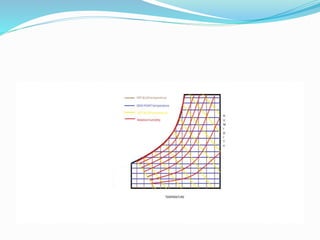
The document defines key terms related to psychrometrics, which is the science of moist air properties and processes. It explains that atmospheric air contains a mixture of gases including nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapor. Moist air contains both air and water vapor, while saturated air contains the maximum possible amount of water vapor. Other terms defined include humidity, dry bulb temperature, wet bulb temperature, relative humidity, vapor pressure, specific humidity, dew point temperature, and enthalpy. The document concludes by explaining that a psychrometric chart graphically represents various psychrometric properties and processes on a single plot.