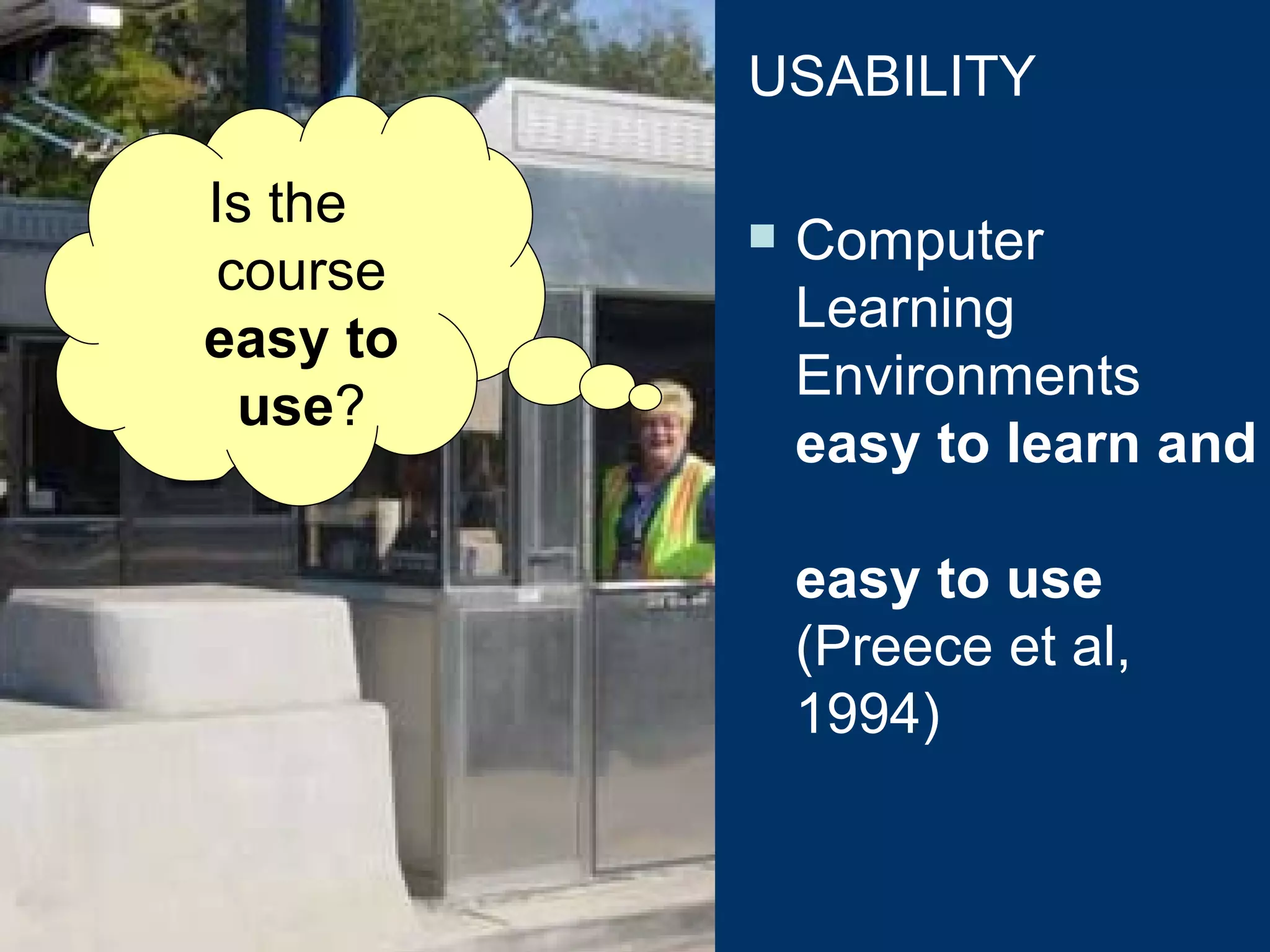
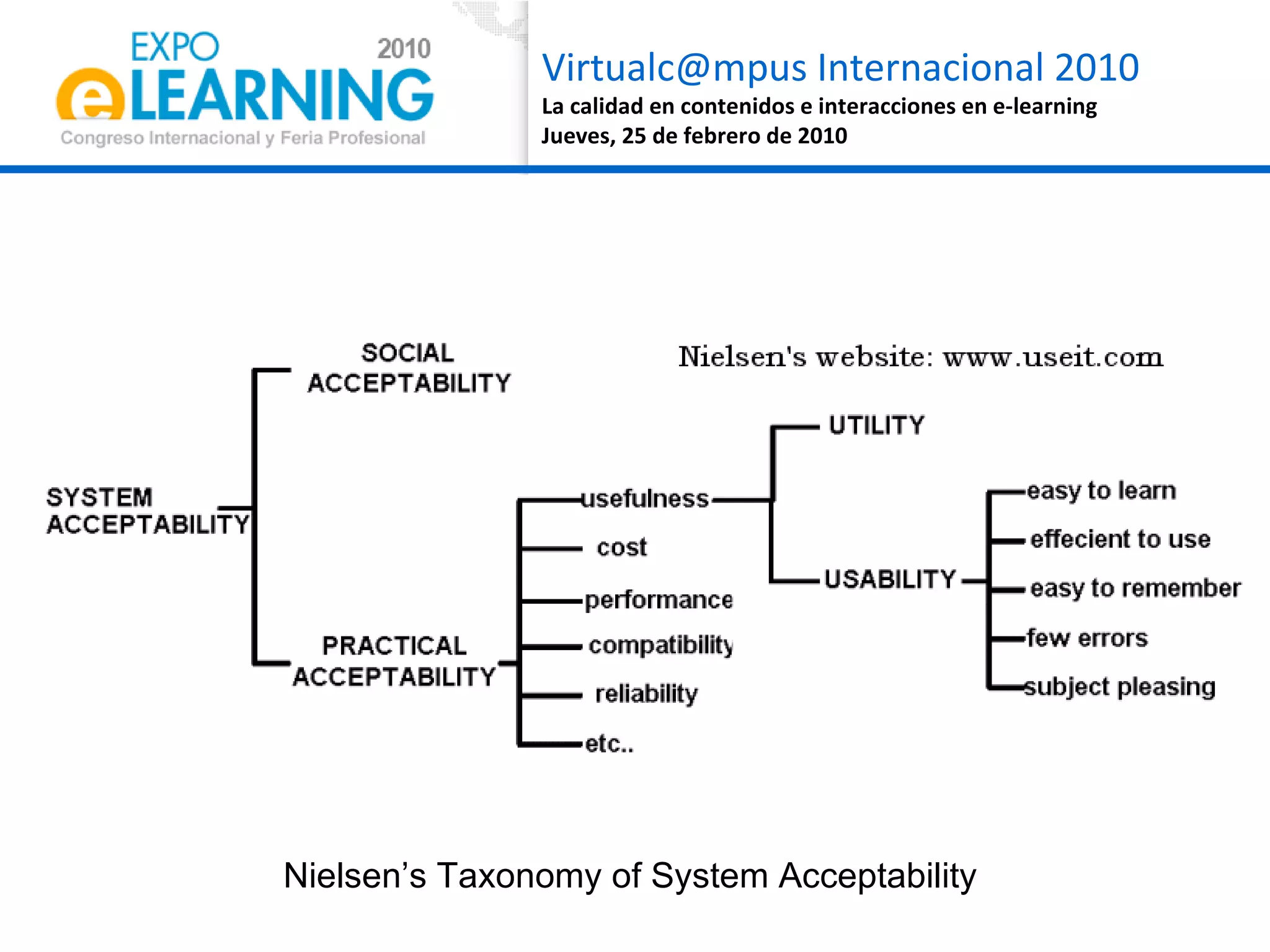
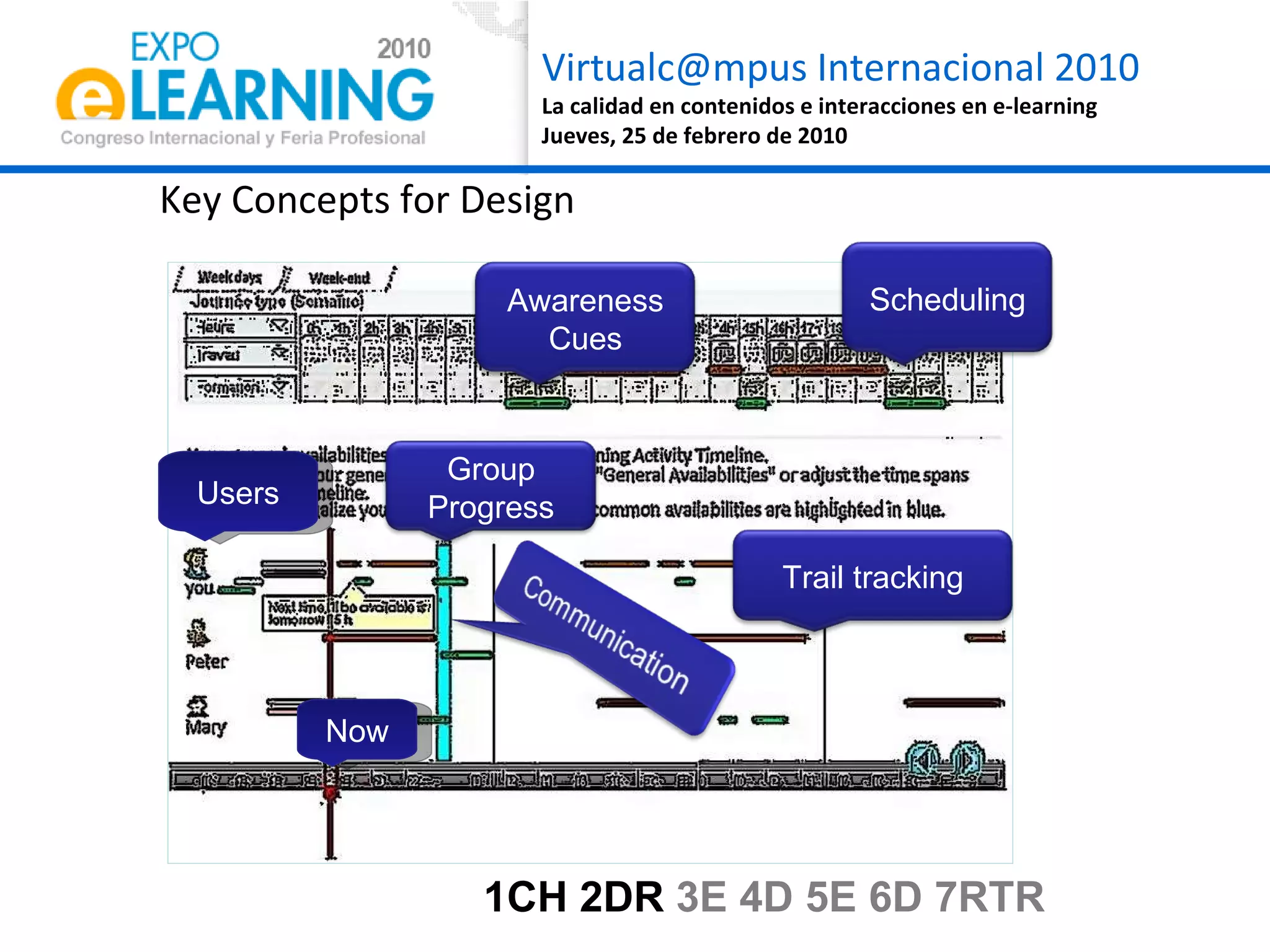
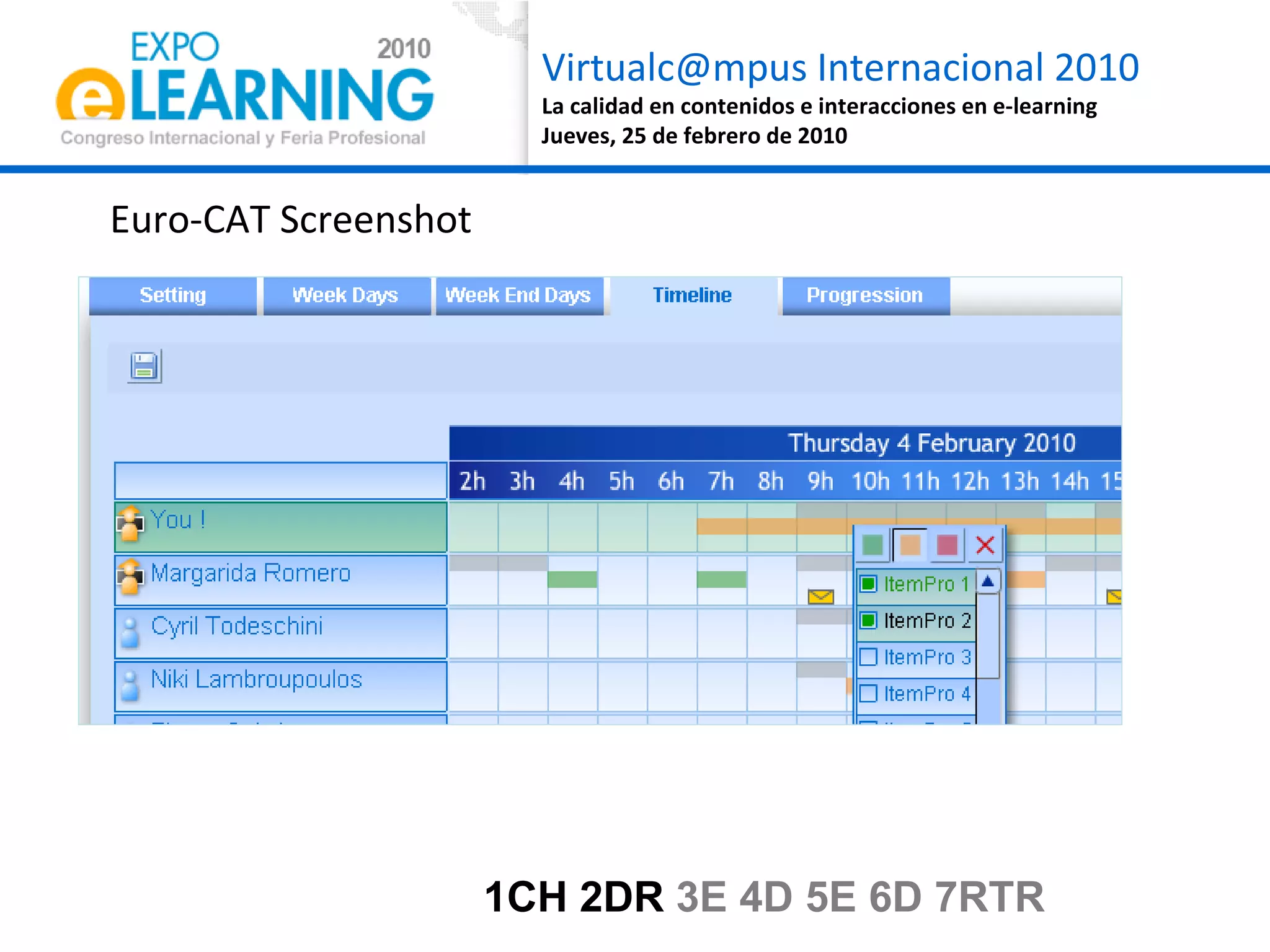
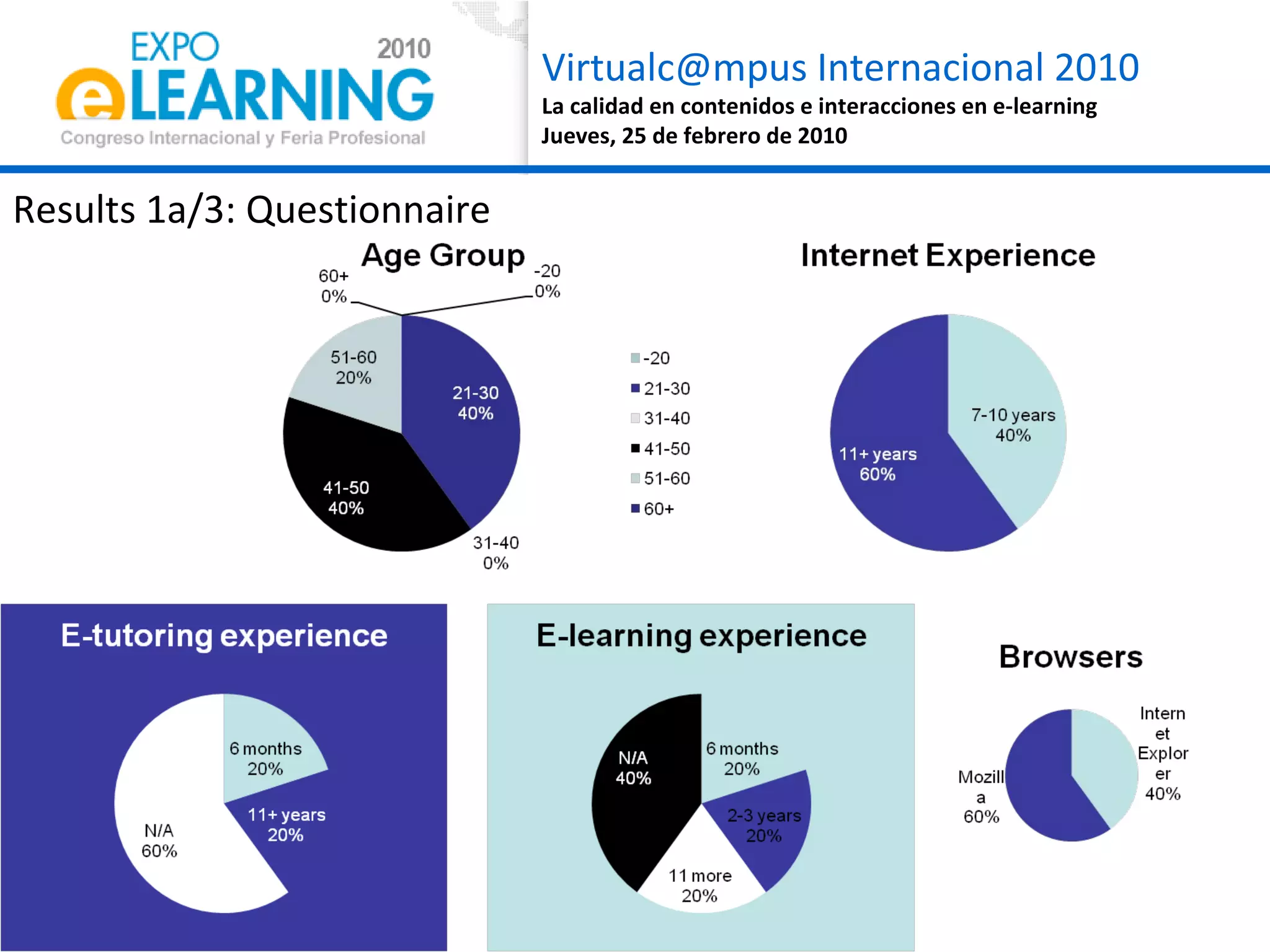
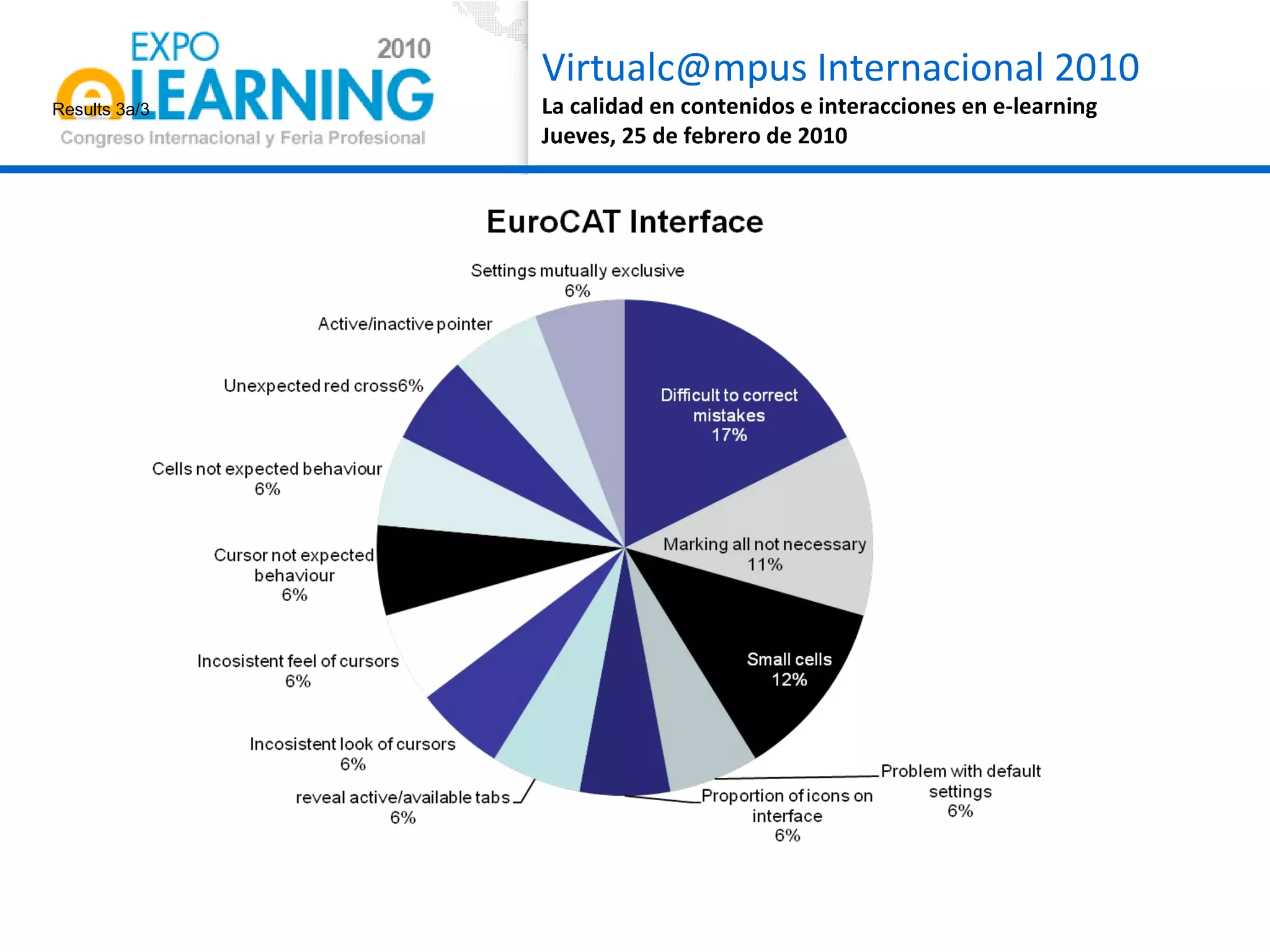
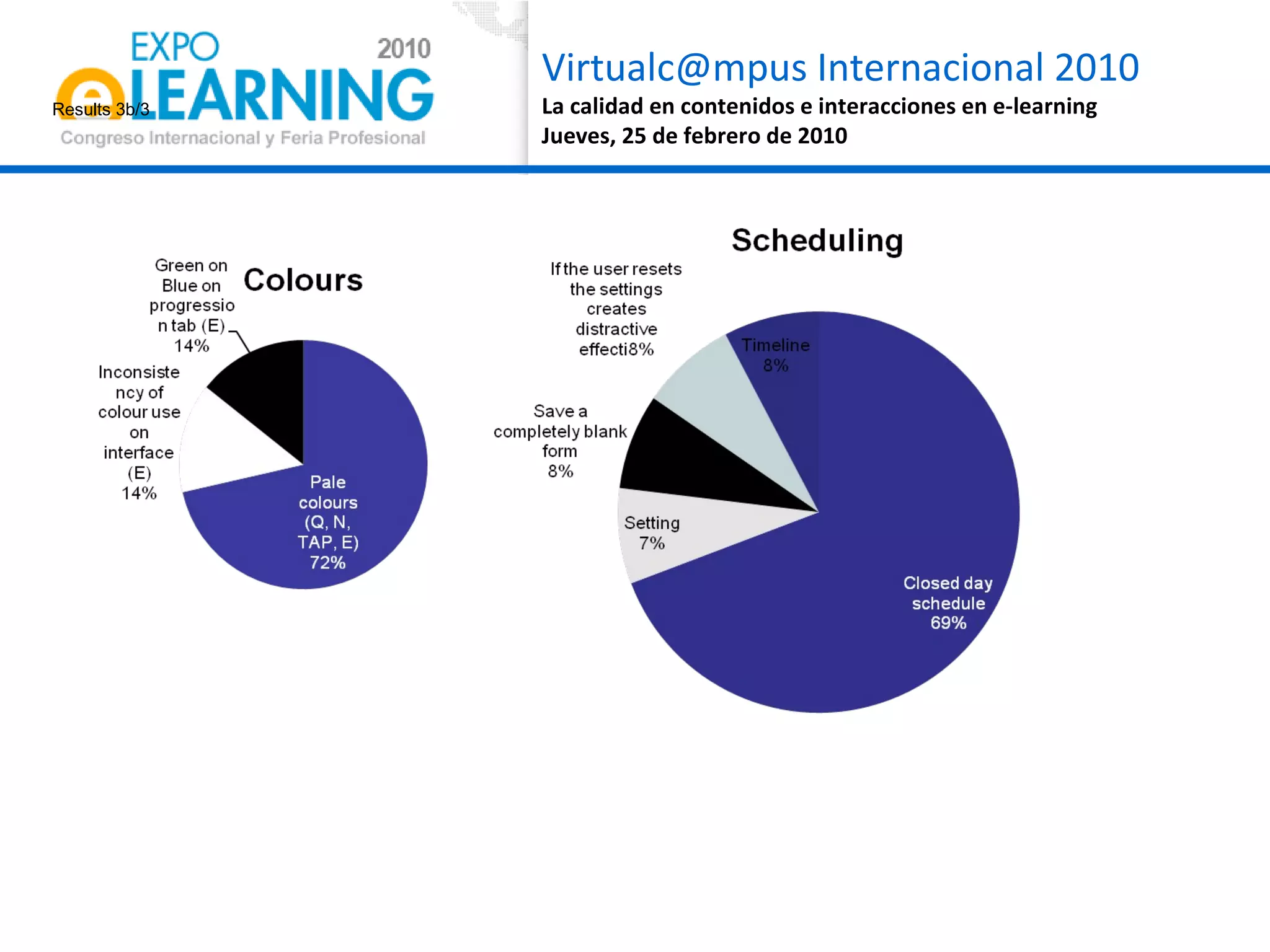
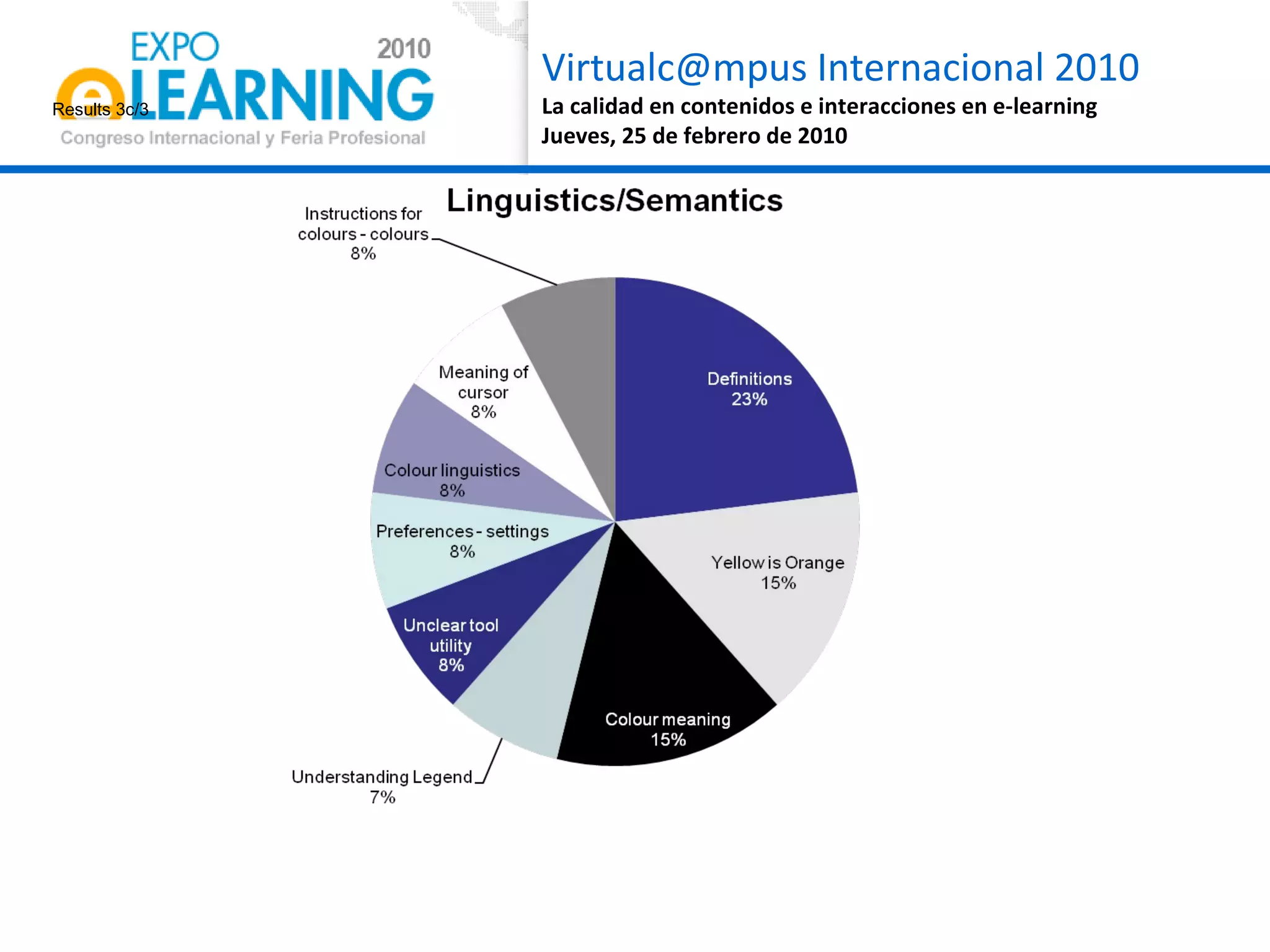
The document discusses quality assurance in computer-supported collaborative learning environments, highlighting the importance of utility, usability, and acceptability through case studies in toll staff training and the Euro-CAT ergonomic evaluation. It emphasizes that effective e-learning requires not only pedagogical criteria but also a strong focus on user experience and ergonomics. The outcomes indicate a need for iterative design and user-centered approaches to enhance learning effectiveness and collaboration awareness in distributed settings.











![As if the learning situation were not enough complex.... we will consider the usability criteria SOCIAL ACCEPTABILITY Not only consider the usefulness and usability, but also robustness, cost and reliability of ICT applications Joel says the course is nuts; for me, is quite boring, and you? No, Joel is nuts, the course is just not enough challenging and interactive [Joel] The course don’t work in my computer… I needed to use my son computer to follow the course…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qualityinelearning-lambropoulos-romero-madrid-100225141912-phpapp01/75/Quality-In-Computer-Supported-Collaborative-eLearning-by-Lambropoulos-Romero-13-2048.jpg)















![Thank you! Questions? Dr. Niki Lambropoulos [email_address] Dr. Margarida Romero [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qualityinelearning-lambropoulos-romero-madrid-100225141912-phpapp01/75/Quality-In-Computer-Supported-Collaborative-eLearning-by-Lambropoulos-Romero-36-2048.jpg)