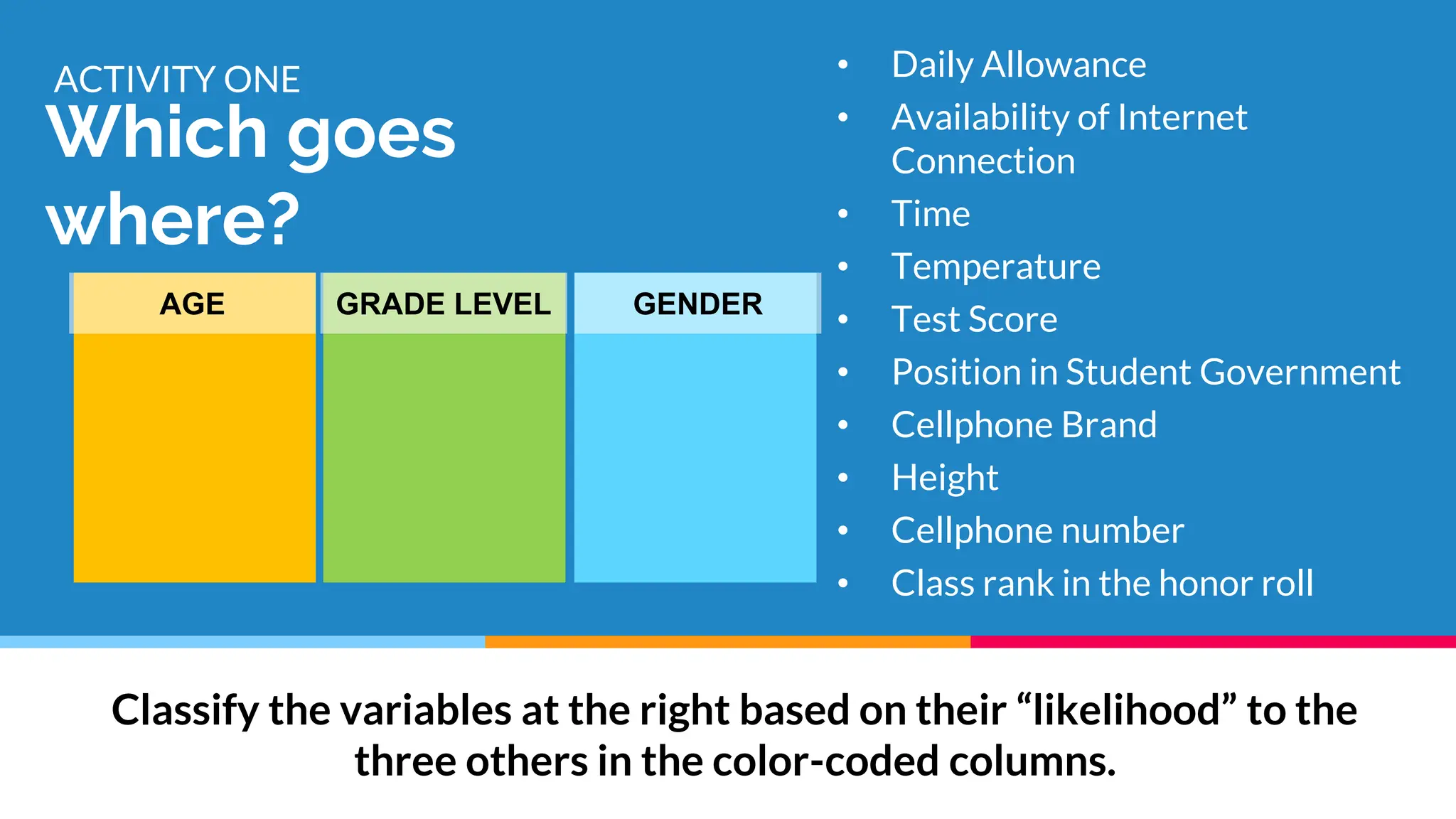
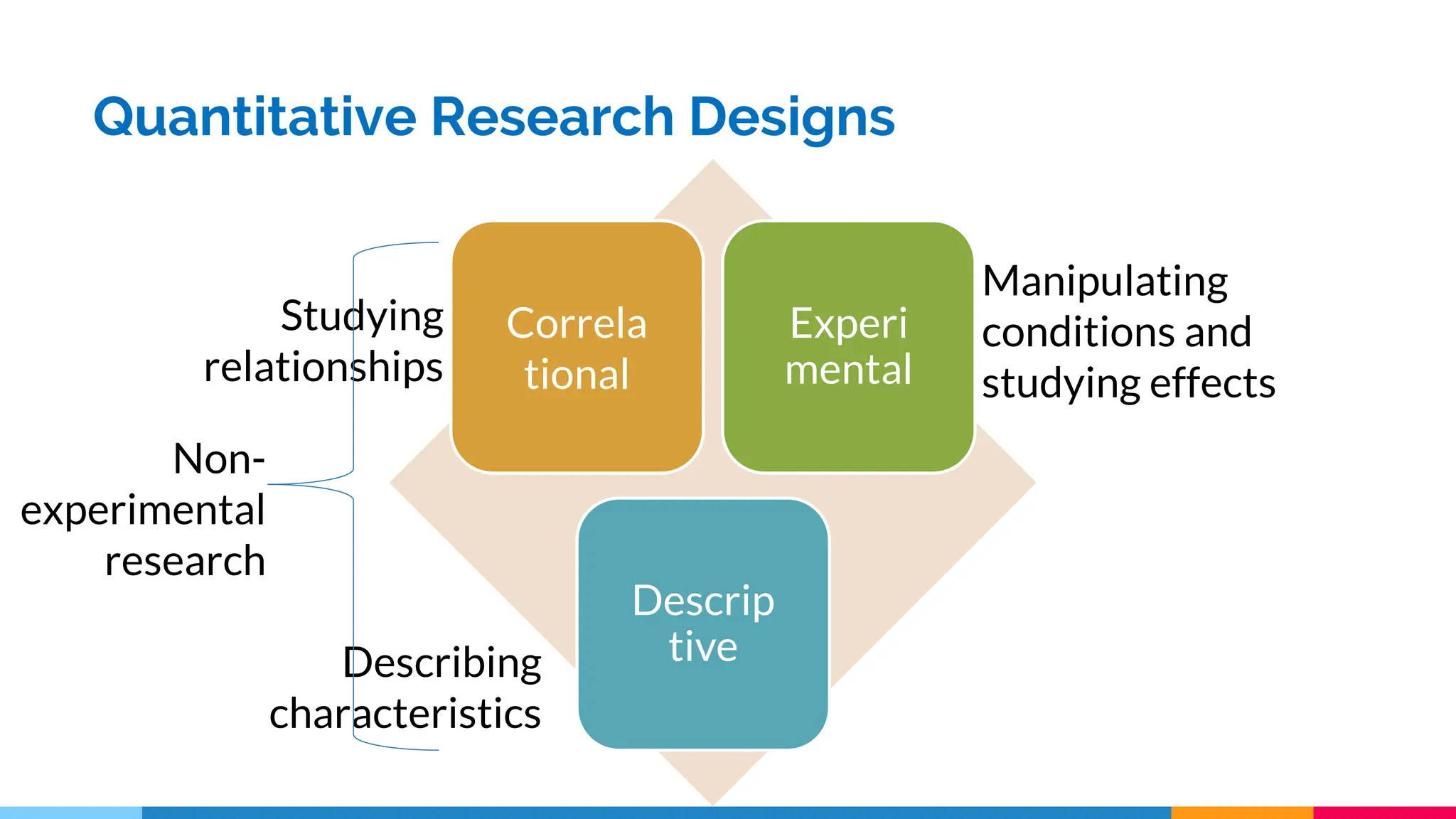
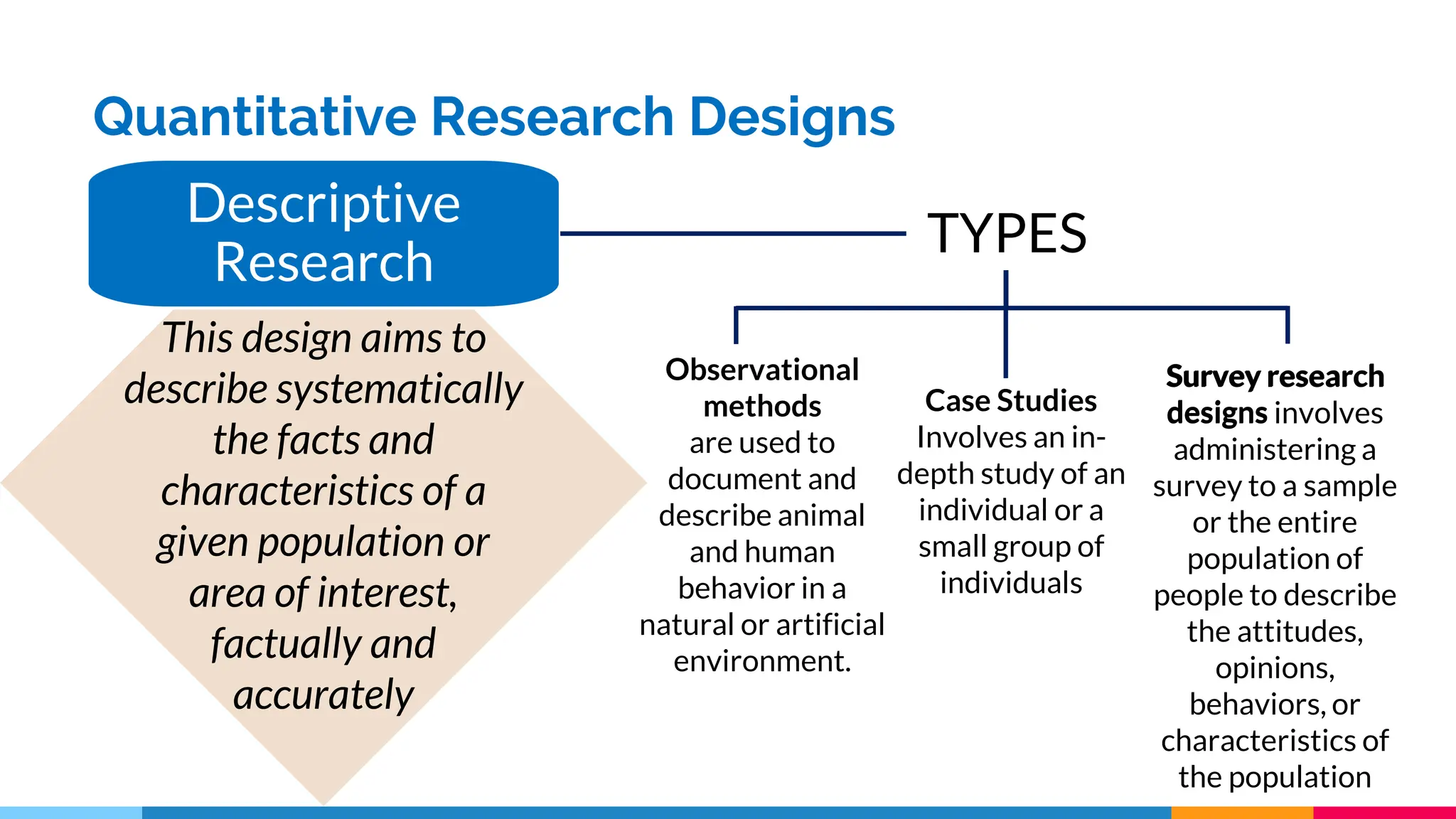
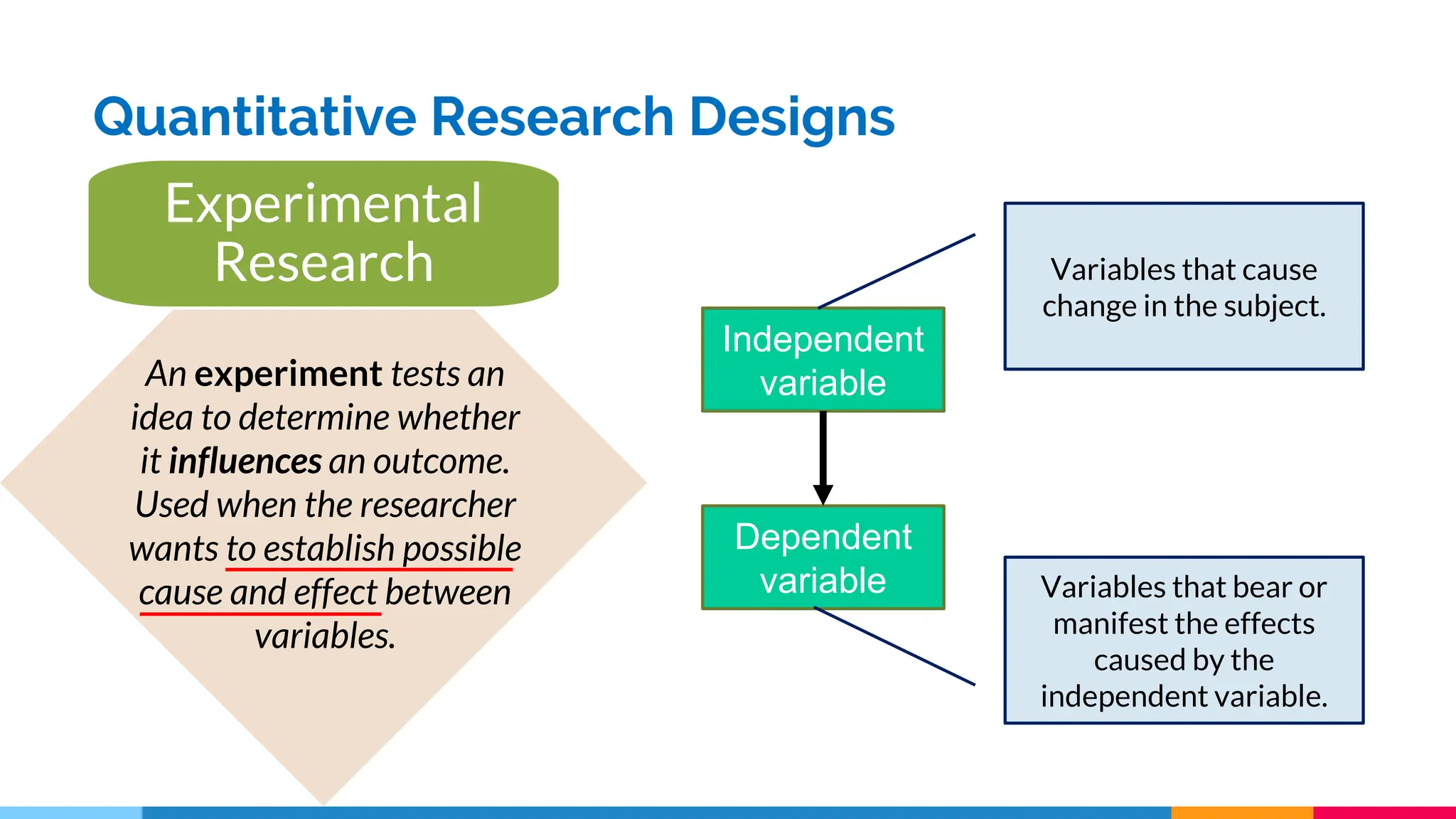
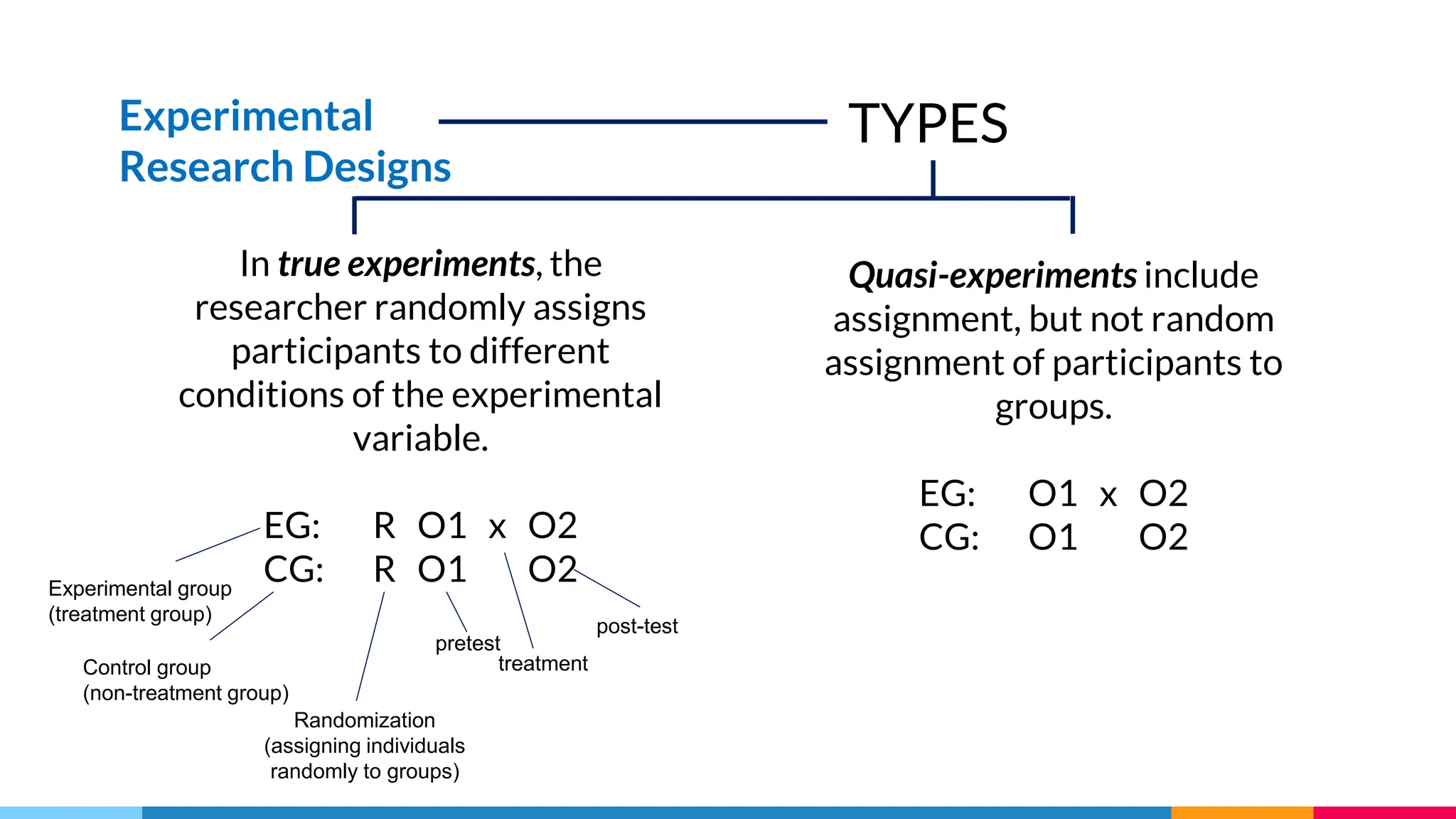
This document discusses quantitative research designs, including descriptive research, correlational research, and experimental research. It defines key aspects of each design, such as their purposes and common methodologies. Descriptive research aims to systematically describe characteristics of a population or area of interest using observational methods like surveys and case studies. Correlational research describes and measures associations between two or more variables, while experimental research tests hypotheses about cause-and-effect relationships between independent and dependent variables using true experiments or quasi-experiments. The document provides examples of research questions for each design and activities for classifying variables and generating quantitative research topics.