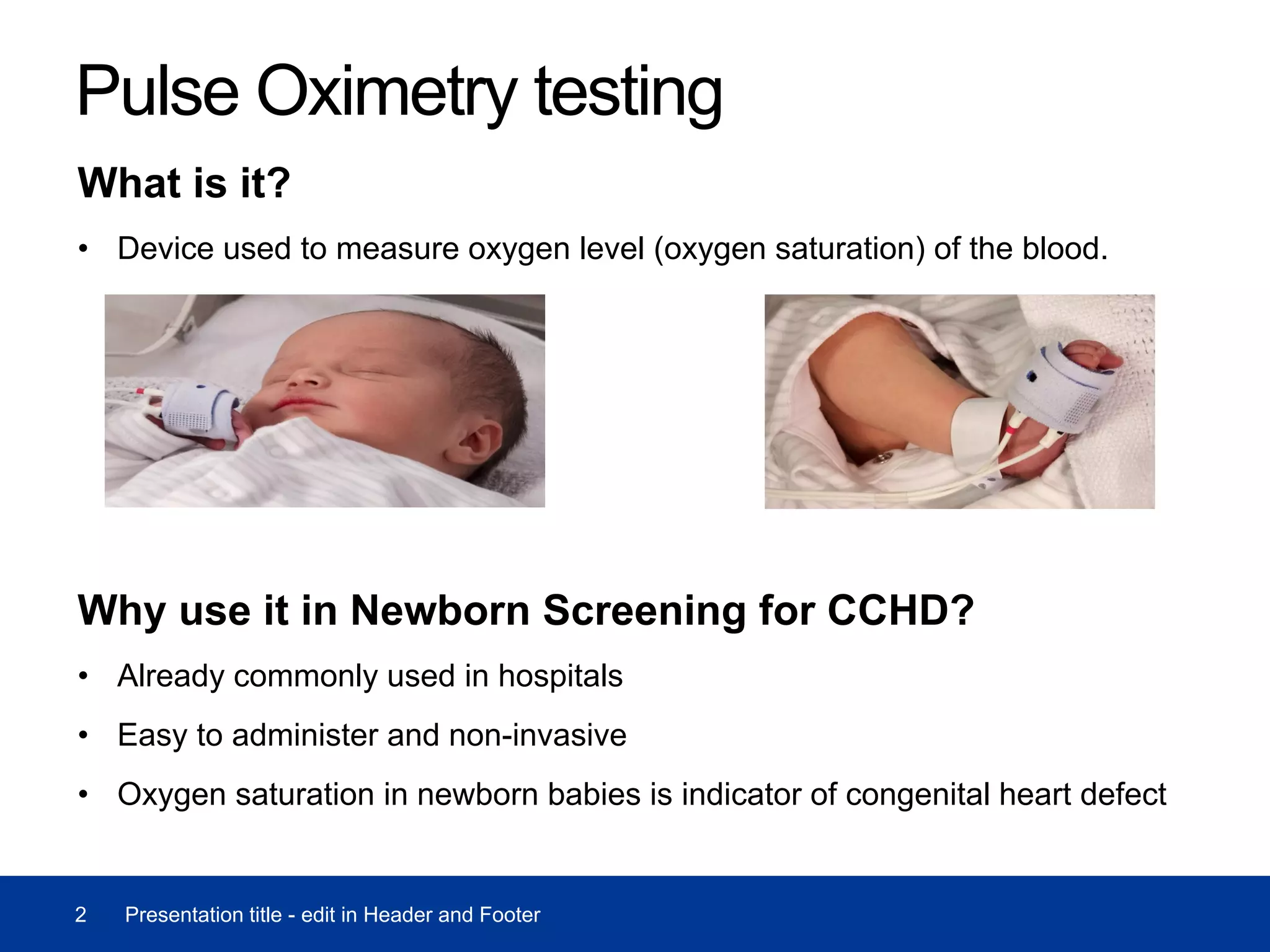
The document discusses the use of pulse oximetry in screening for critical congenital heart disease (CCHD) in newborns, highlighting its accuracy, acceptability, and cost-effectiveness based on trials. A pilot program screened 32,597 newborns, identifying 8 true positive CCHD cases and 239 screen positive instances, while noting some challenges such as staffing constraints. Further cost-effectiveness analysis is recommended by the UK National Screening Committee to evaluate the benefits of this screening method.