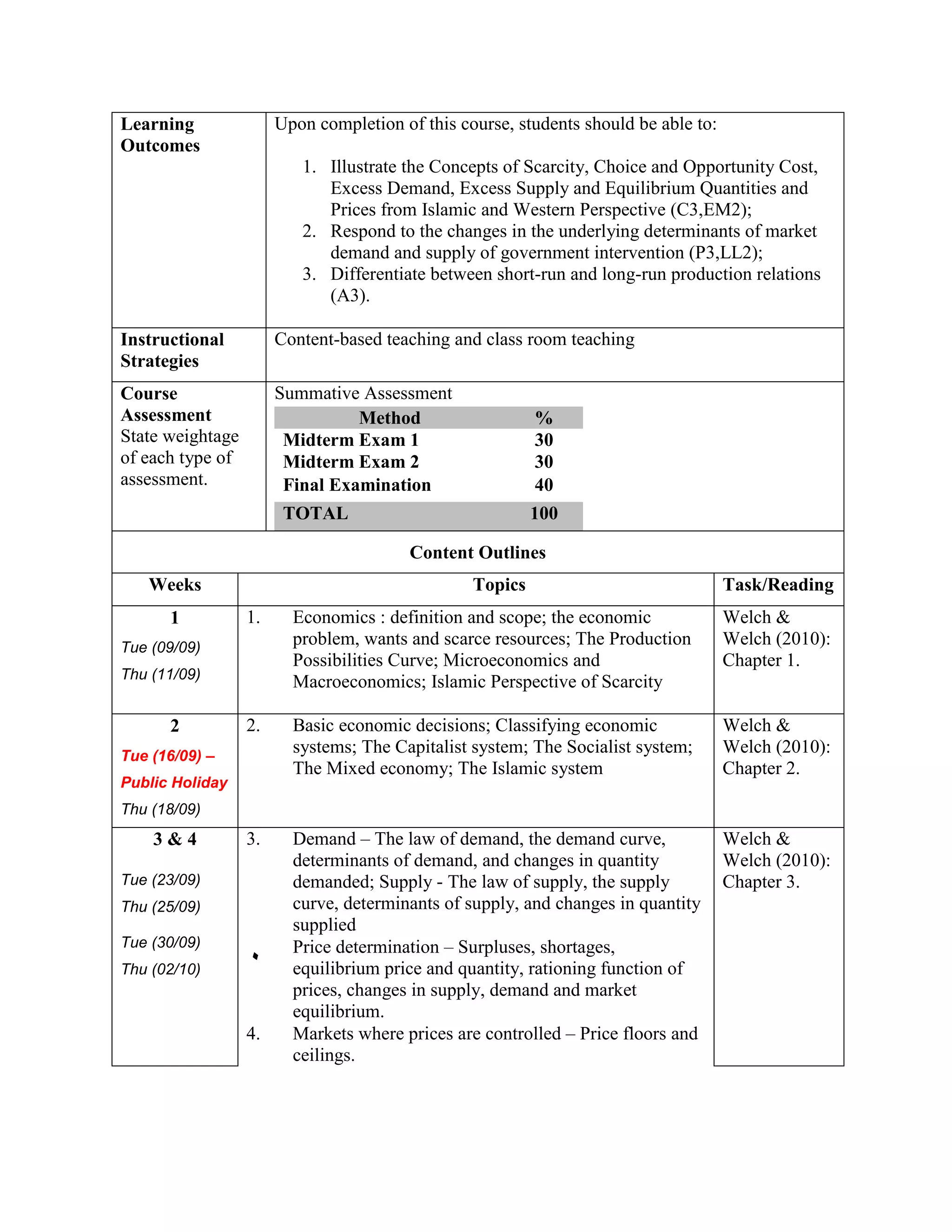
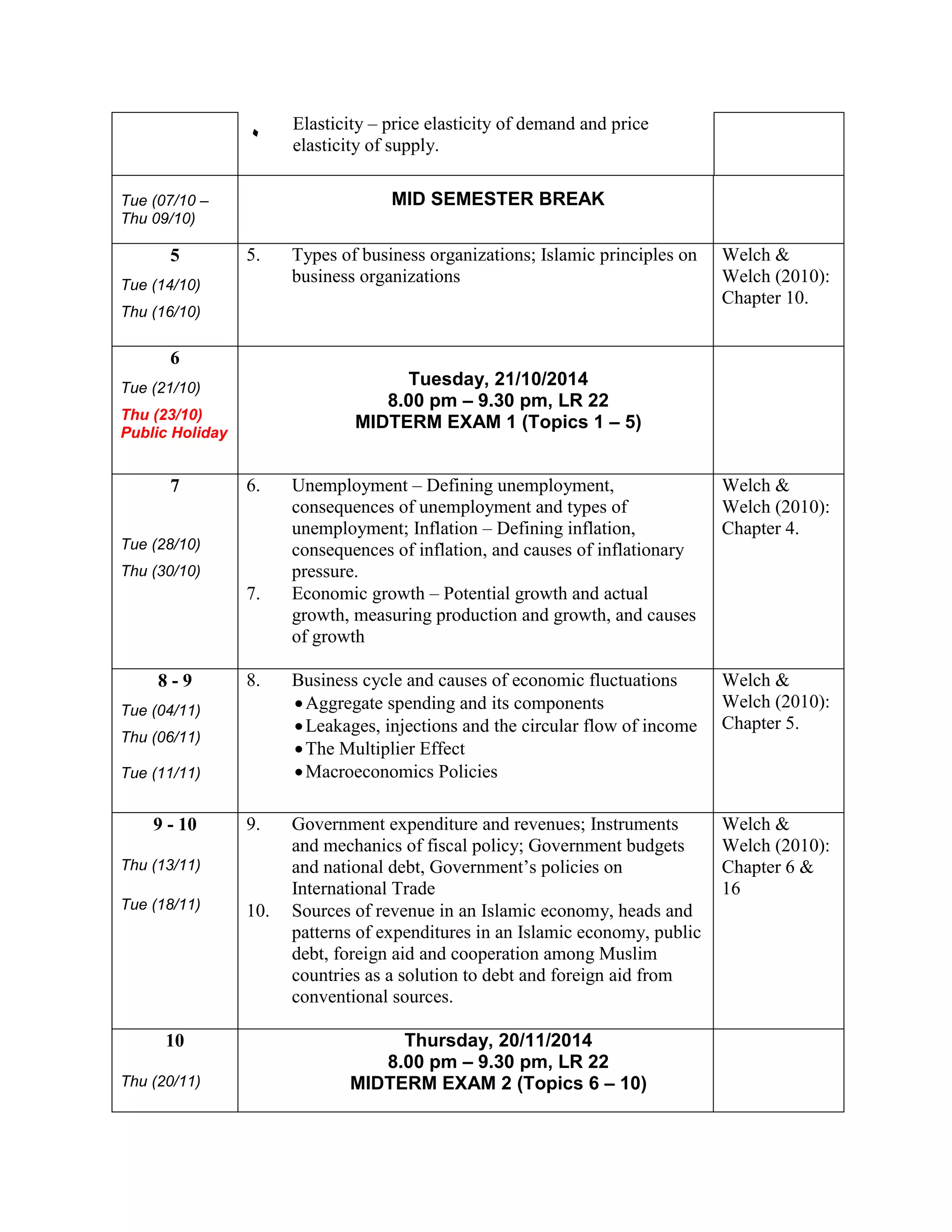
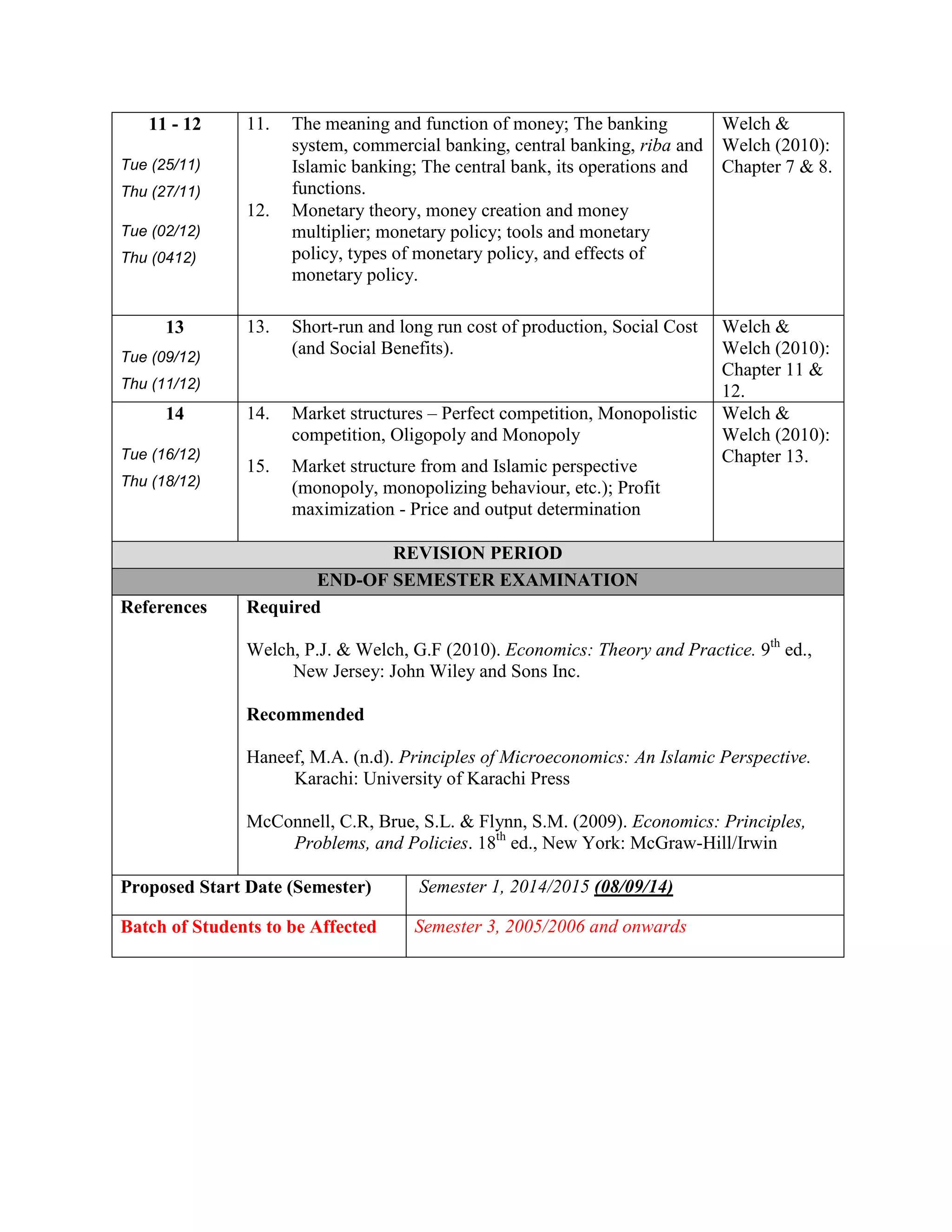
This document outlines a course on Introduction to Economics offered at the International Islamic University Malaysia. The 3-credit, 3-hour course is offered every semester to political science students. It introduces both conventional and Islamic perspectives on microeconomic and macroeconomic concepts. Topics include scarcity, production possibilities, demand and supply, market structures, unemployment, inflation, economic growth, fiscal and monetary policy. Assessment includes two midterm exams and a final exam. The course aims to familiarize students with relevant economic theories and enable them to apply economic policies through an Islamic lens.