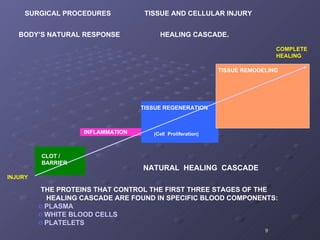
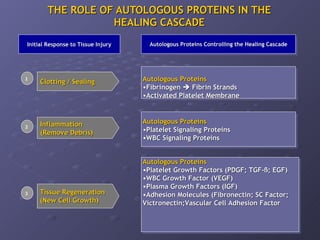
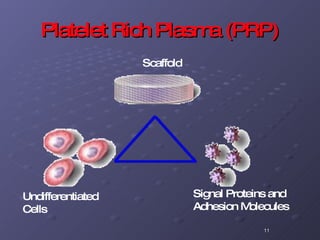
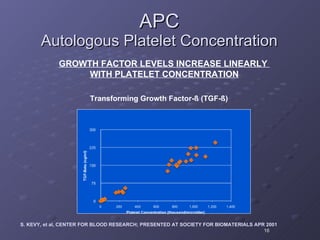
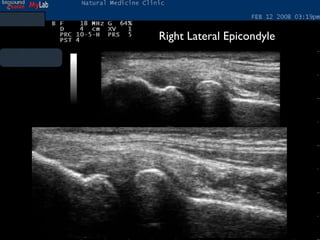
The document discusses platelet autografting and platelet rich plasma (PRP) therapy. It explains that delivering concentrated autologous proteins from a platelet concentrate to a surgical site may improve healing by enhancing the early phases of the body's natural healing cascade. It provides details on research studies that have found PRP therapy reduces pain and improves function for tendinopathy, plantar fasciitis, and macular holes compared to controls. One study found a single PRP injection significantly improved outcomes for patients with chronic elbow tendinosis who had previously failed non-surgical treatments.







![DELIVERING A CONCENTRATION OF AUTOLOGOUS PROTEINS TO THE SURGICAL SITE MAY IMPROVE THE HEALING RATE Hemostatic Barrier Inflammation Debridement Tissue Regeneration Tissue Remodeling Body’s Response to Tissue Injury [Time] Application of proteins from a platelet concentrate may dramatically improve the early phases of the Healing Cascade](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prpmatrixgrafts-12688376870055-phpapp02/85/Prp-Matrix-Grafts-8-320.jpg)