This document discusses different types of conjunctions:
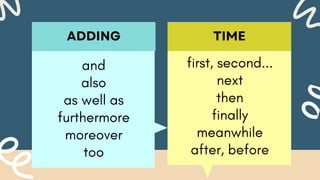
1. Coordinating conjunctions like FANBOYS (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) that link ideas and show how they relate.
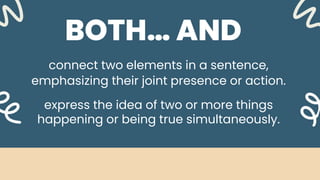
2. Correlative conjunctions like neither...nor, either...or, not only...but also, both...and, whether...or that join elements within a sentence.
3. Subordinating conjunctions like until, if, while, that connect independent clauses to dependent clauses.
4. Conjunctive adverbs like however, moreover, namely, nevertheless, meanwhile, subsequently, and furthermore connect and transition between ideas.