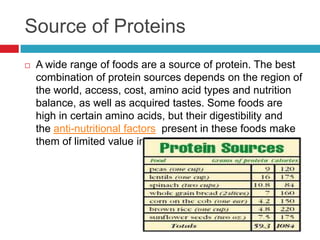
Protein is made up of amino acids and is important for growth, repair of body tissue, and energy. There are essential amino acids that the body cannot produce and must be obtained through food. Complete proteins contain all essential amino acids and are found in animal products, soy, and poi. Proteins have different structures and functions, such as antibodies that defend the body, contractile proteins that enable movement, and enzymes that speed up chemical reactions. High protein diets are recommended for building muscle while low protein diets may be prescribed for kidney or liver disease. Protein deficiency can cause conditions like kwashiorkor with symptoms of apathy, diarrhea, and edema.