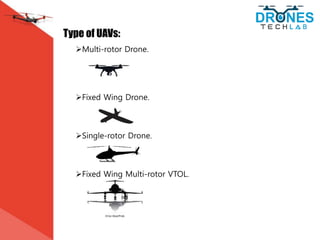
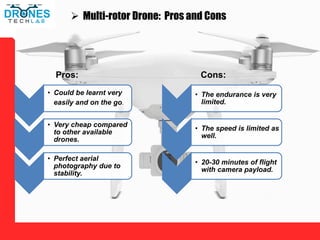
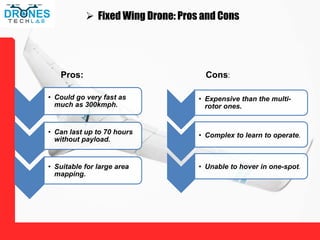
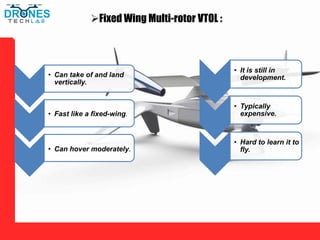
This document discusses different types of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs or drones). It describes multi-rotor drones, fixed wing drones, single rotor drones, and fixed wing multi-rotor VTOL drones. For each type, it provides details on their propulsion methods and pros and cons. It also lists many applications of drones such as firefighting, security/surveillance, inspections, science/research, aerial photography, surveying, cargo delivery, agriculture, mining, construction, and search and rescue. Drones are useful tools for these tasks due to their ability to provide aerial views and access difficult or dangerous areas.