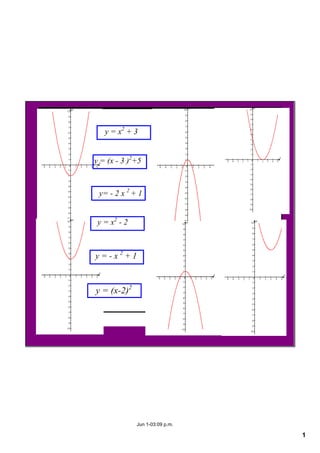
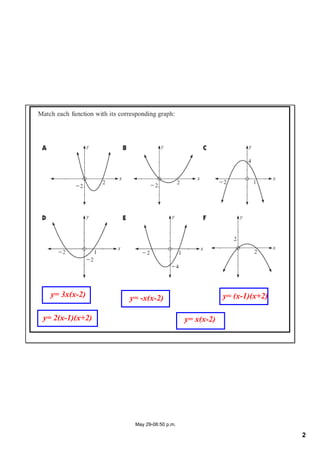
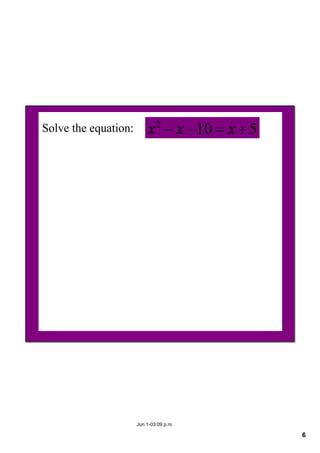
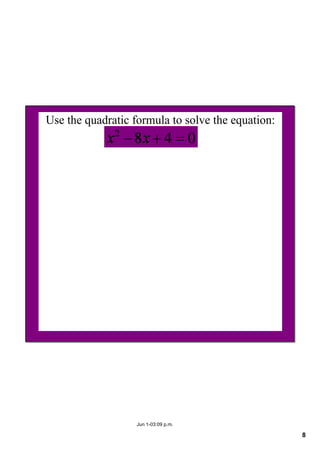
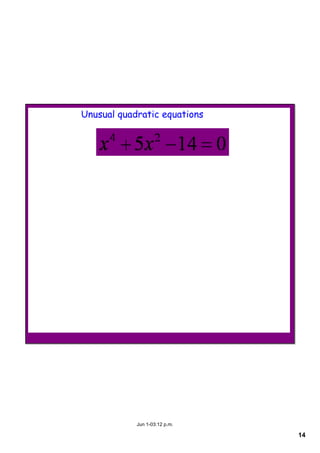
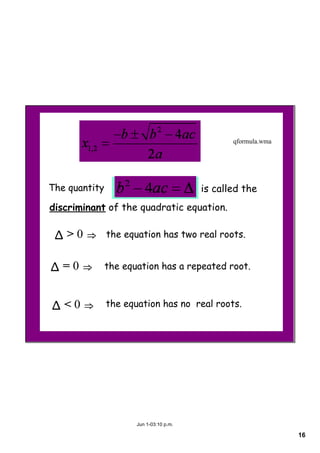
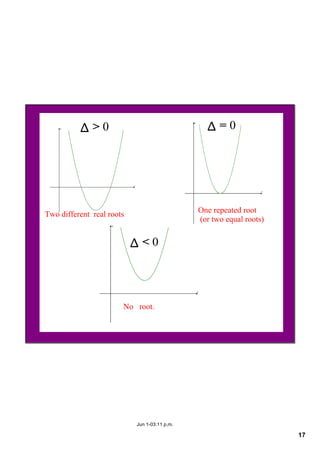
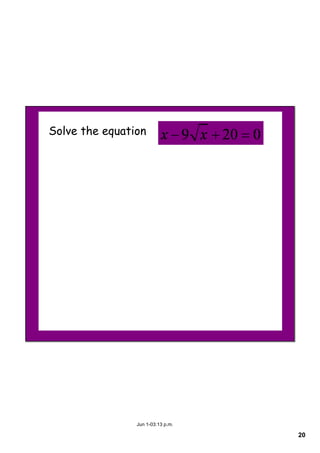
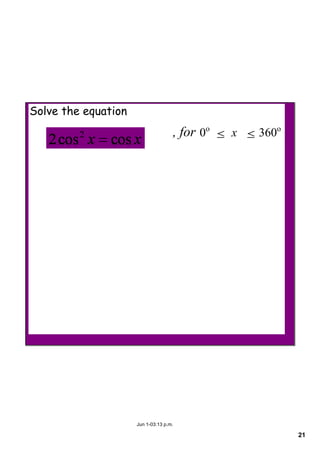
This document appears to be notes from a lesson on quadratic equations. It covers solving quadratic equations using different methods like factorisation, the quadratic formula, and completing the square. It also discusses using the discriminant to determine the number and type of solutions, including cases where there are two real solutions, a repeated root, or no real solutions. It includes examples of solving quadratic equations and finding discriminants. The lesson content suggests students will learn to solve and analyze quadratic equations using various techniques.