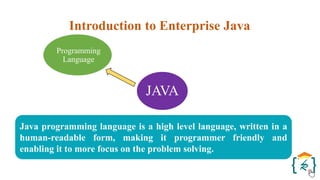
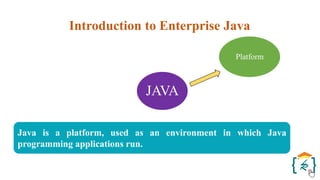
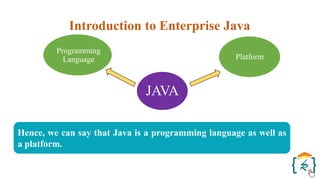
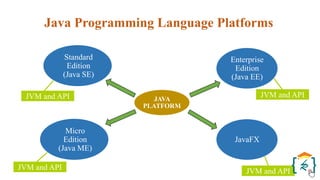
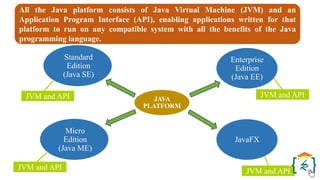
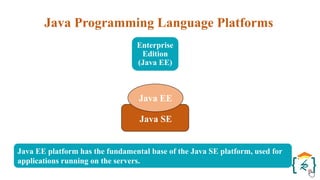
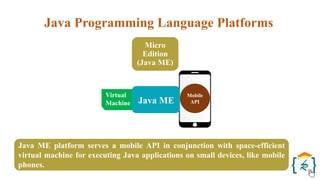
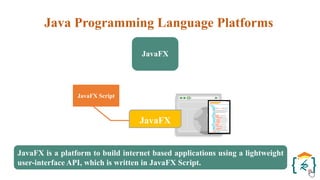
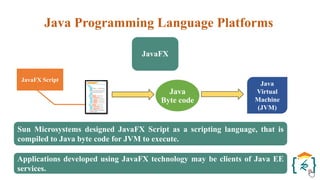
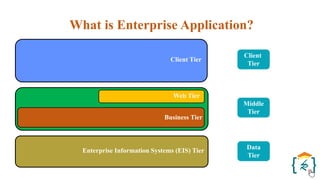
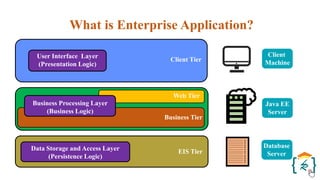
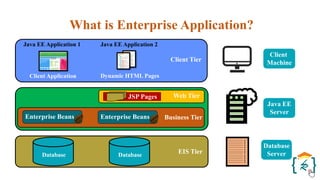
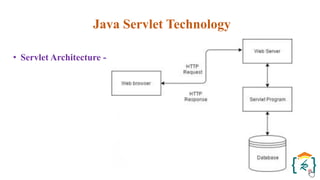
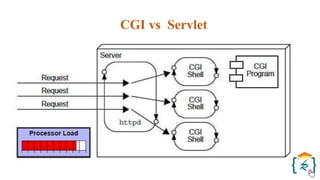
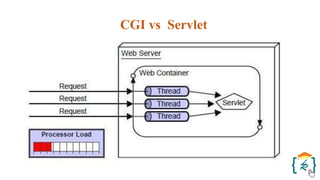
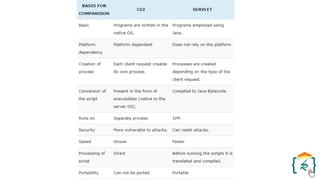
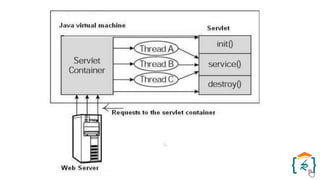
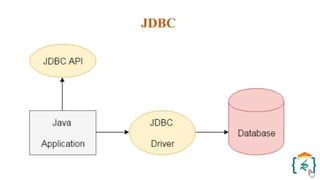
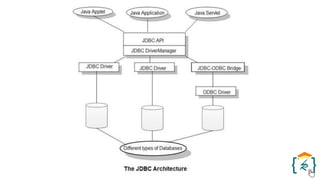
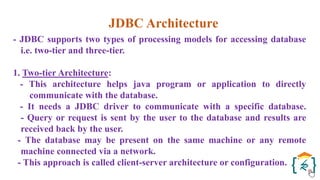
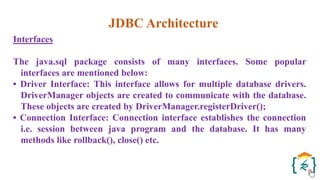
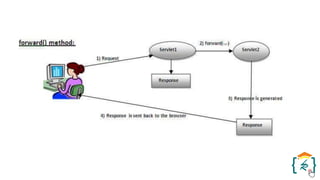
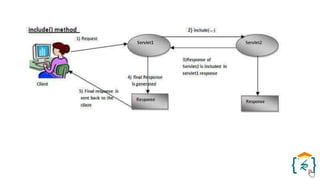
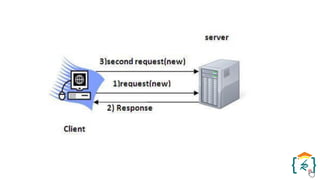
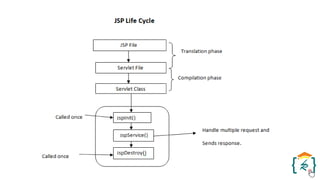
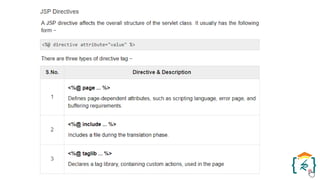
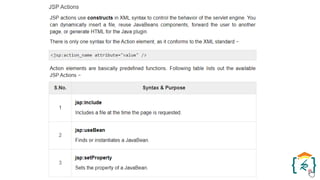
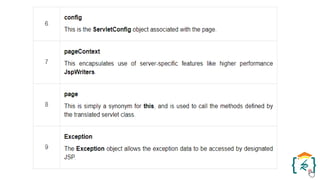
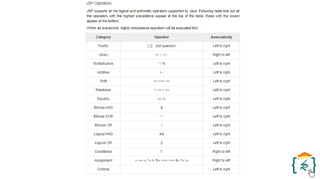
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to the Java programming language and its various platforms, including Java SE, Java EE, Java ME, and JavaFX. It discusses the components of Java, such as the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and Application Programming Interface (API), as well as the servlet technology and Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) for database operations. The document also outlines the life cycle of servlets, the advantages of servlets over CGI, and the JDBC architecture for connecting Java applications to databases.