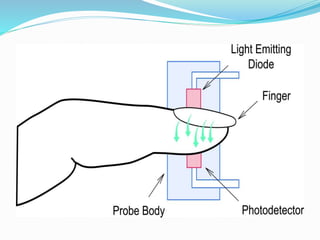
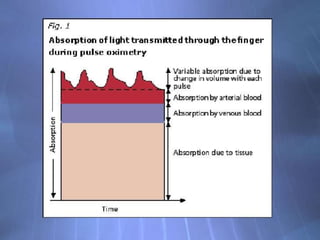
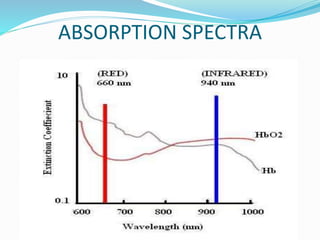
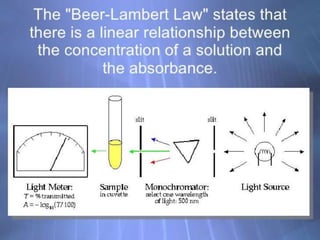
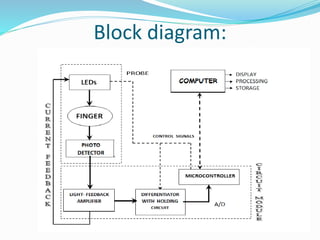
This document discusses pulse oximetry, which is a non-invasive method to determine a patient's oxygen saturation level by measuring the absorption of red and infrared light as it passes through pulsating blood vessels. It works by shining two wavelengths of light (red and infrared) through a sensor placed on the patient's finger or earlobe, and measuring the amount of light absorbed. This absorption data is then used to calculate the percentage of oxygenated hemoglobin in the blood. The document outlines the history, components, working principle, advantages and limitations of pulse oximetry.