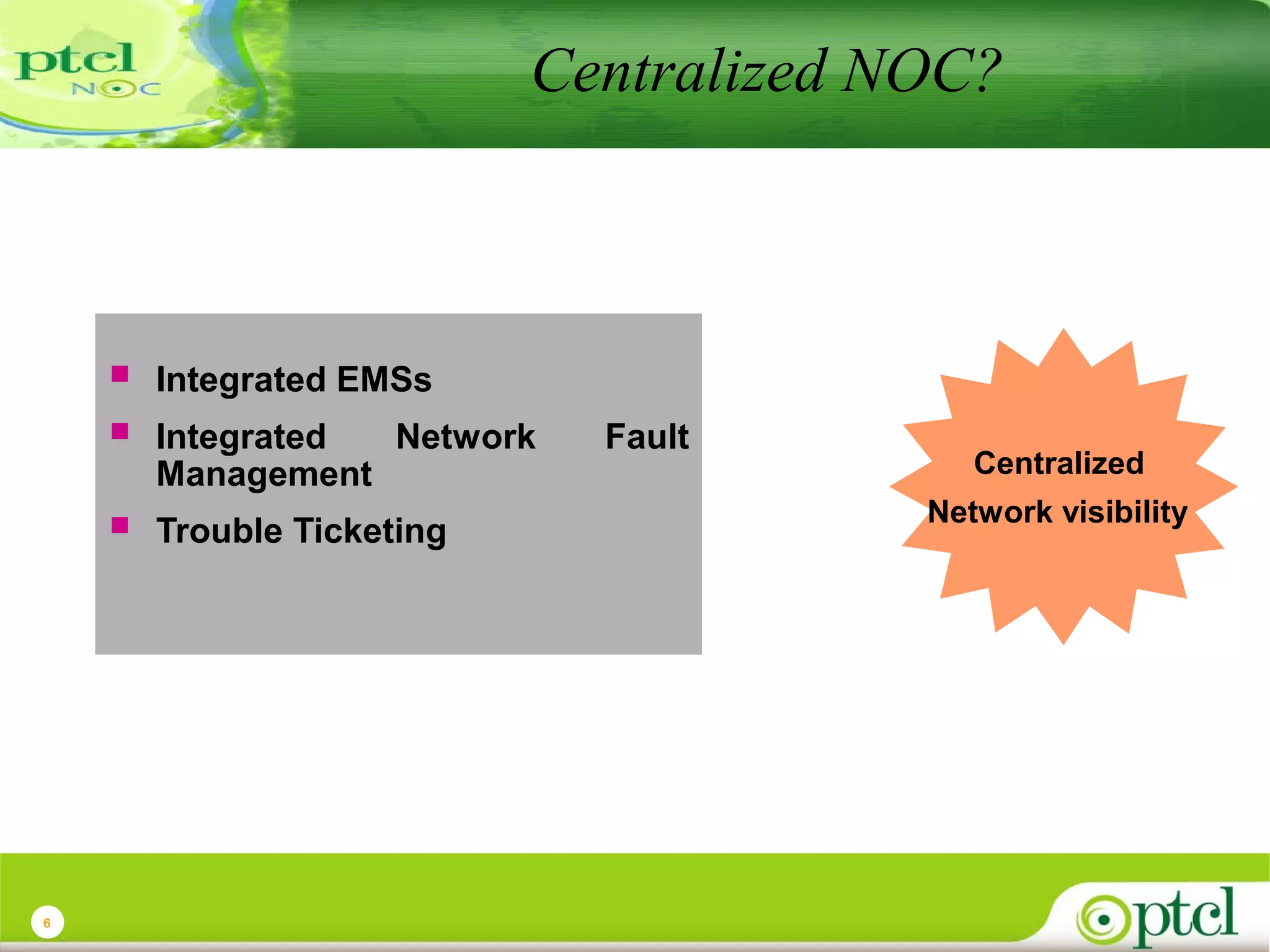
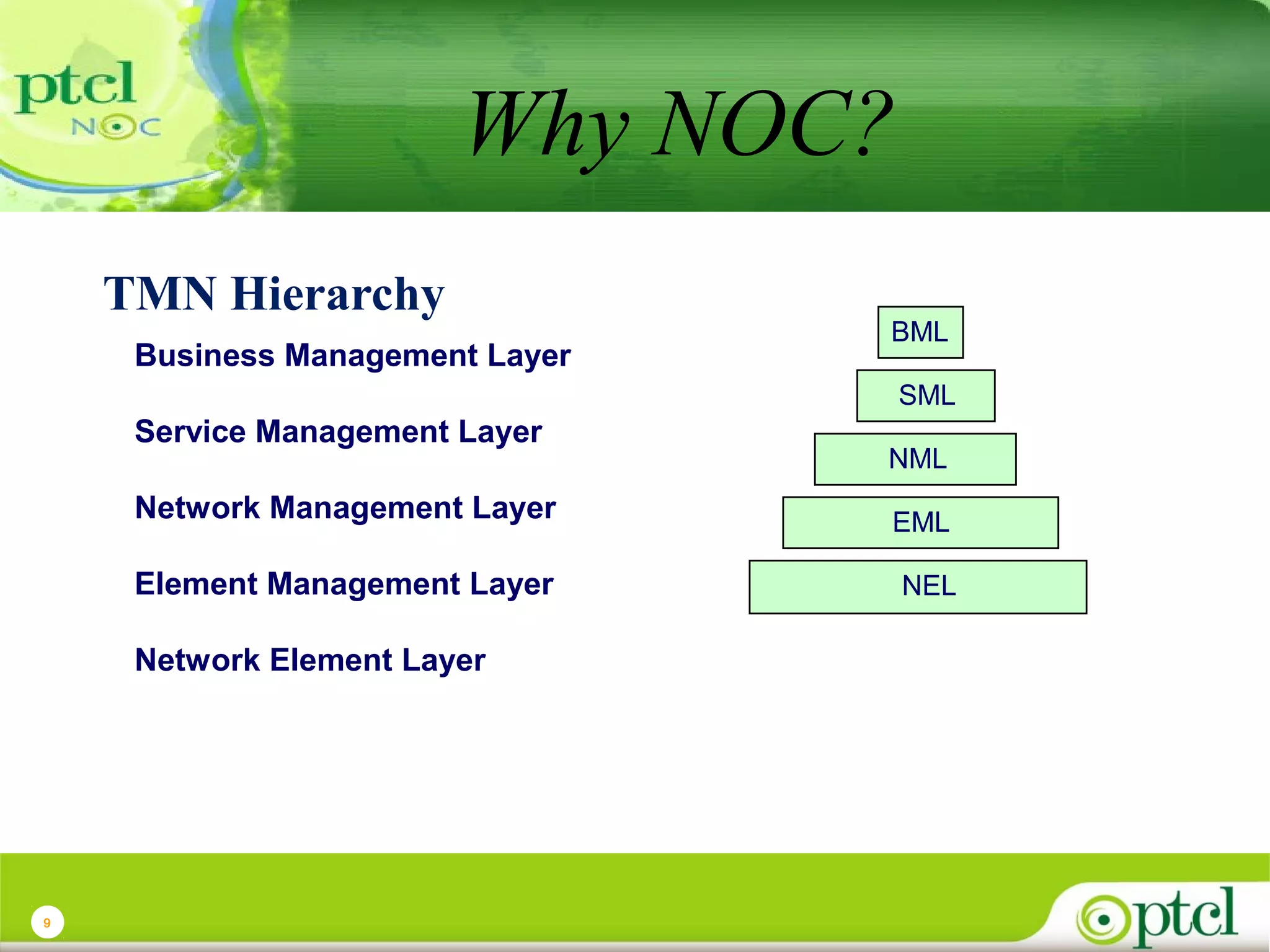
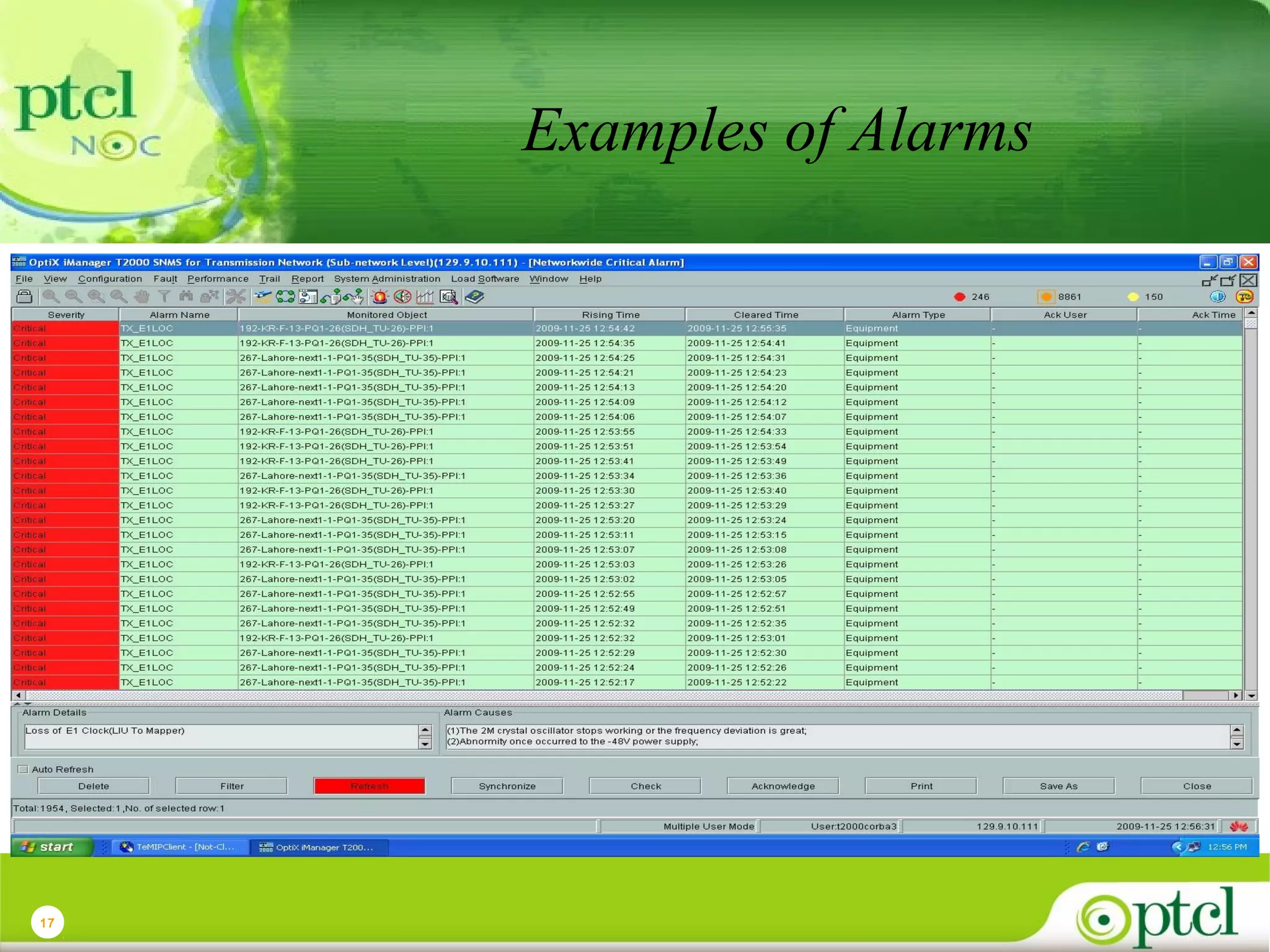
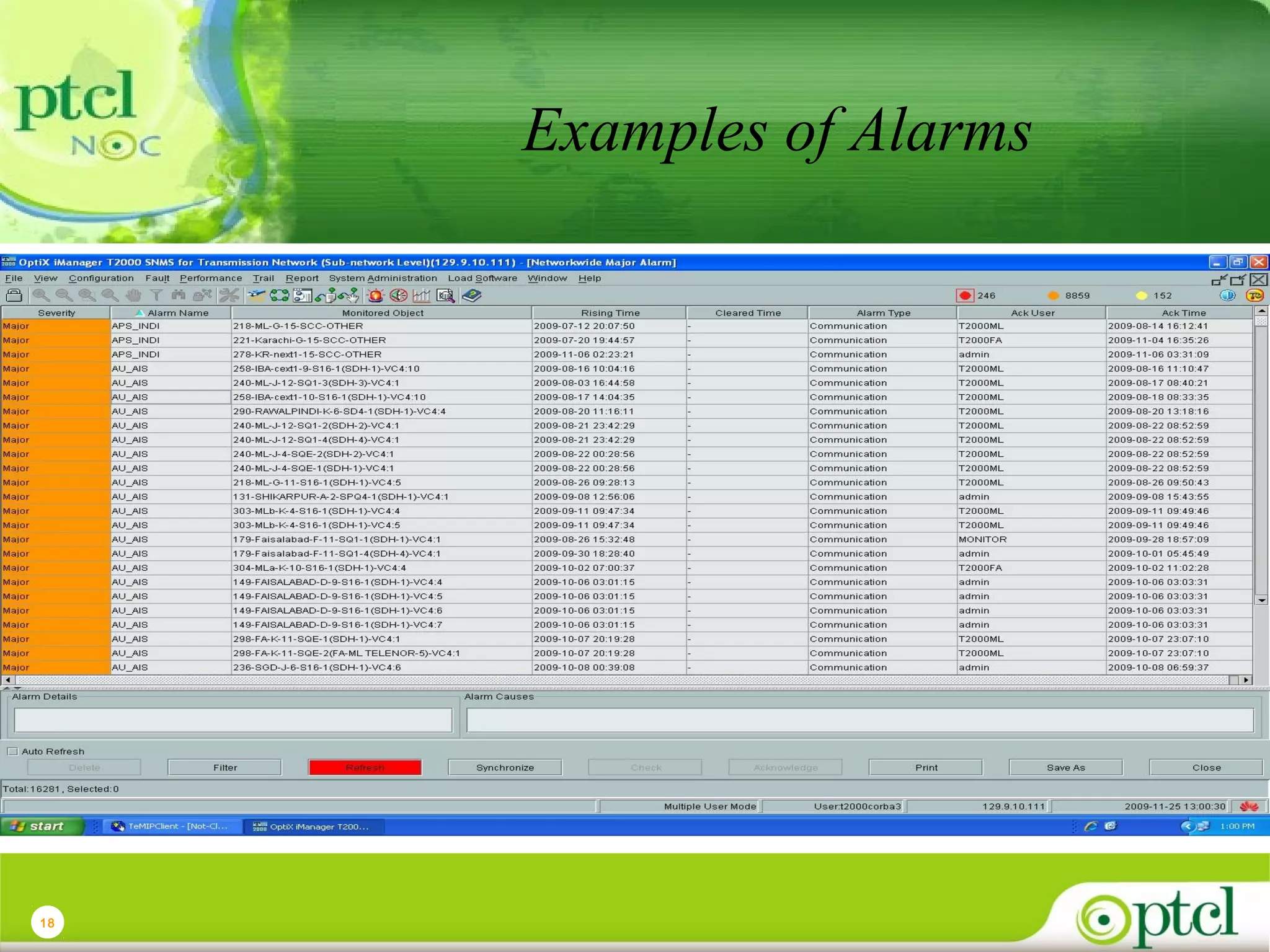
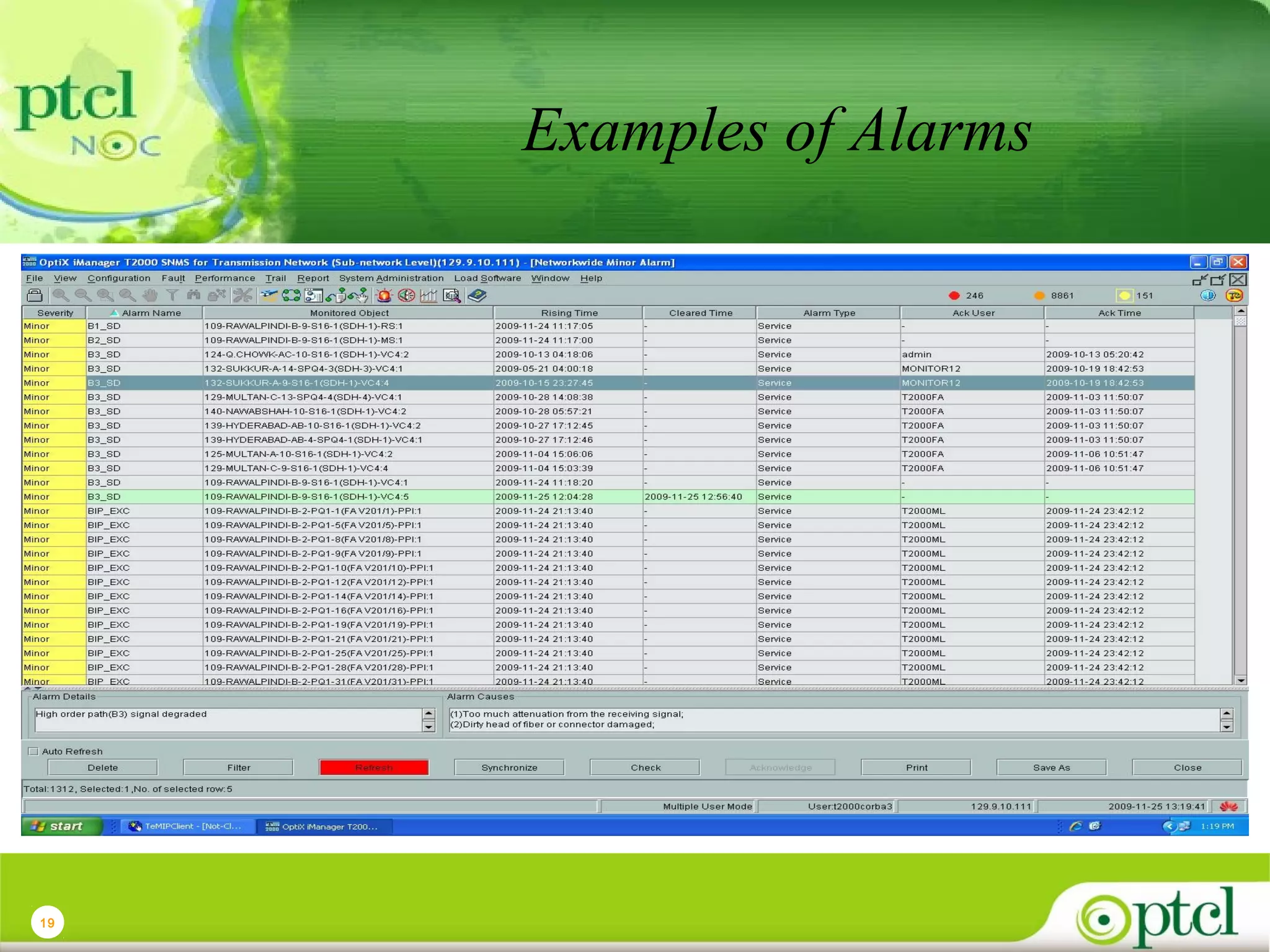
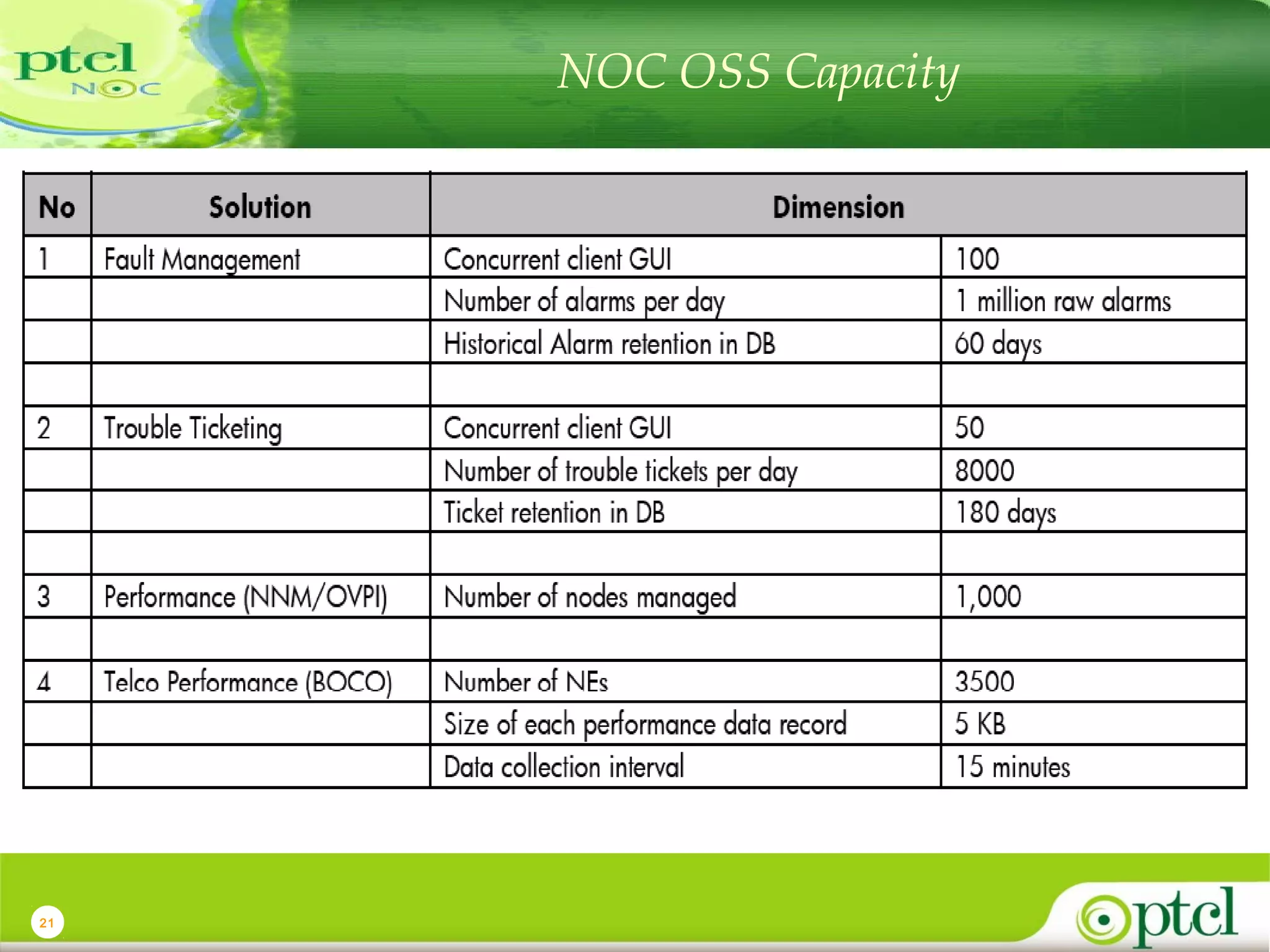
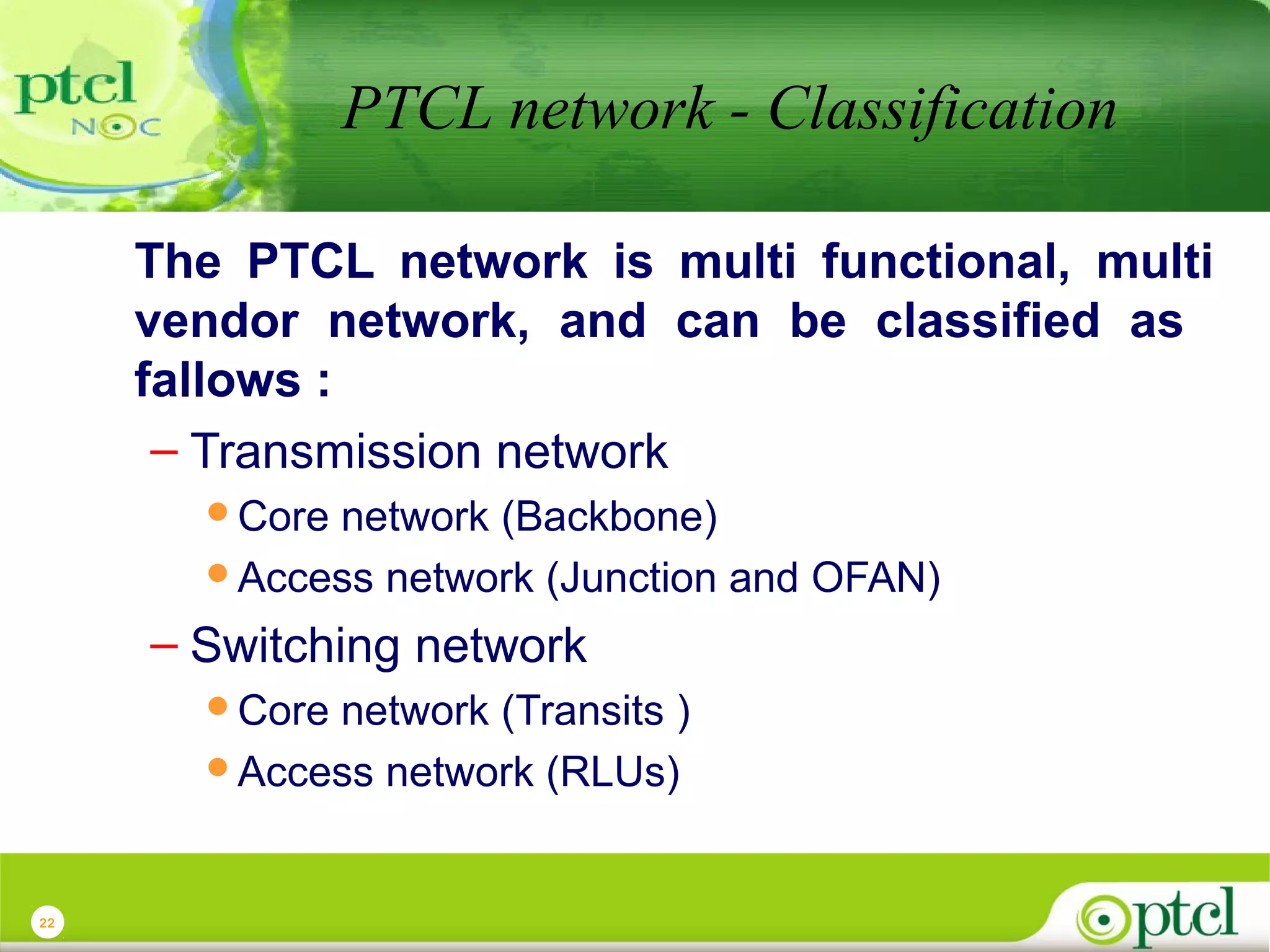
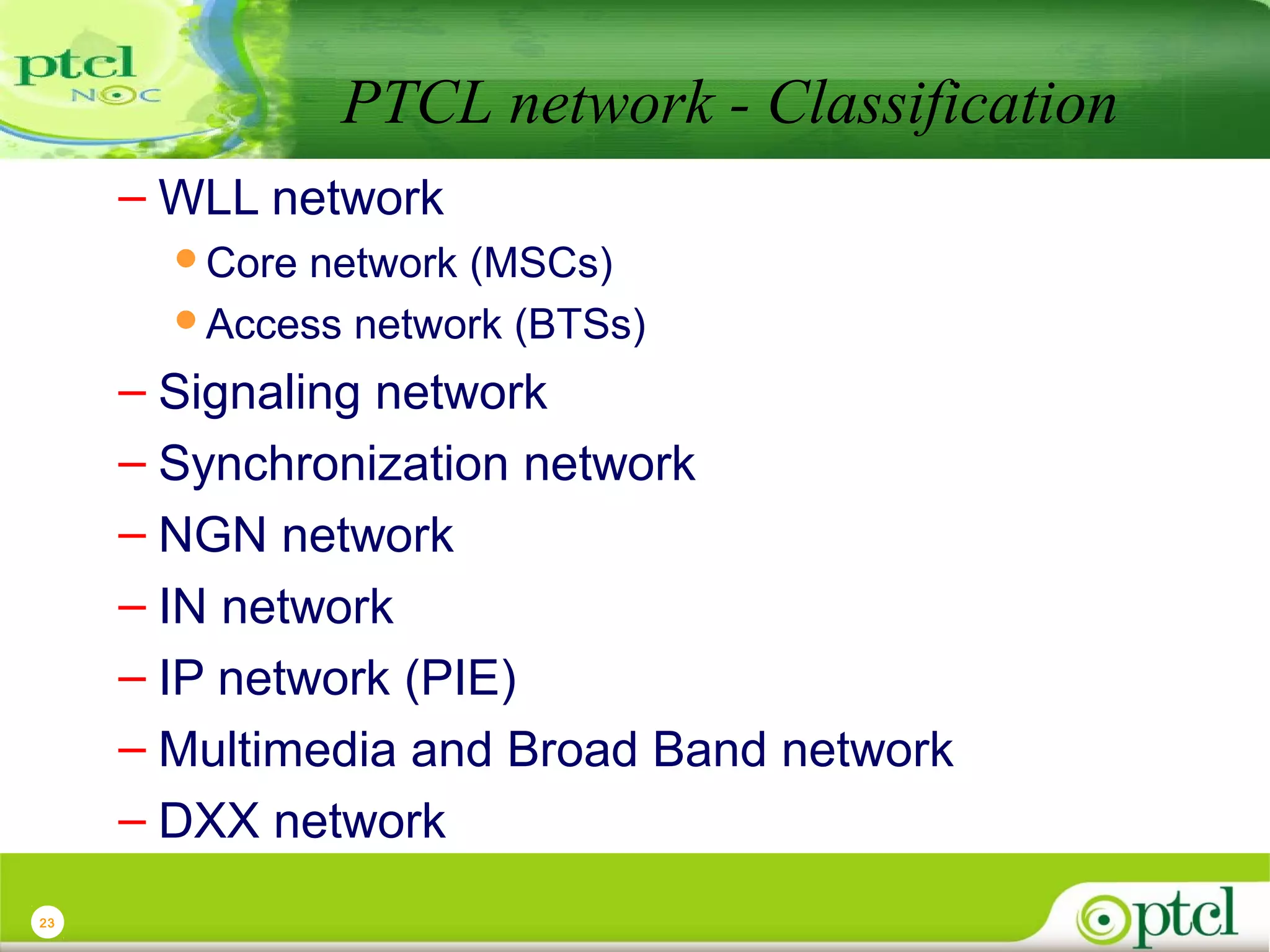
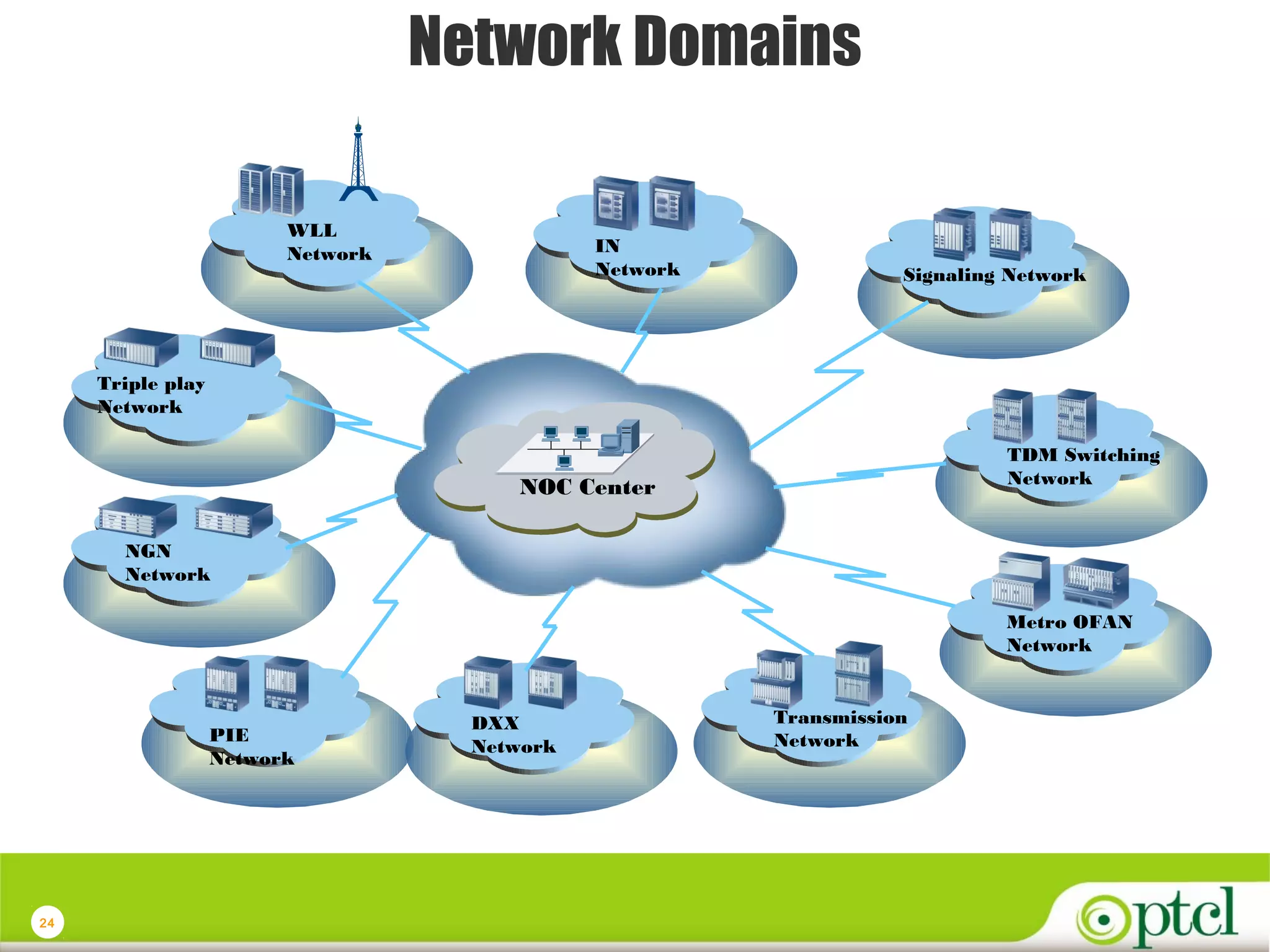
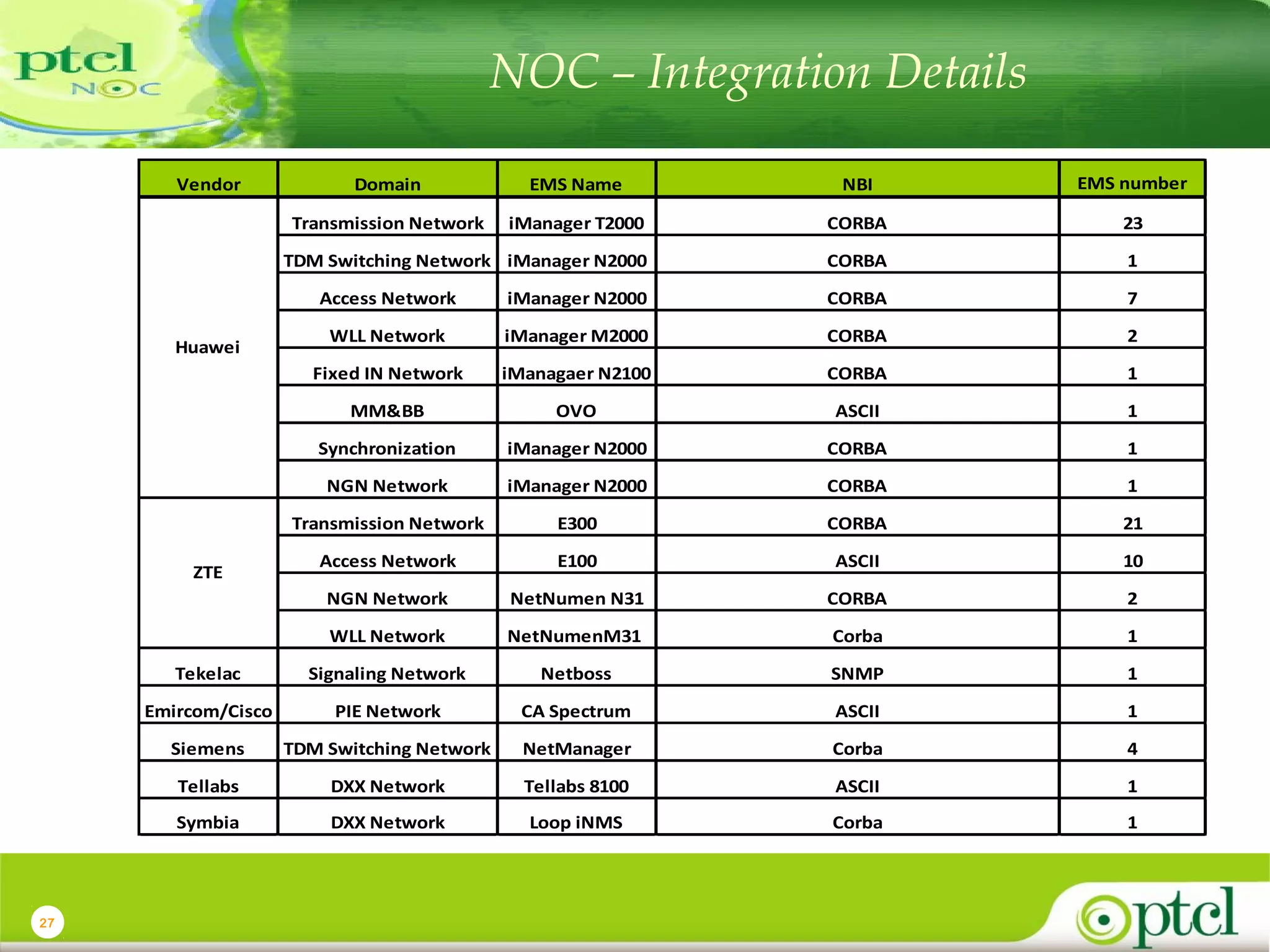
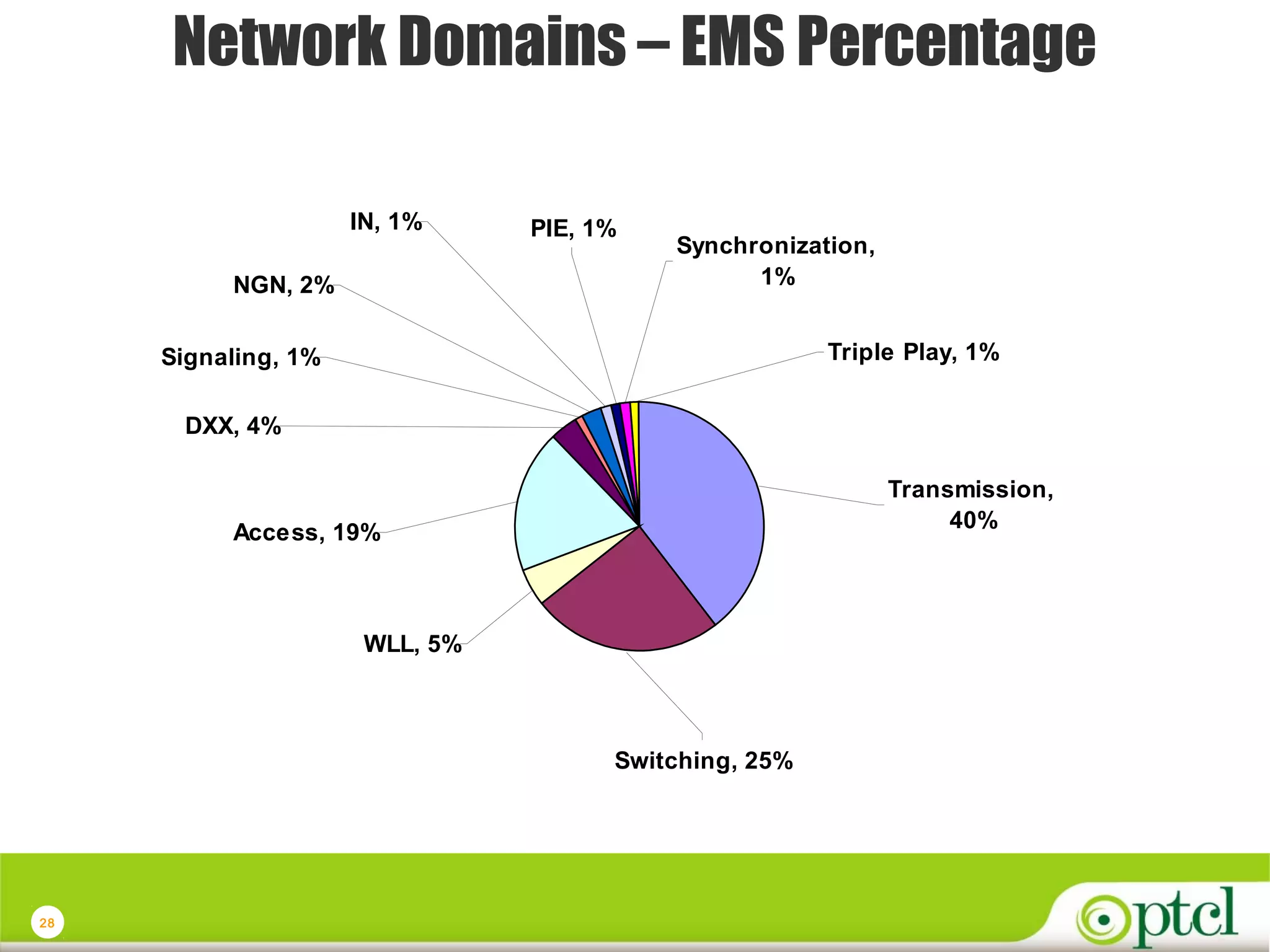
The document discusses PTCL's National Network Operations Center (NOC). The NOC monitors and manages PTCL's networks using a set of Operations Support Systems and standardized processes. It provides centralized visibility and control of PTCL's multi-vendor, multi-technology networks. The NOC aims to improve network availability, fault resolution times, and operational efficiency through consolidated network monitoring, trouble ticketing, and performance reporting. It integrates data from over 35 Element Management Systems across PTCL's transmission, switching, access, wireless and other network domains.