1) An oblique plane is a plane surface that is inclined to one of the principal planes, with one of its sides, diagonals, or diameter parallel to the principal plane and inclined to the other principal plane.
2) There are three steps to drawing projections of oblique planes: initial position, intermediate position, and final position.
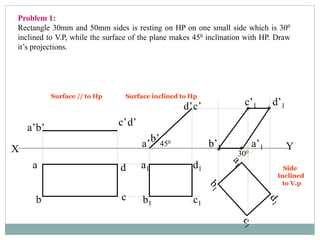
3) Three example problems are provided to demonstrate drawing projections of different shapes (rectangle, pentagon, rhombus) placed at various orientations relative to the principal planes.