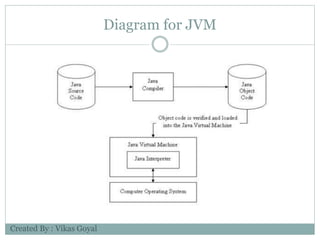
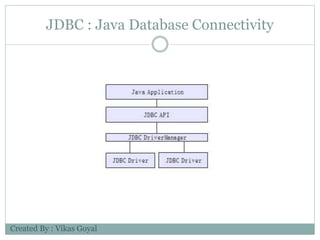
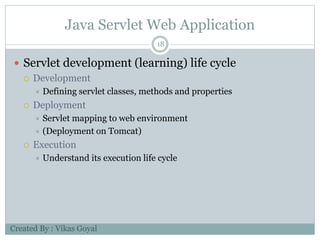
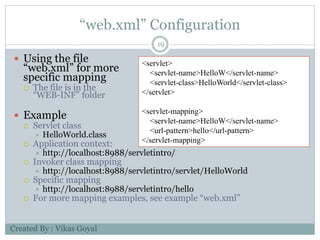
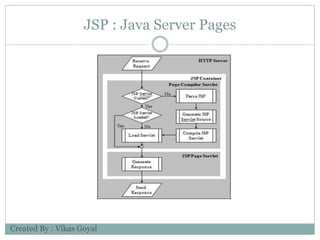
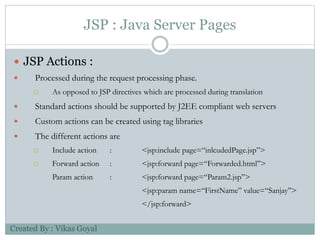
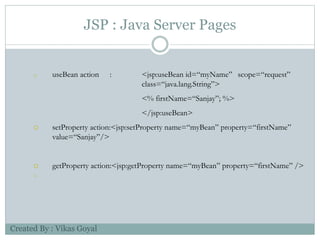
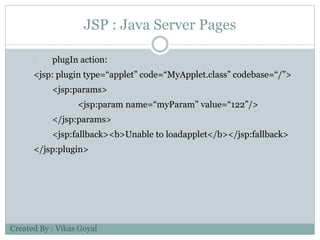
The document provides an overview of key concepts in advanced Java programming including the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), assertions, Java Database Connectivity (JDBC), Java servlets, and Java Server Pages (JSP). It describes the JVM as a software layer that converts Java bytecode into machine code so it can run on any platform. It also outlines the components of the JVM and how assertions are used for programming by contract and verifying pre- and post-conditions. The document further explains how JDBC provides Java applications access to databases via SQL and the different types of JDBC drivers. It also summarizes how servlets handle HTTP requests and the basic servlet classes, and how JSP pages are compiled