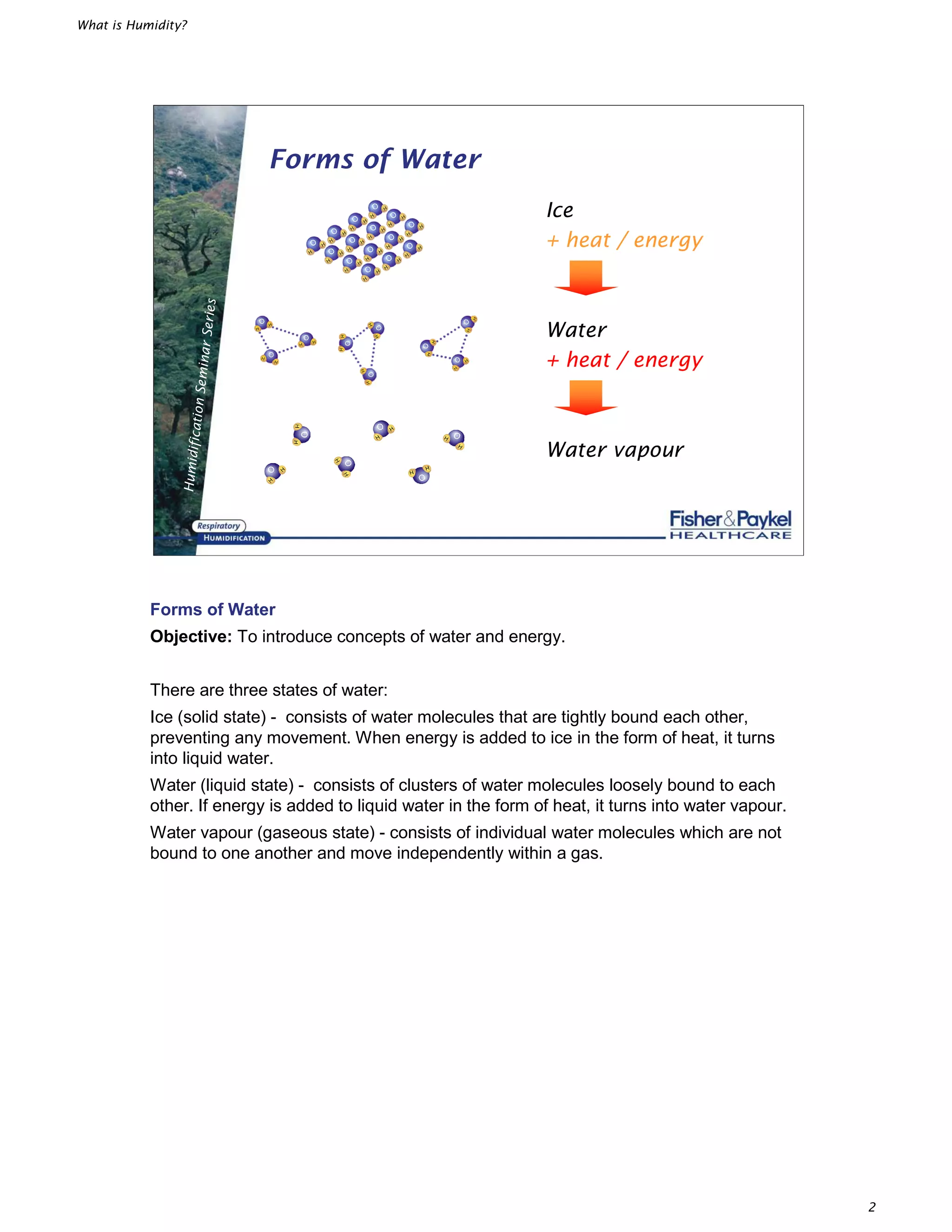
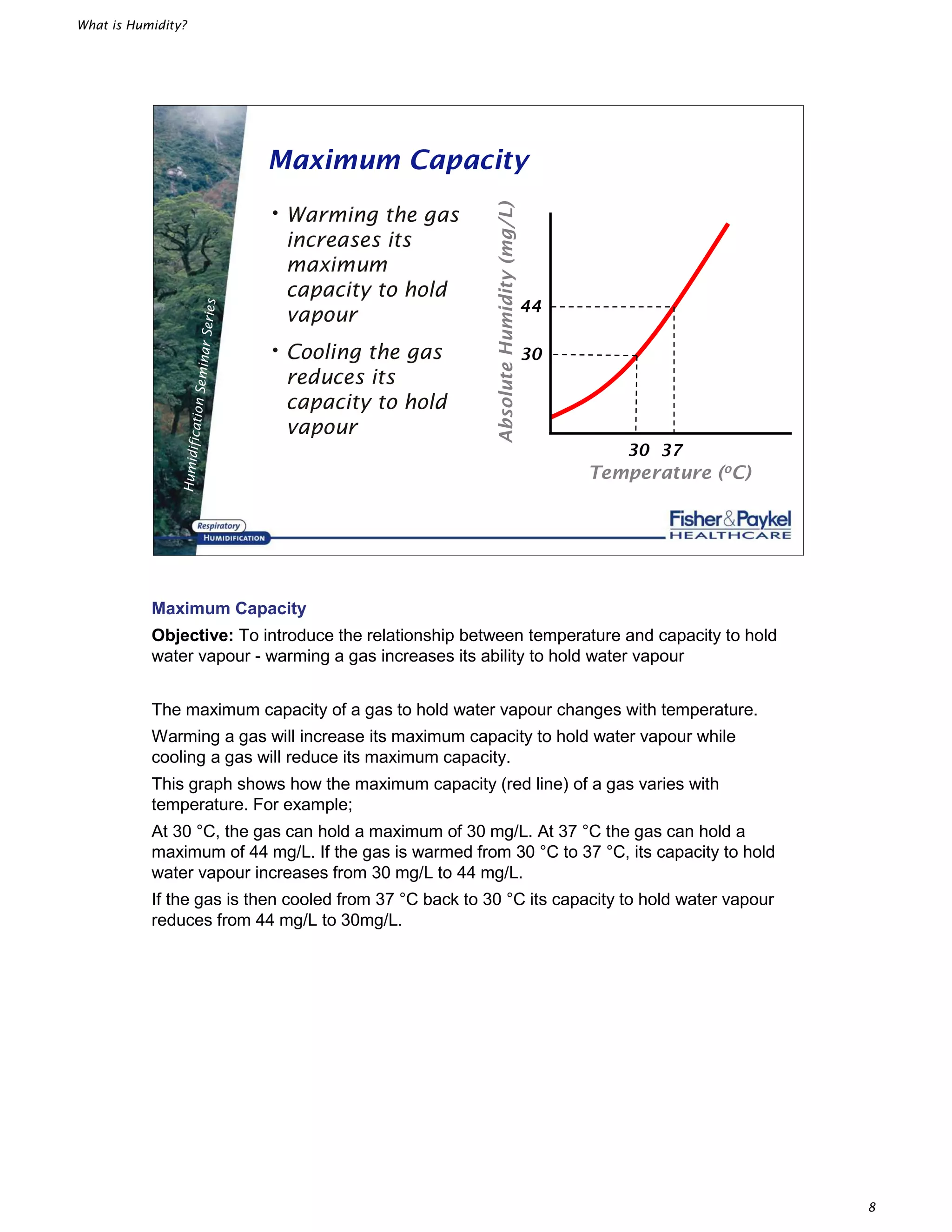
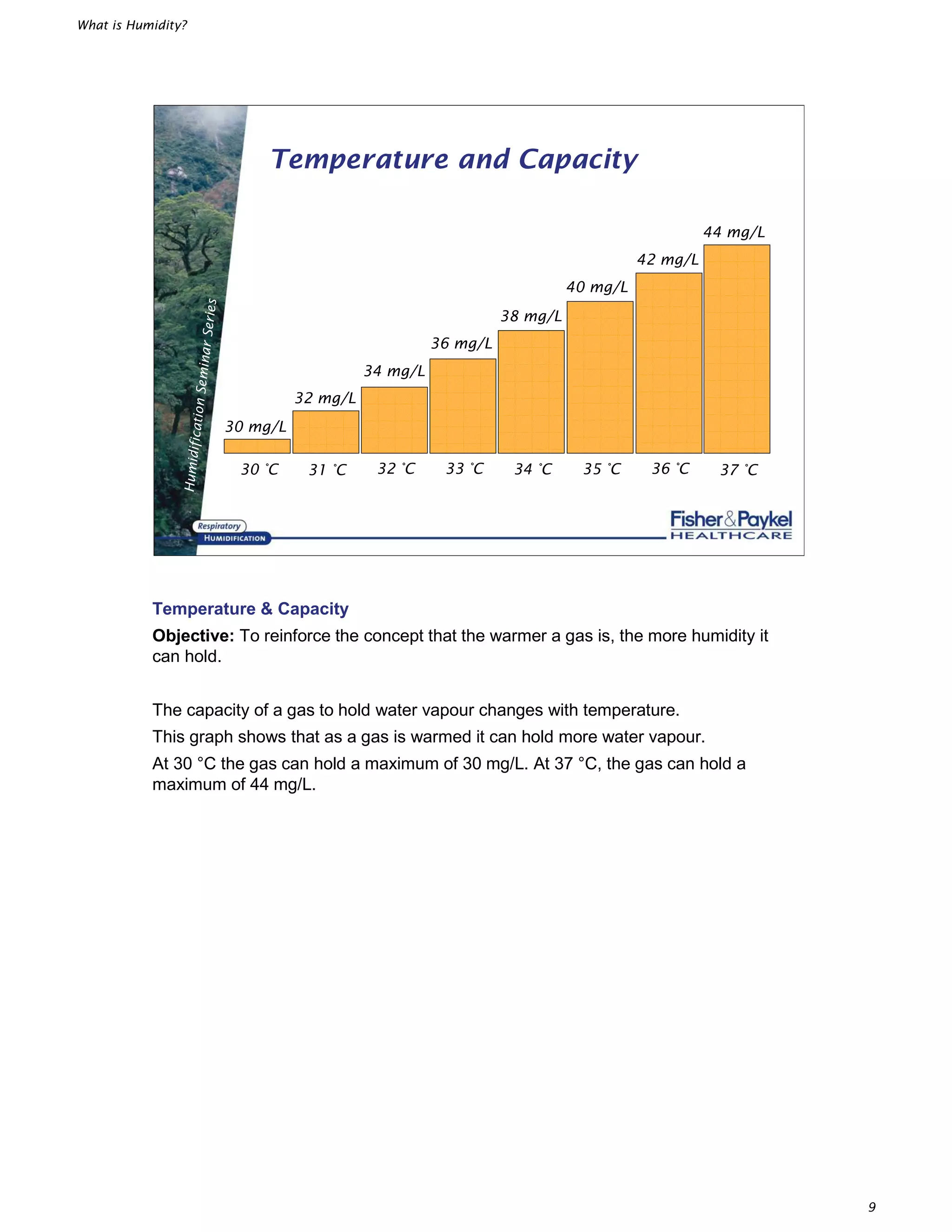
This document defines several key terms related to humidity:
- Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor in a gas. It can be expressed in terms of absolute humidity, relative humidity, and dewpoint.
- Absolute humidity is the actual amount of water vapor per liter of gas, measured in mg/L. Relative humidity expresses the amount of water vapor as a percentage of the maximum the gas can hold at a given temperature. Dewpoint is the temperature at which the gas reaches 100% relative humidity.
- The maximum amount of water vapor a gas can hold depends on temperature - the warmer the gas, the more water vapor it can hold before reaching saturation.