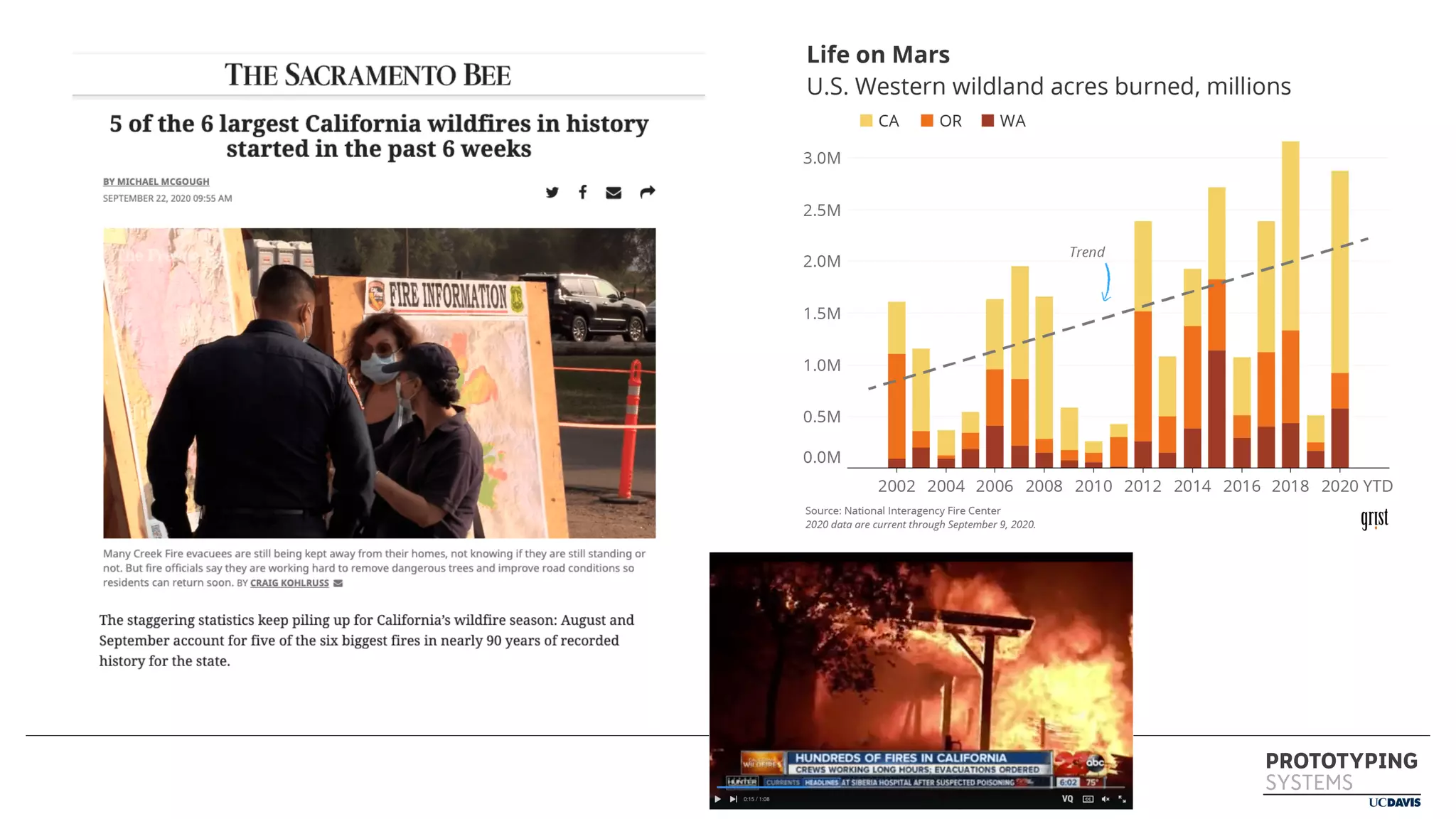
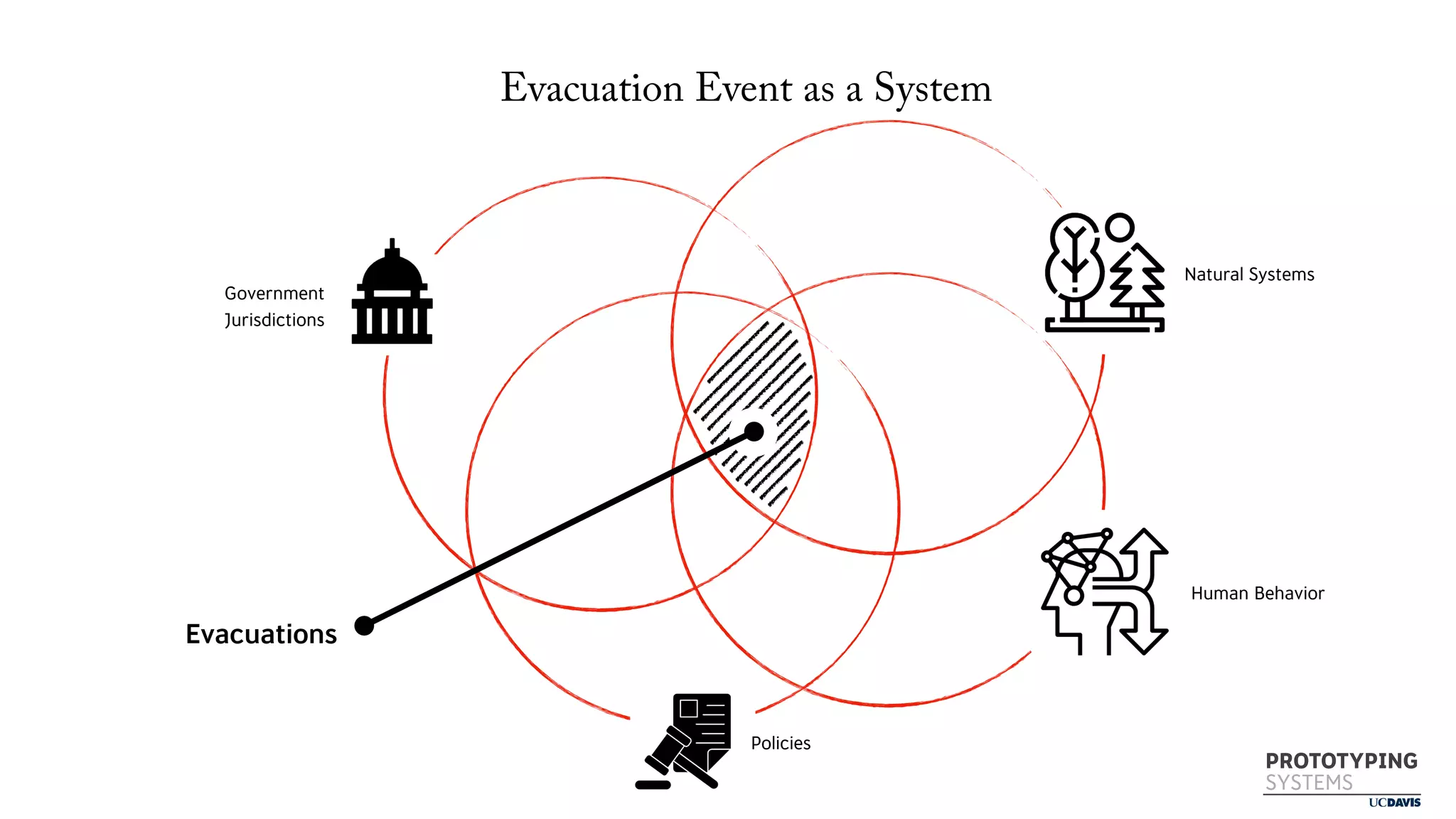
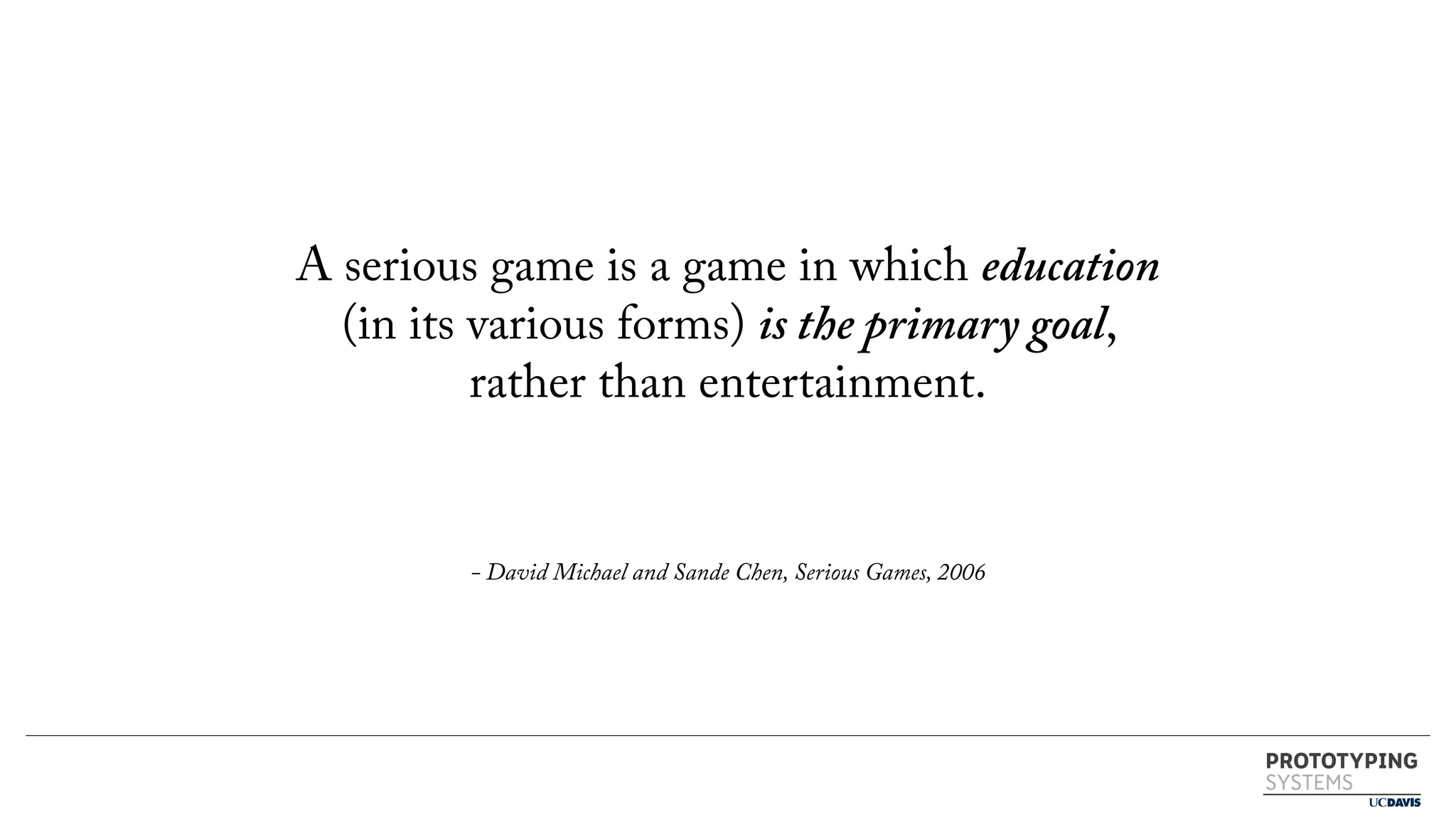
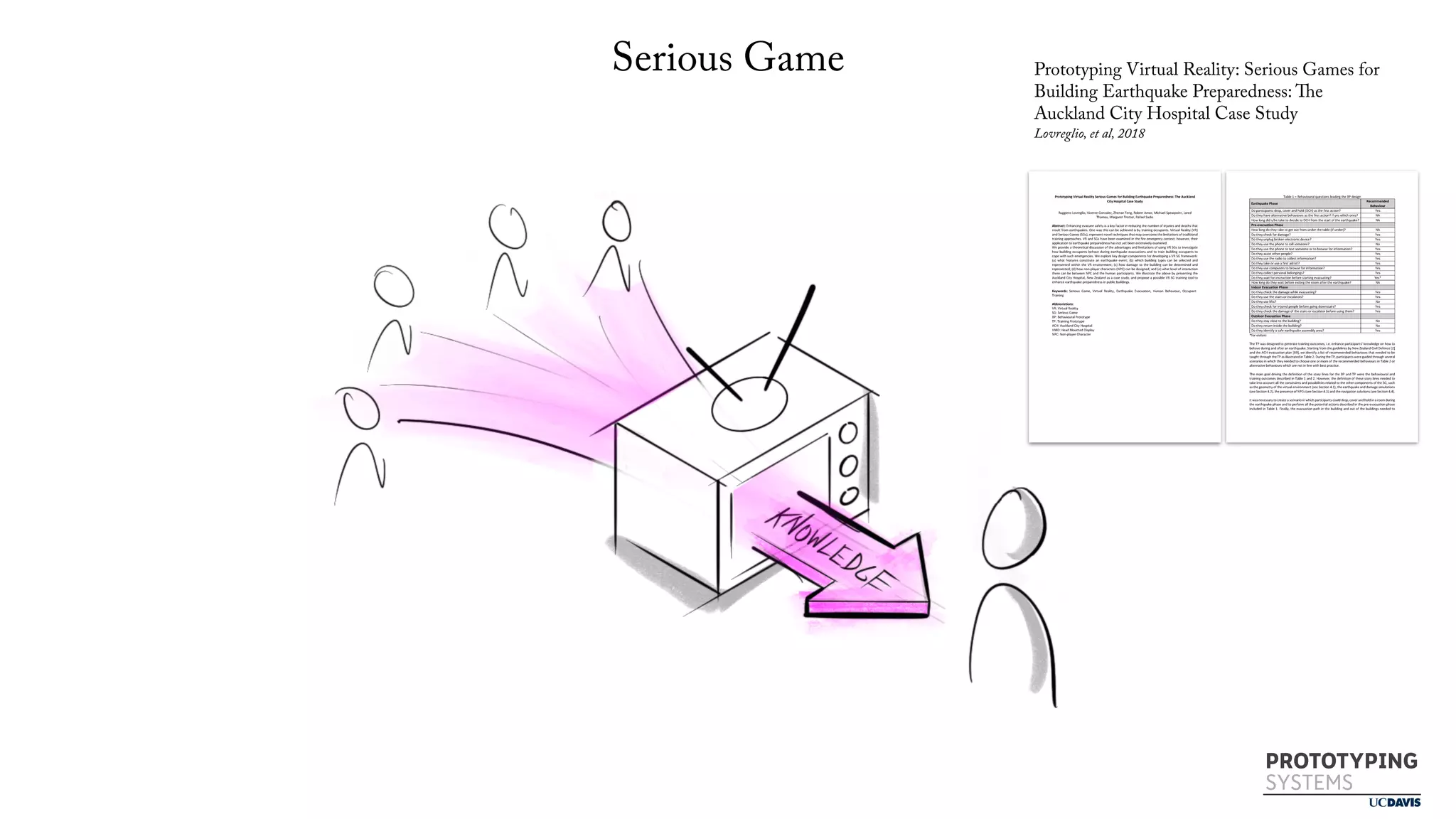
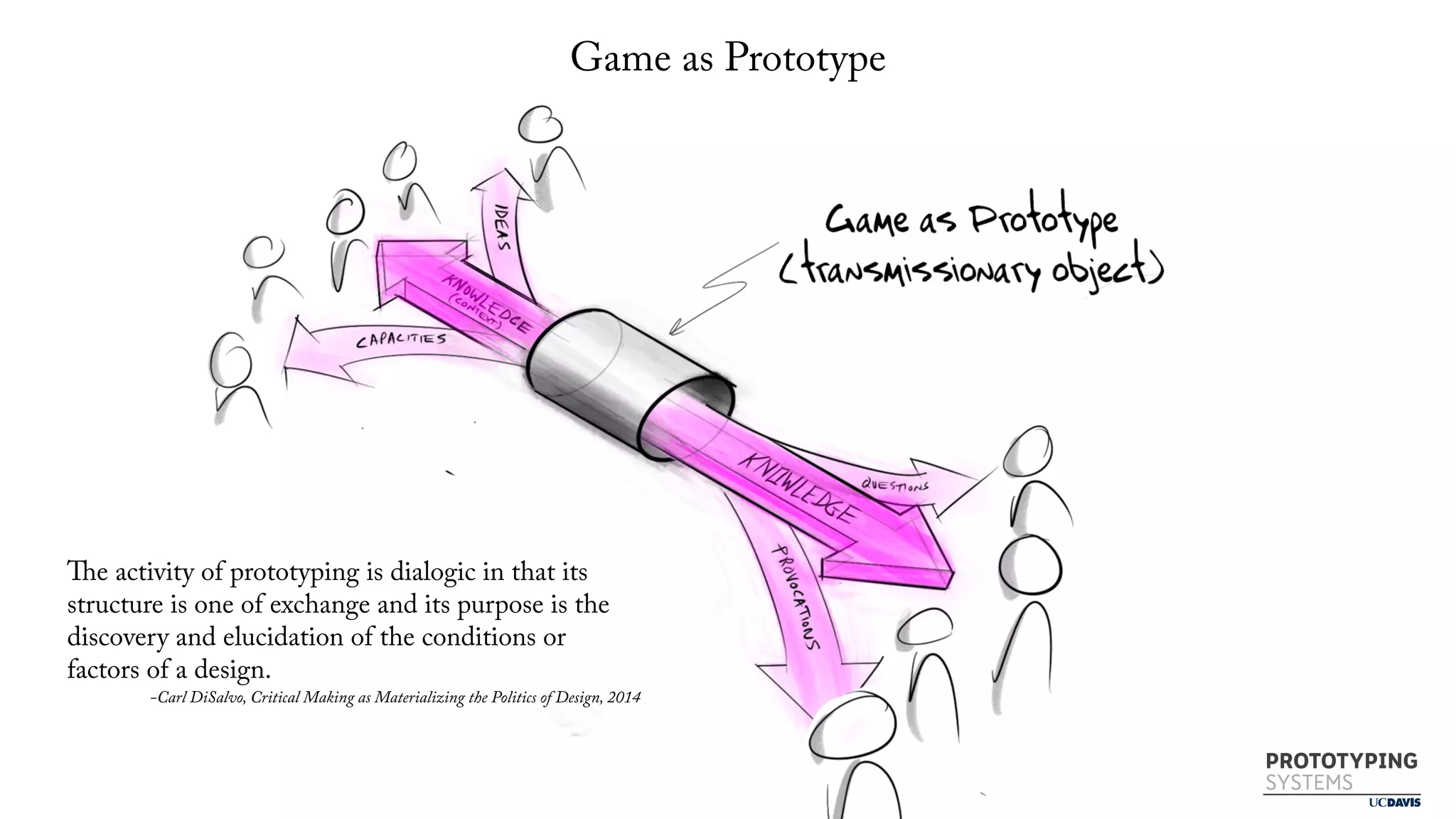
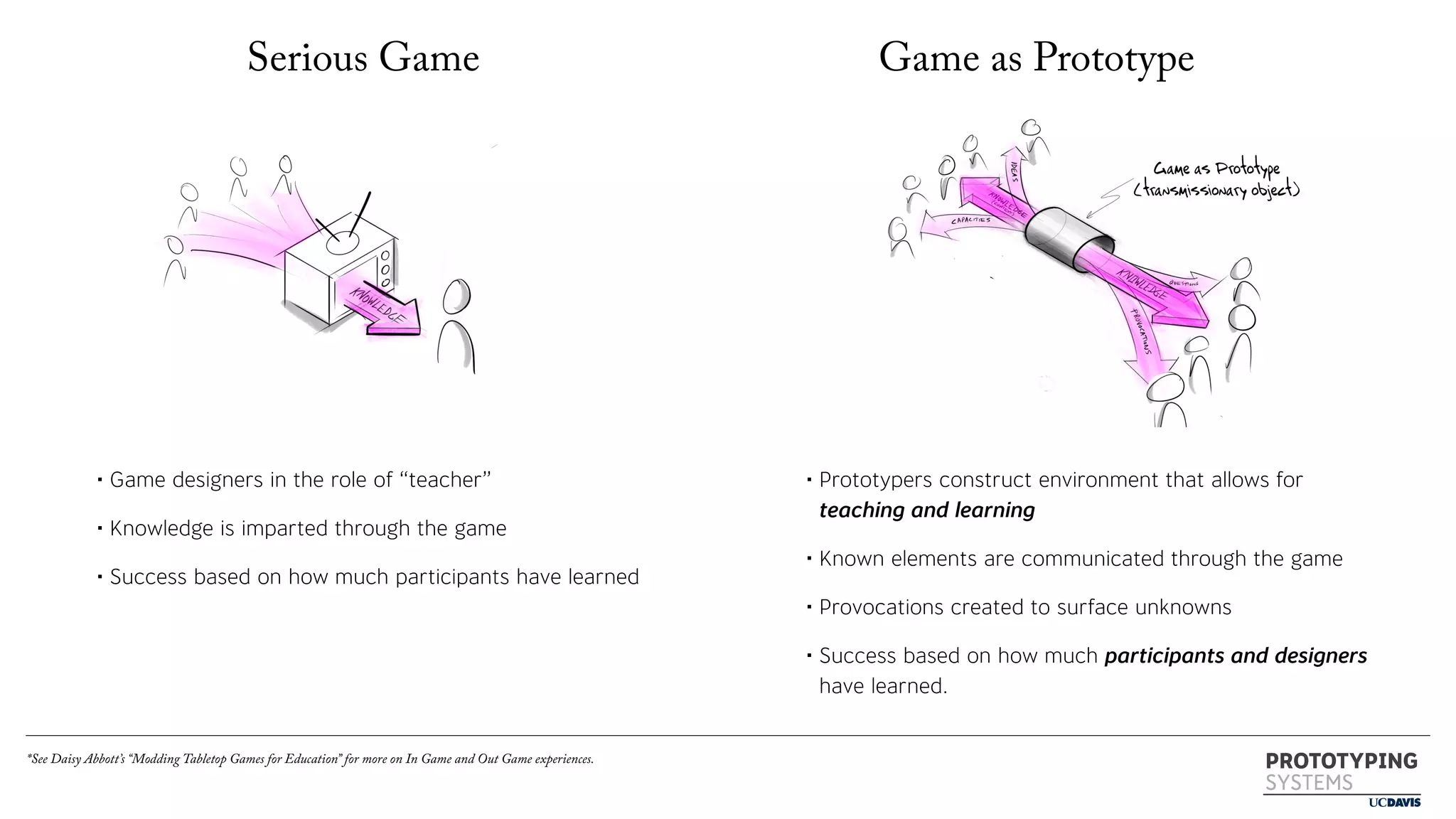
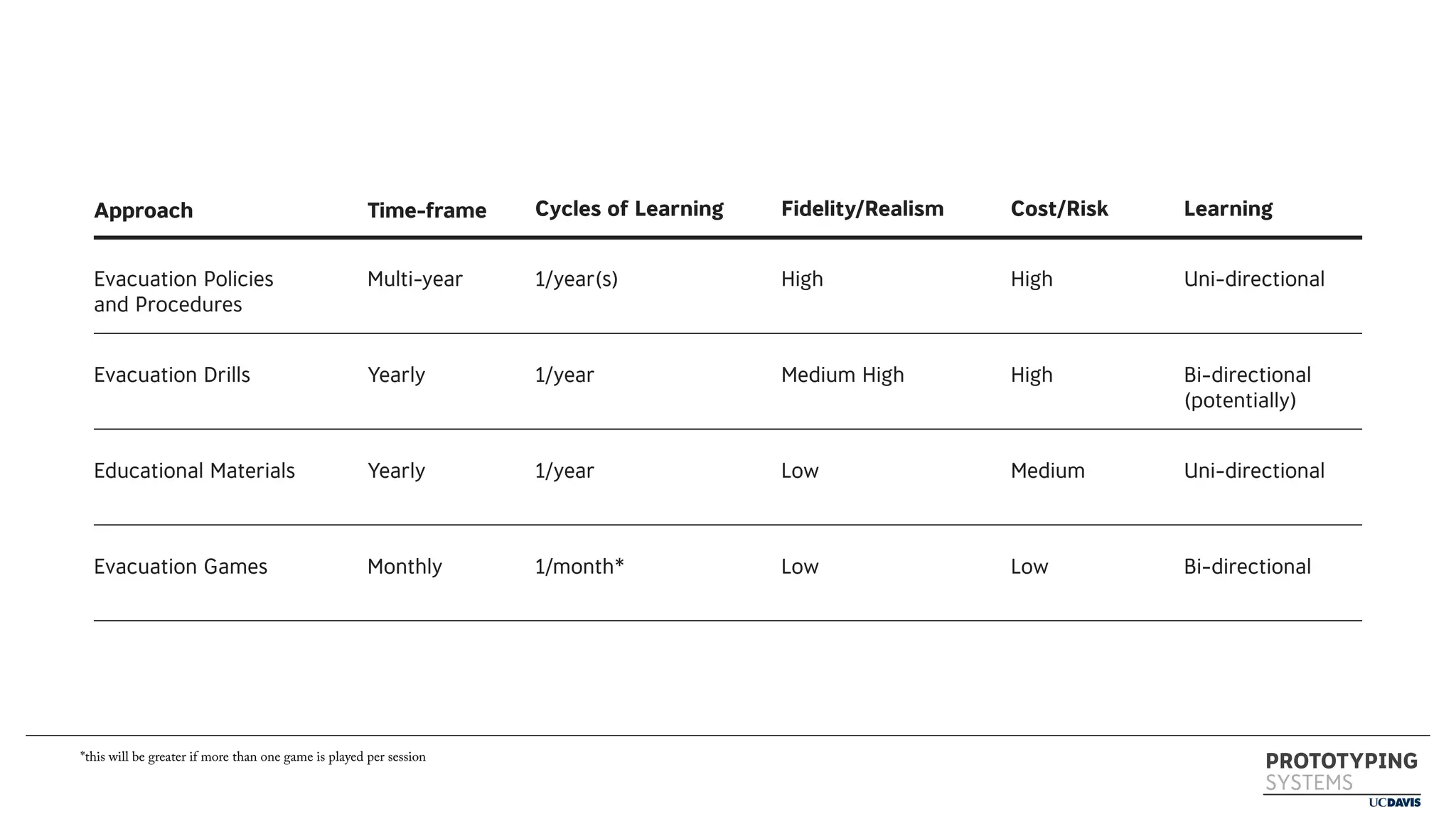
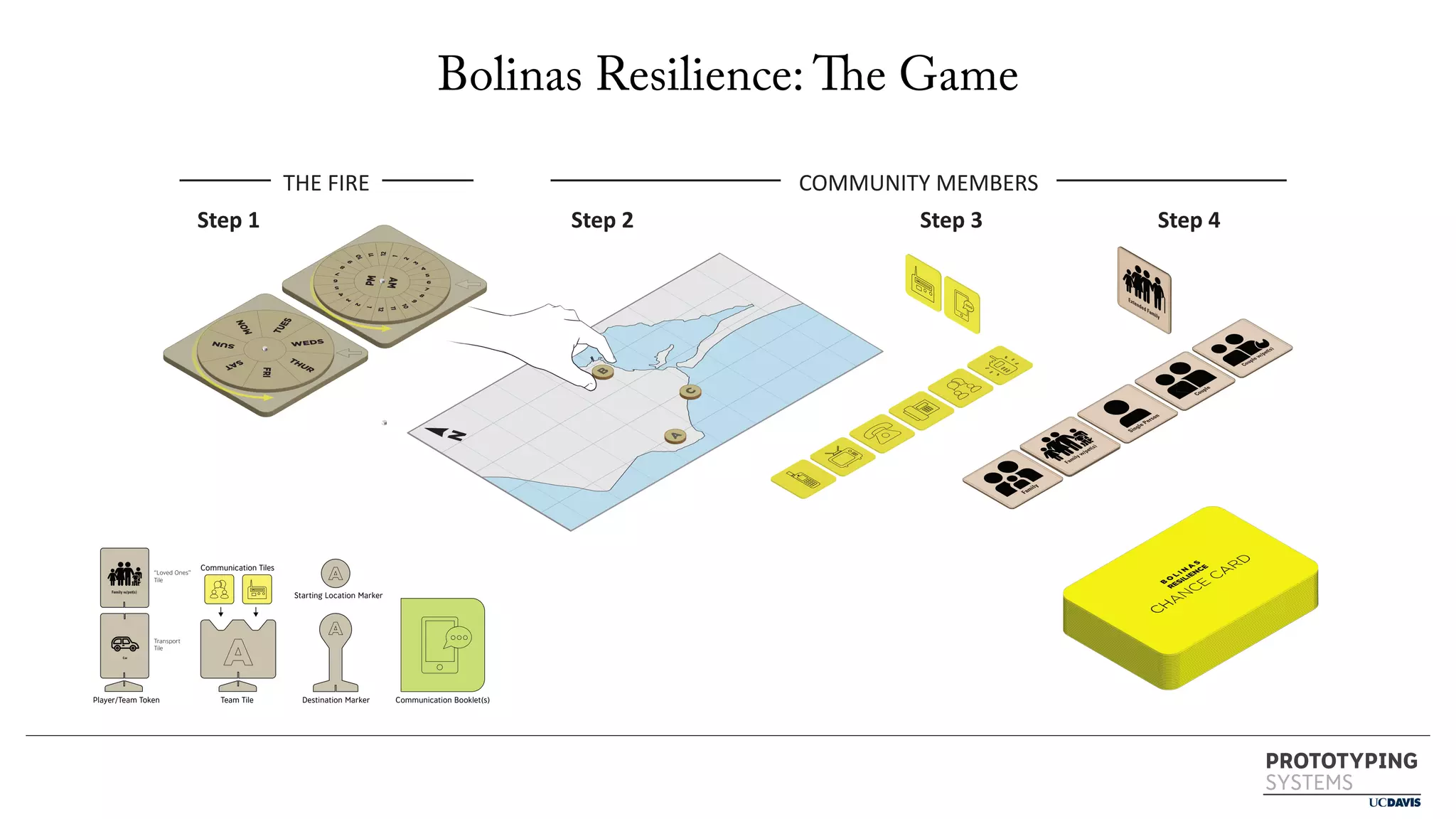
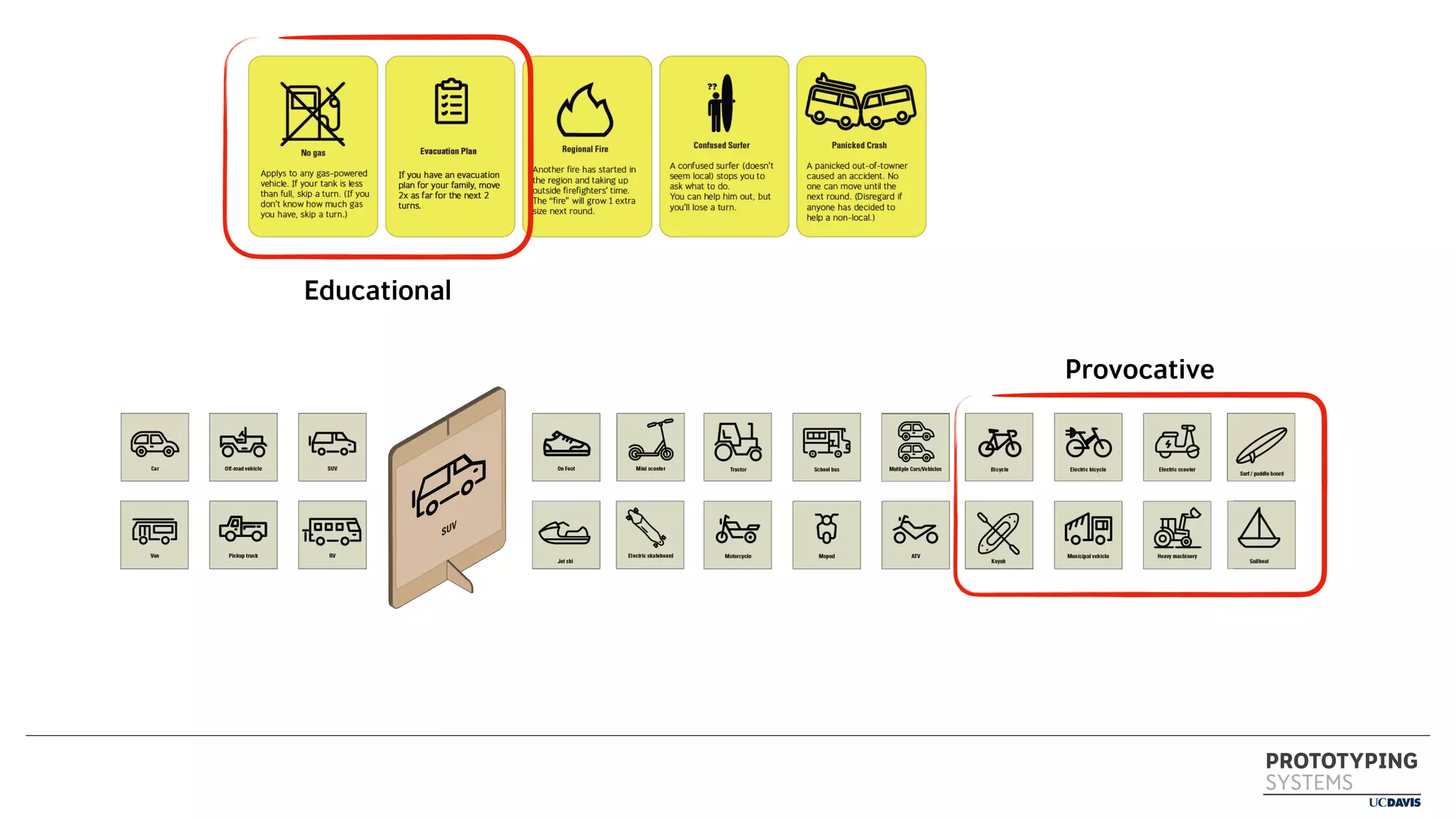
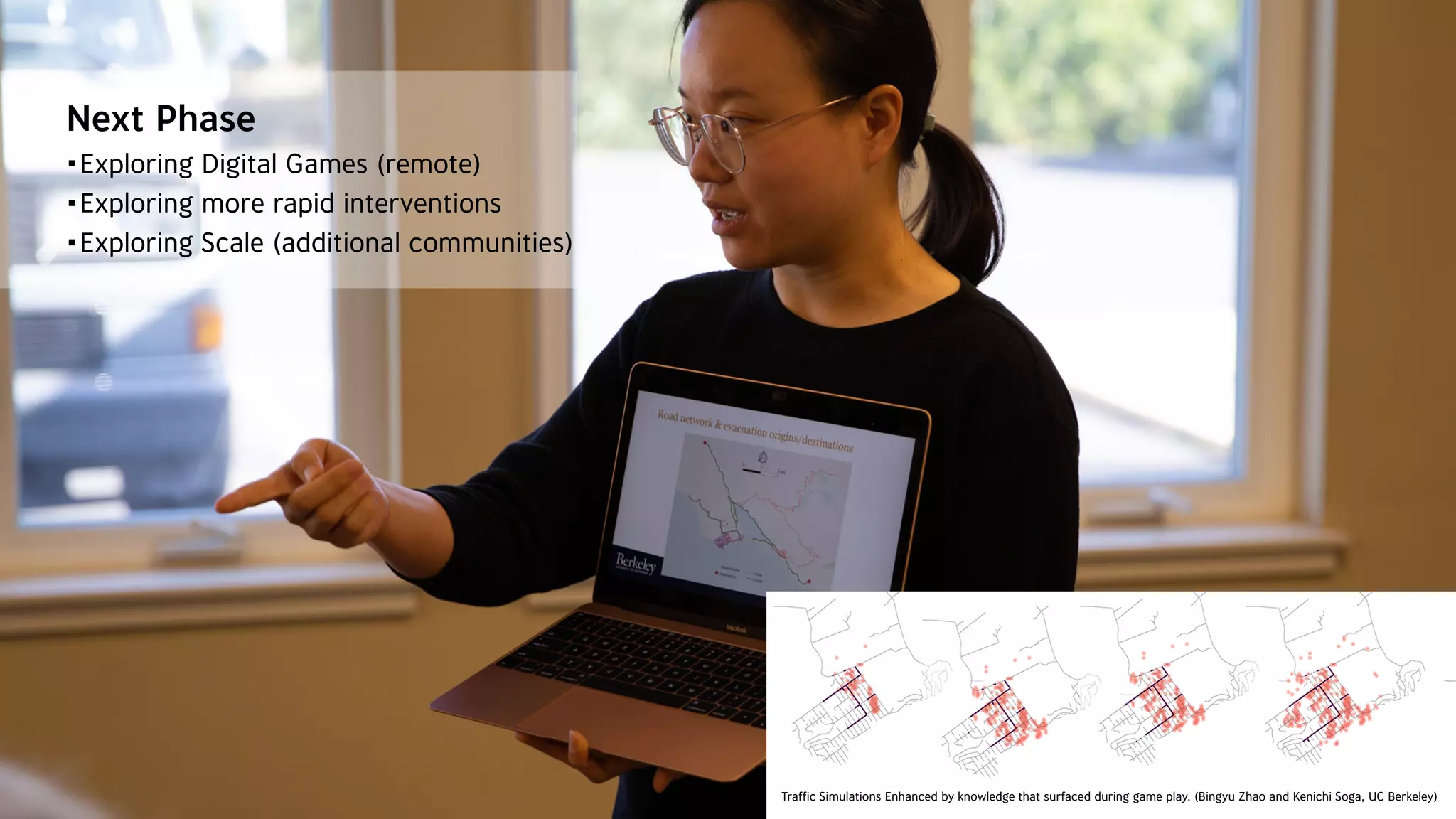
The document discusses the use of prototyping systems and serious games as tools for engaging communities in disaster response, particularly in wildfire evacuations. It emphasizes the importance of collaboration among various stakeholders and highlights the need for a systemic approach to design challenges that incorporates diverse perspectives. Additionally, it outlines a framework for prototyping and its application in educational settings to enhance preparedness and learning in emergency situations.