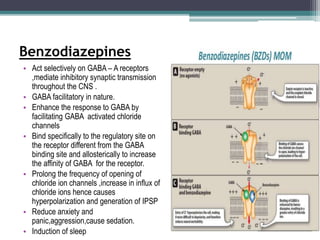
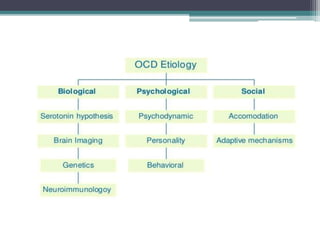
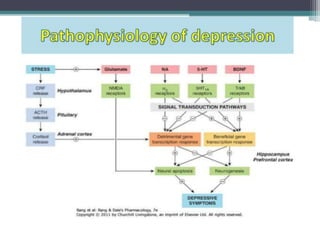
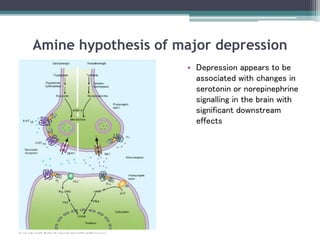
This document summarizes psychiatric disorders and their pharmacotherapy. It discusses anxiety disorders, obsessive compulsive disorder, depression, bipolar disorder, and mania. For each disorder, it covers definitions, types, biological mechanisms, and common drug treatments. The key drugs discussed are benzodiazepines, SSRIs, SNRIs, and atypical antipsychotics for anxiety, OCD, and mood disorders.