- Bronchopulmonary sequestration is a rare congenital abnormality where non-functioning lung tissue receives blood supply from the systemic circulation rather than the pulmonary circulation.
- It can be intralobar, located within a normal lung lobe, or extralobar, located outside the normal lung with its own pleura.
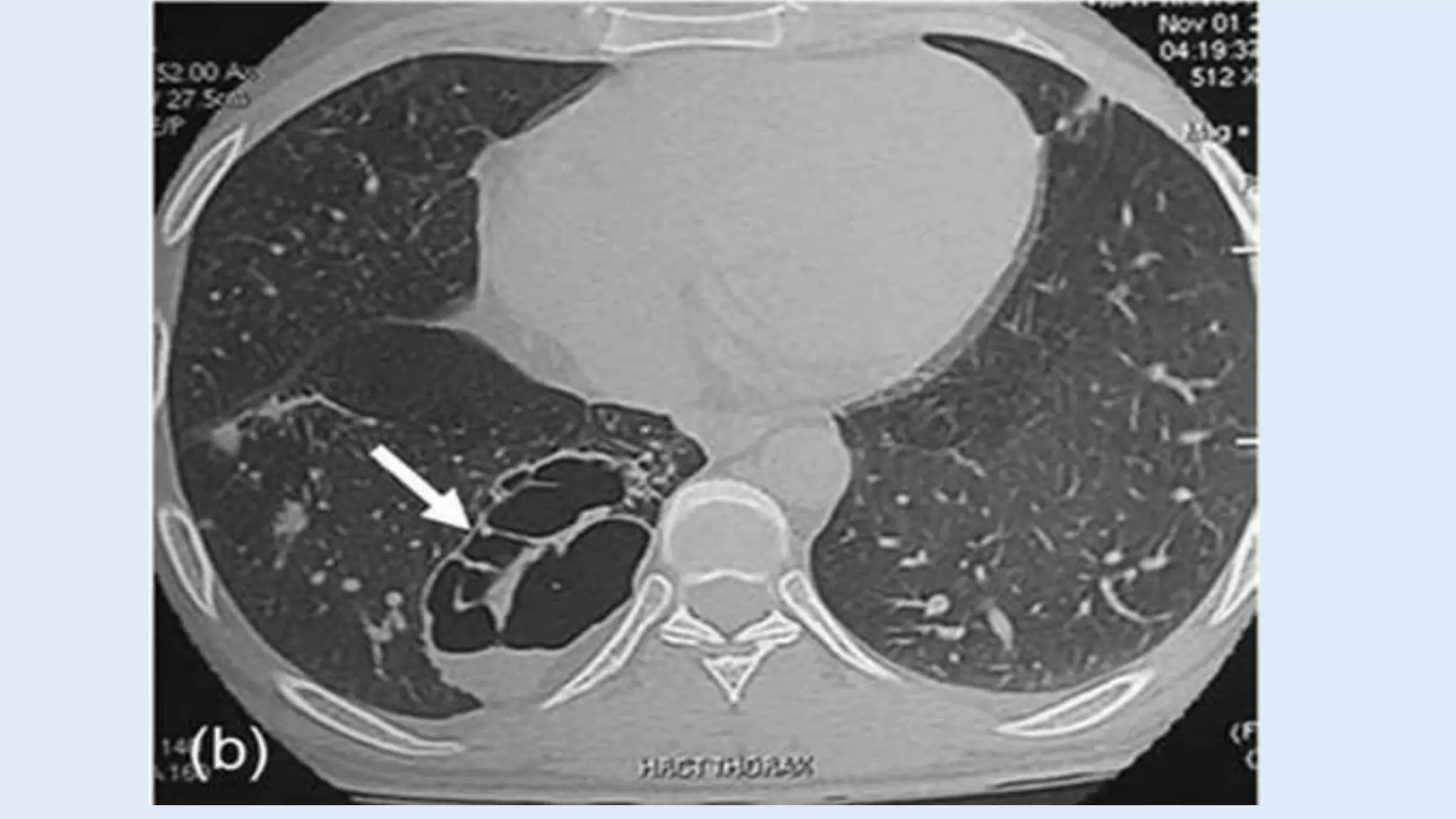
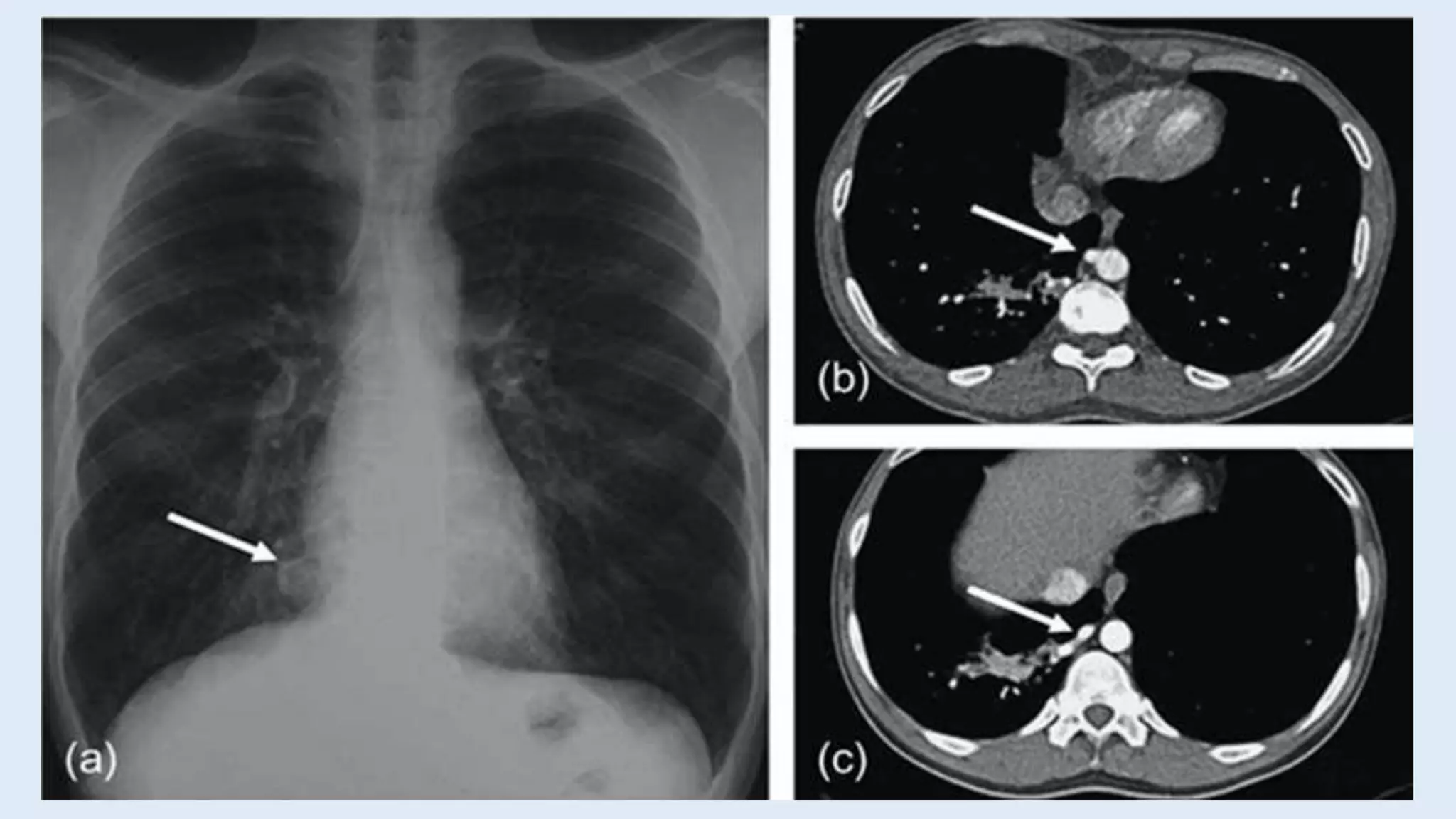
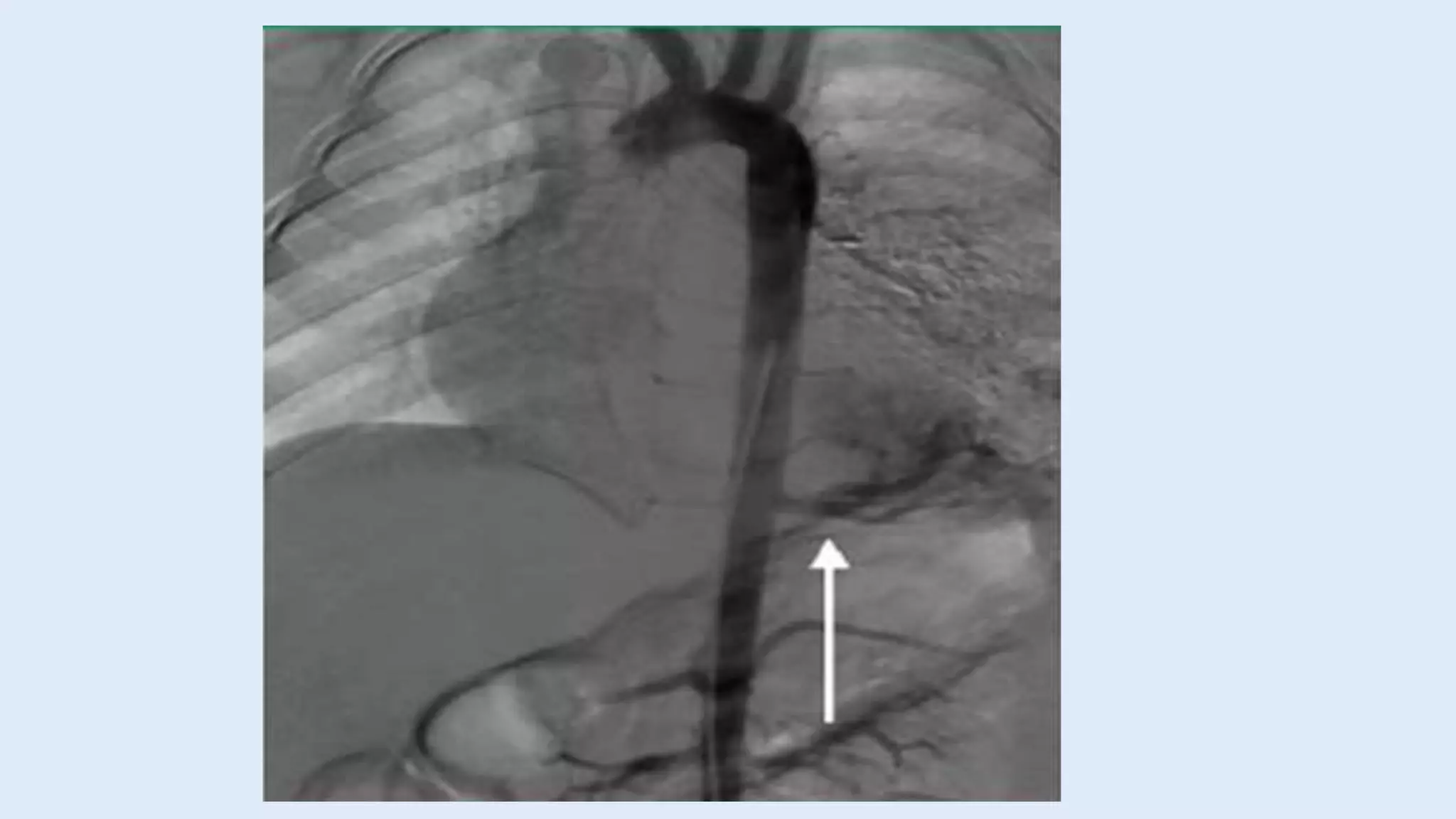
- Presentation depends on type, size, and location but includes respiratory distress in infants or recurrent pulmonary infections. Chest imaging finds a dense lung mass and CT/MRI identify the aberrant blood supply.
- Surgical resection is recommended for symptomatic cases or high-risk asymptomatic cases to prevent complications like infection. Small extralobar cases may be observed.



![Extralobar Sequestration
Less Common 25%
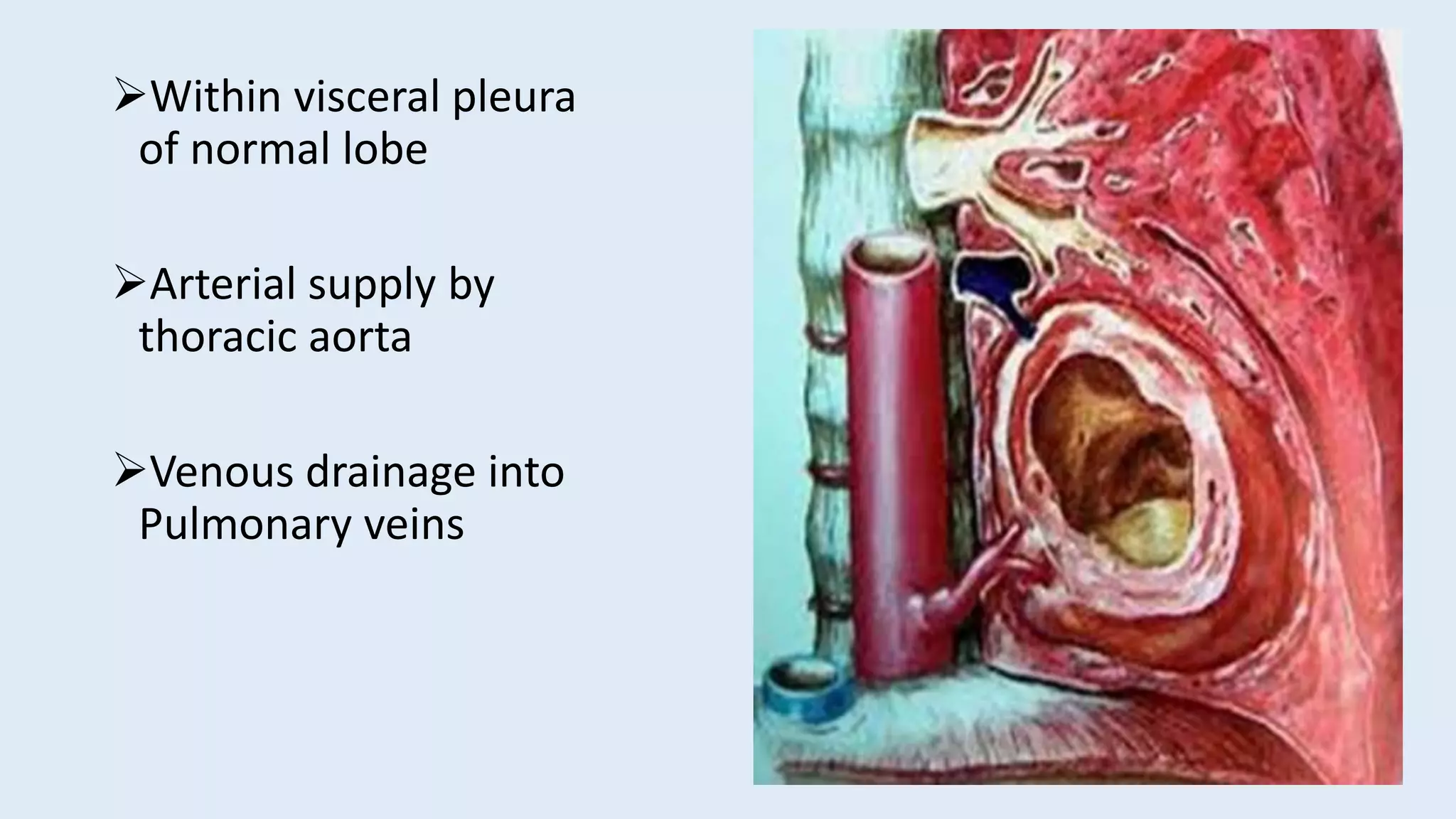
Located outside the normal lung and has its own visceral Pleura
Male predominance.
ELS are more common on the left side [between the left lower
lobe and hemi diaphragm (80%)].
They may also be found within or below the diaphragm or in
retroperitoneum](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonarysequestration-190922164440/75/Pulmonary-sequestration-8-2048.jpg)