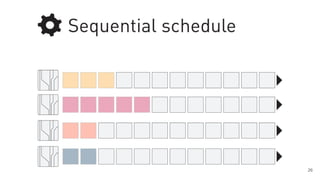
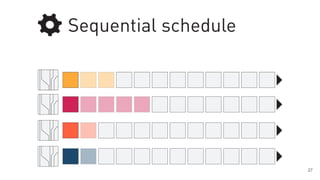
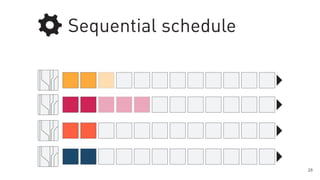
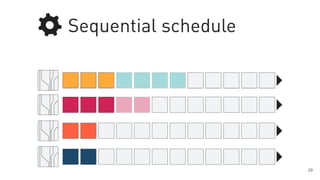
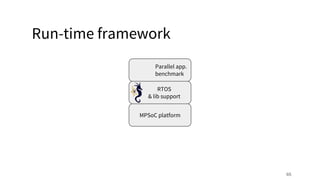
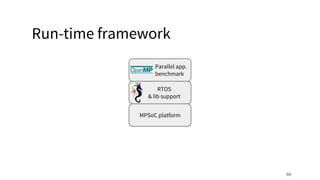
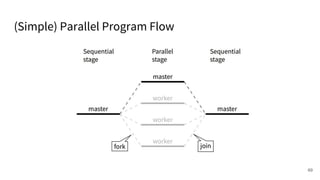
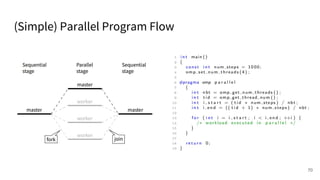
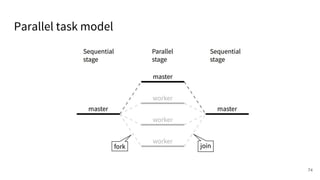
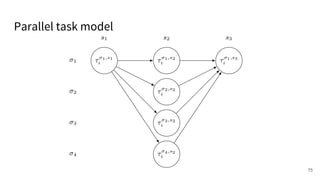
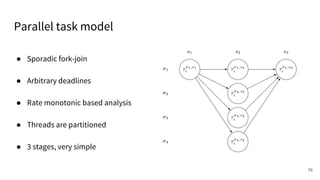
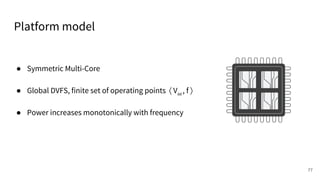
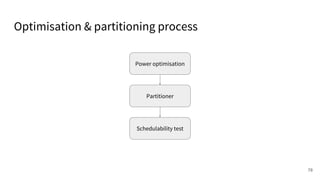
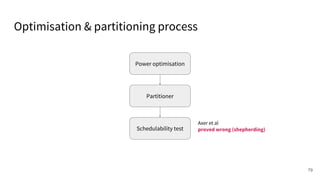
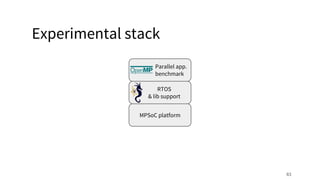
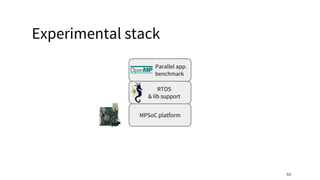
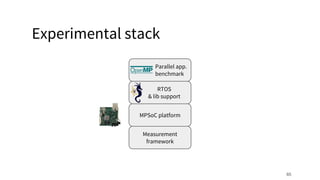
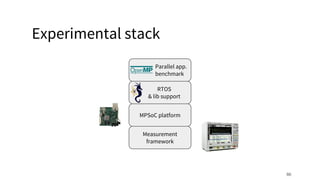
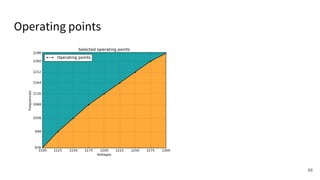
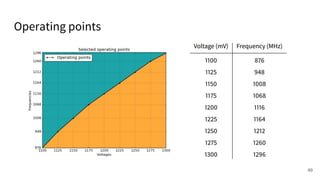
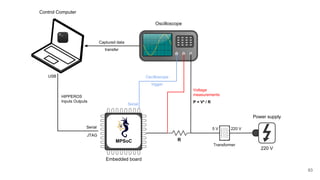
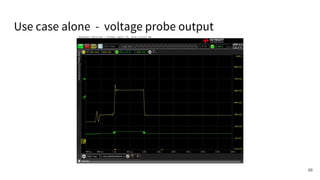
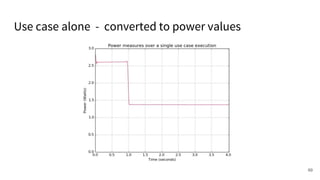
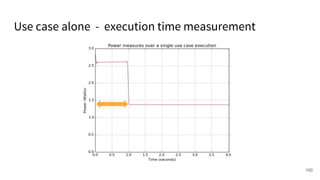
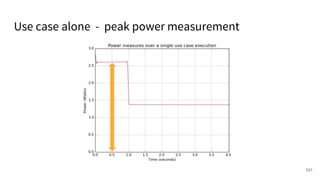
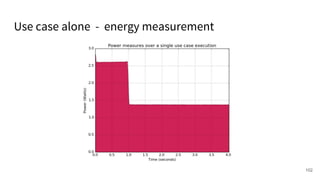
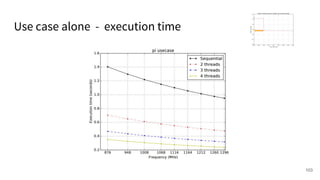
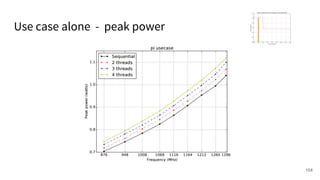
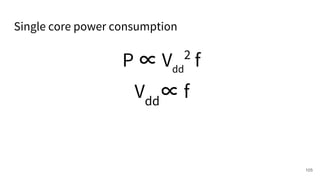
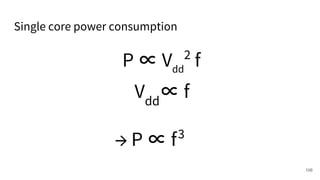
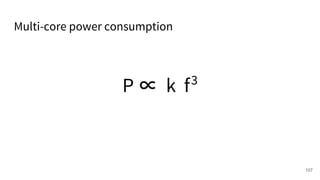
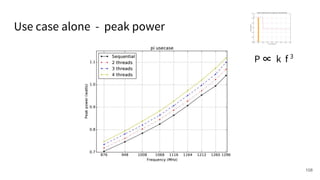
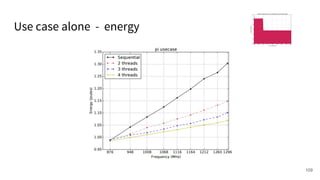
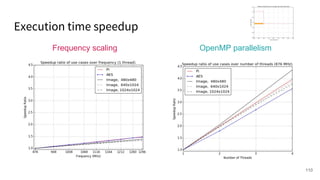
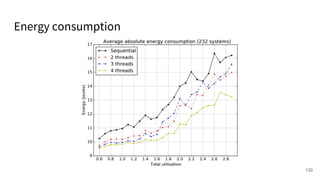
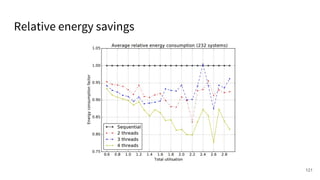
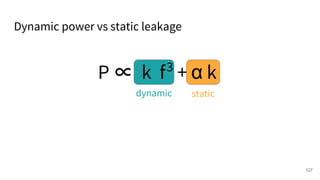
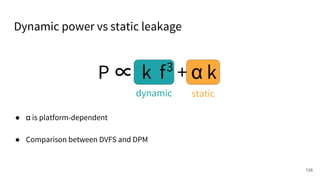
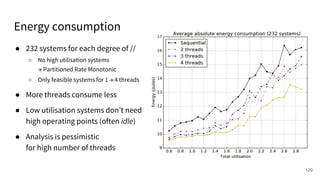
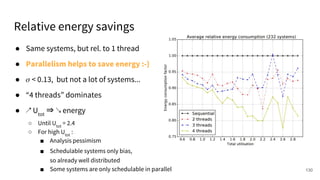
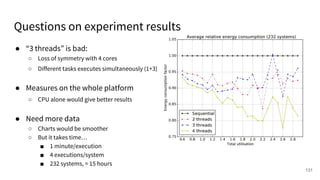
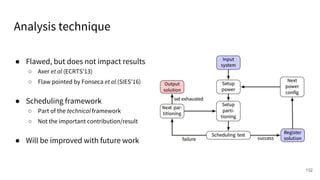
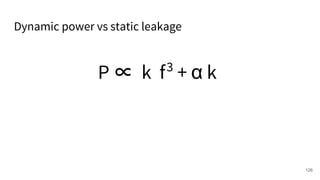The document discusses a framework for quantifying energy consumption in fork-join parallelism on embedded real-time operating systems. It aims to reduce energy use while meeting real-time requirements by utilizing power-aware multi-core scheduling and evaluating its effectiveness through practical experiments. The findings indicate that parallelization can lead to energy savings of up to 25% across the entire system.