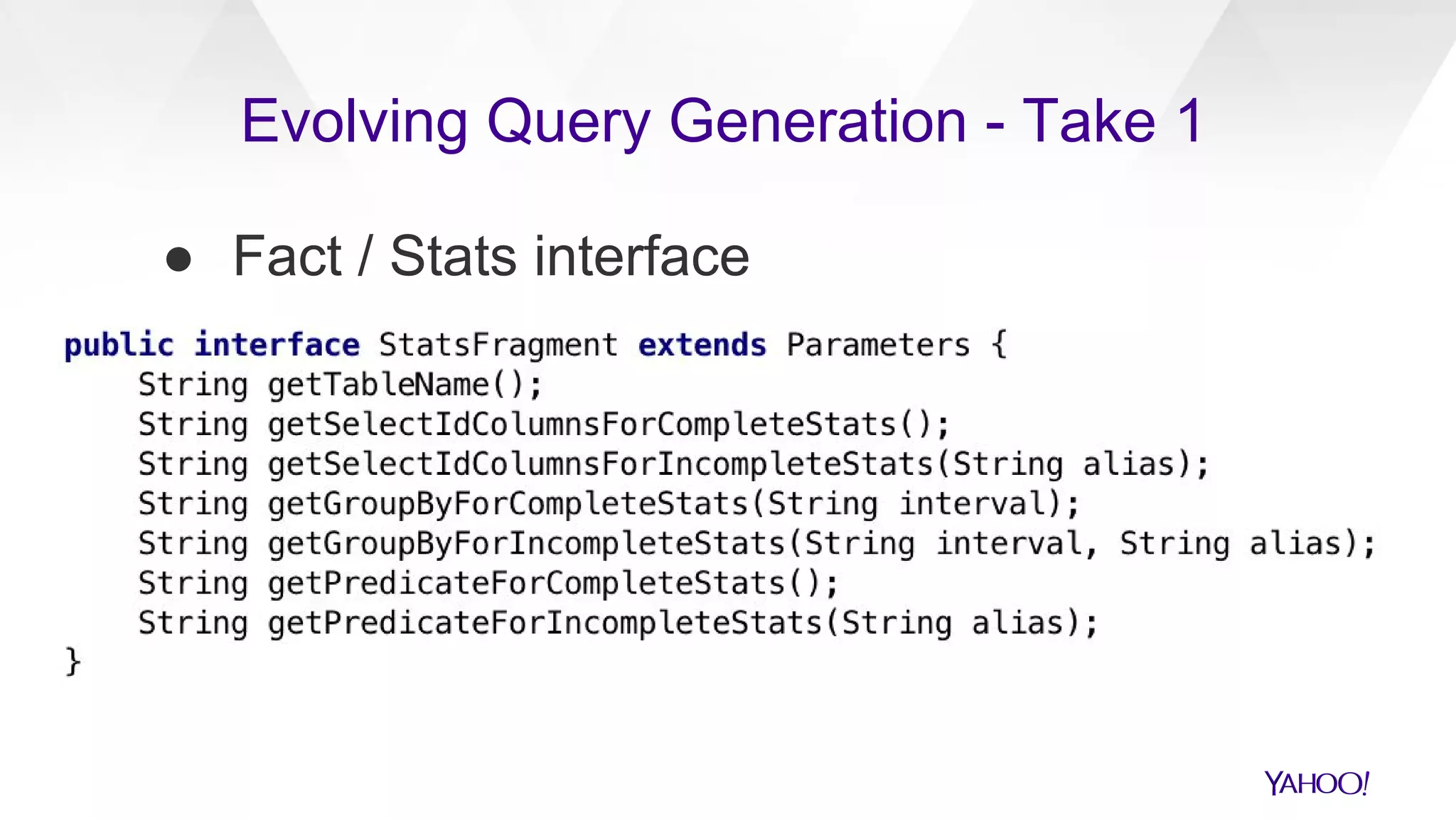
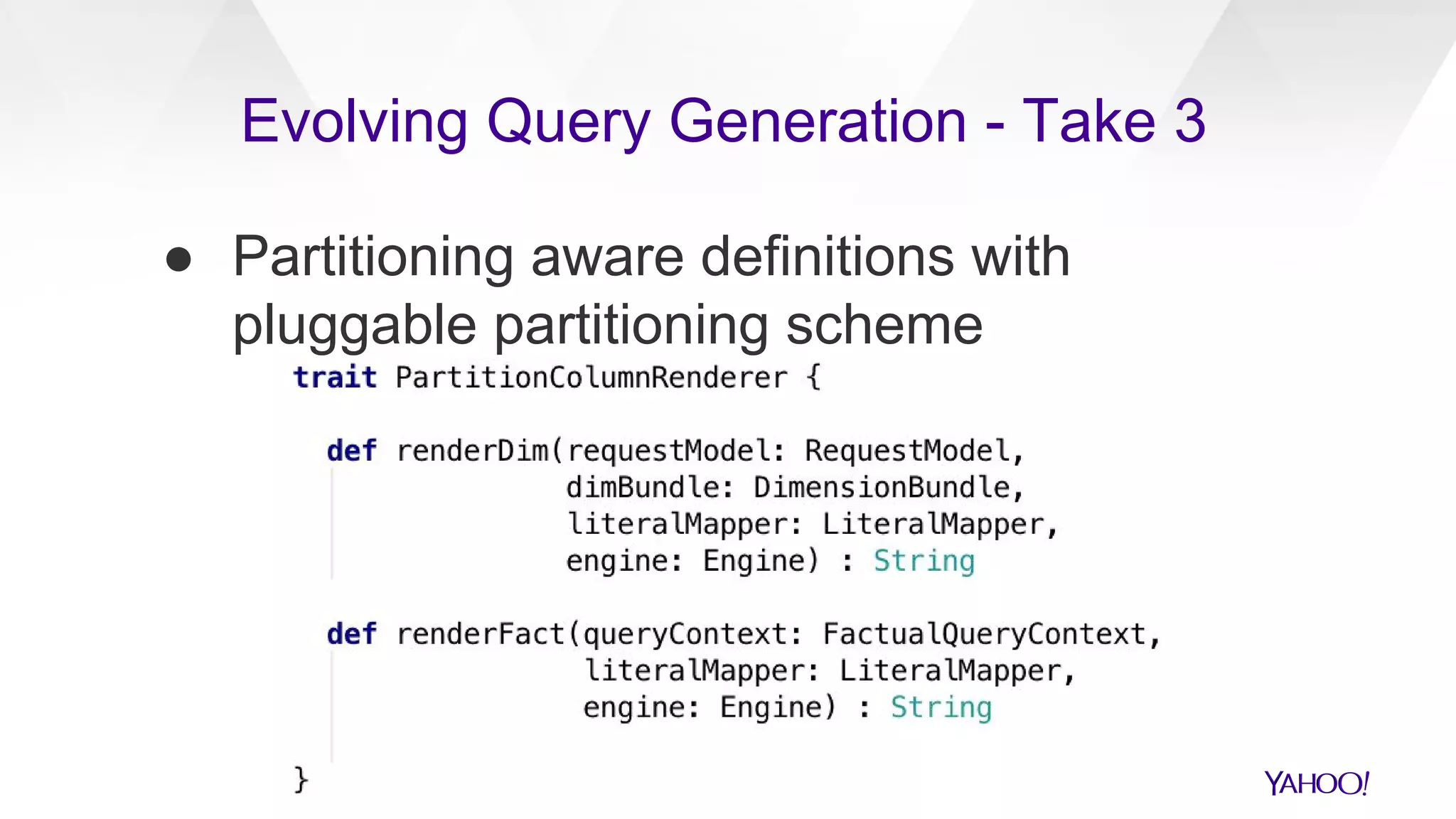
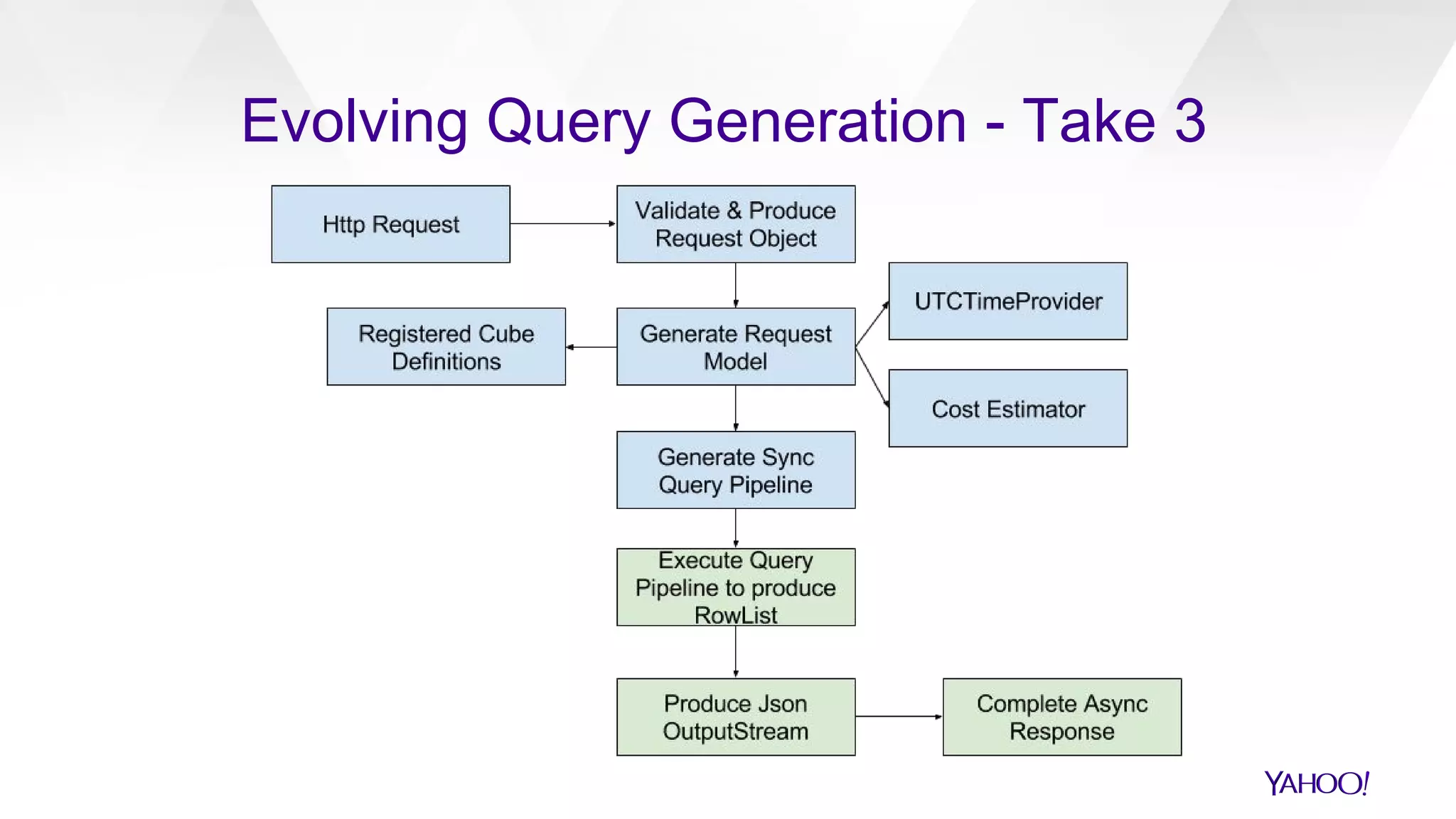
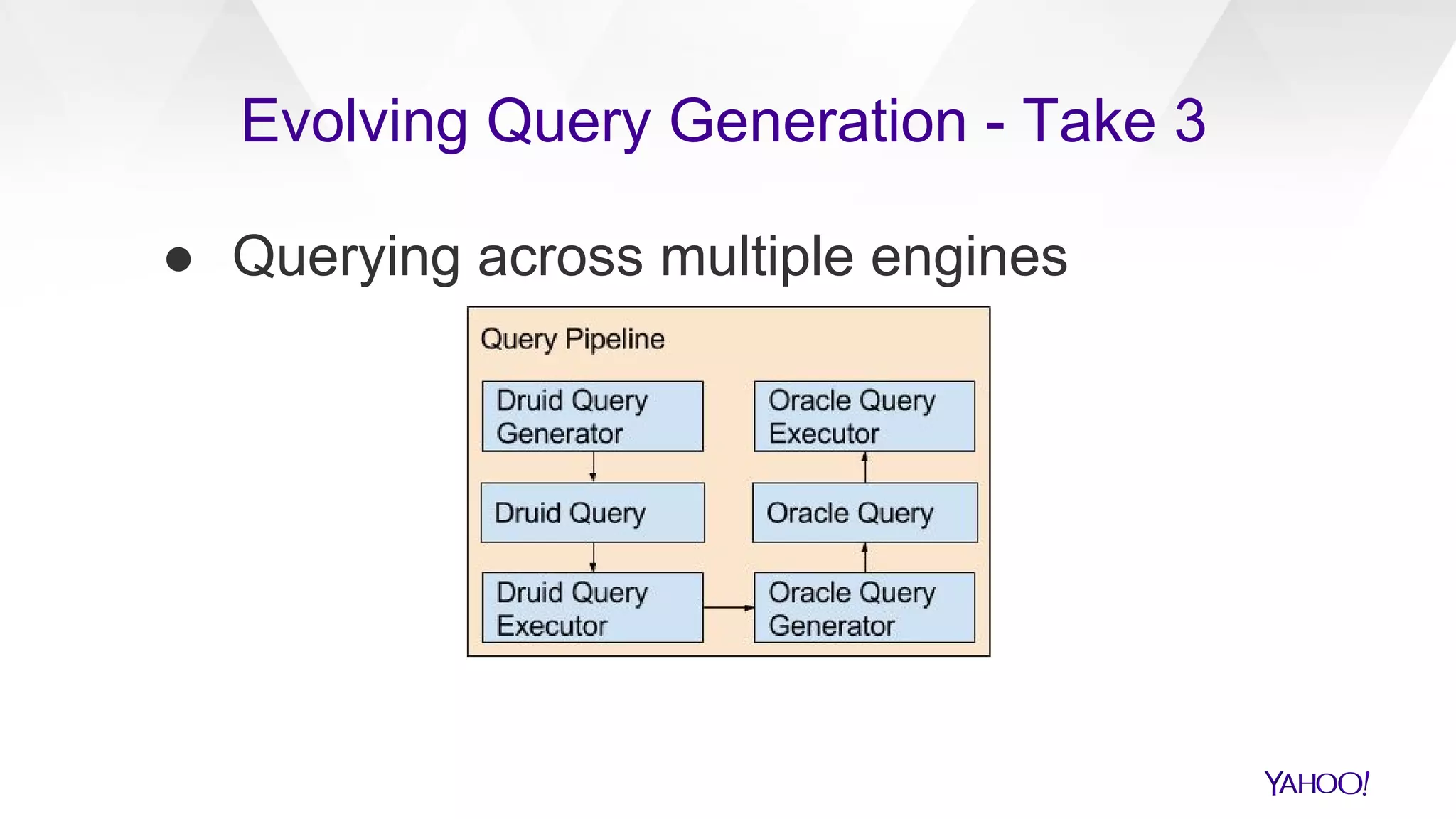
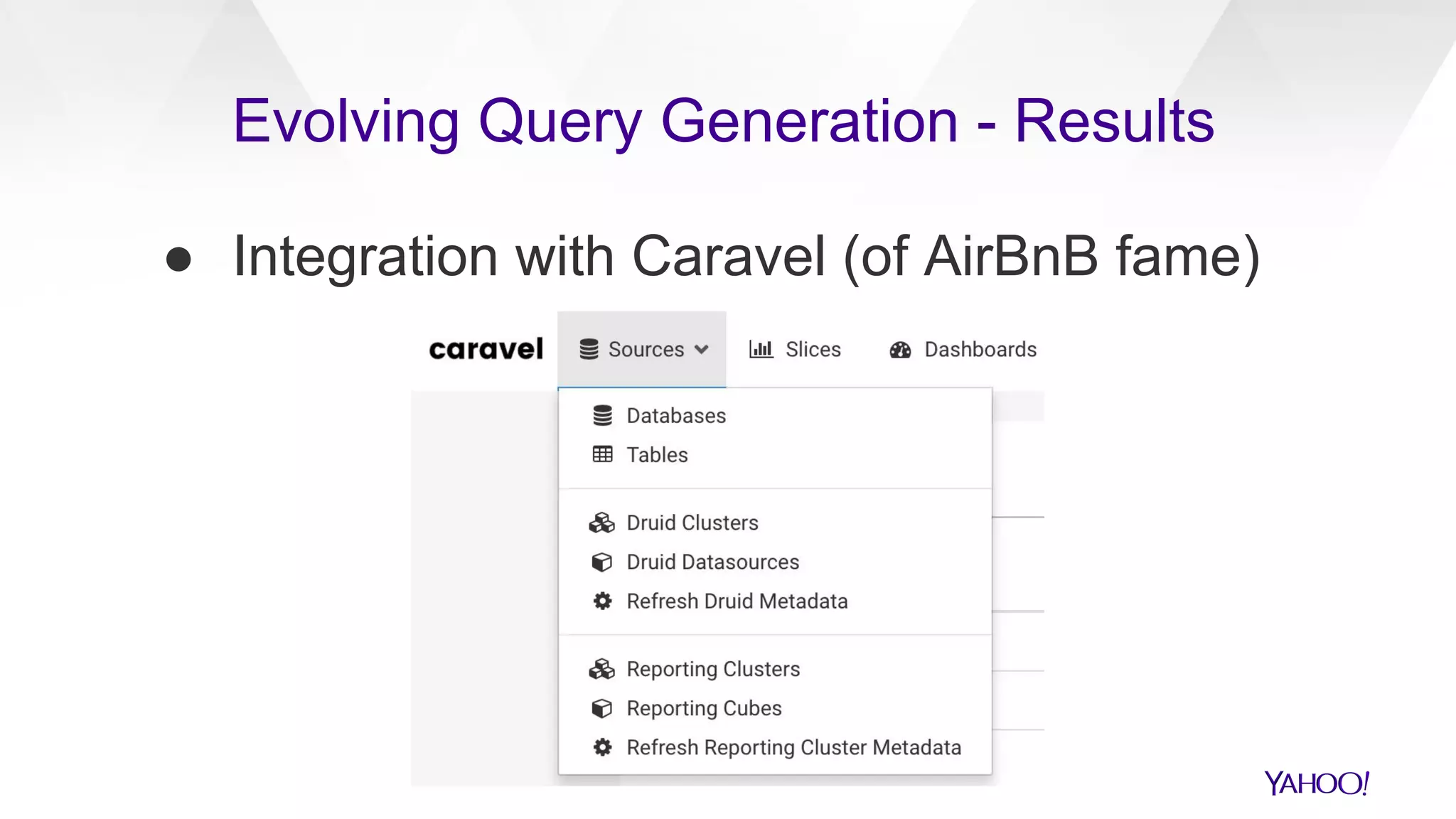
The document discusses the evolution of query generation across multiple data stores, led by Hiral Patel, a Senior Principal Architect at Yahoo. It outlines methods for optimizing OLAP queries using various technologies and frameworks while addressing challenges such as scaling and specific data store selections. The future work includes further enhancements to the query generation process and a mention of team contributors involved in the project.