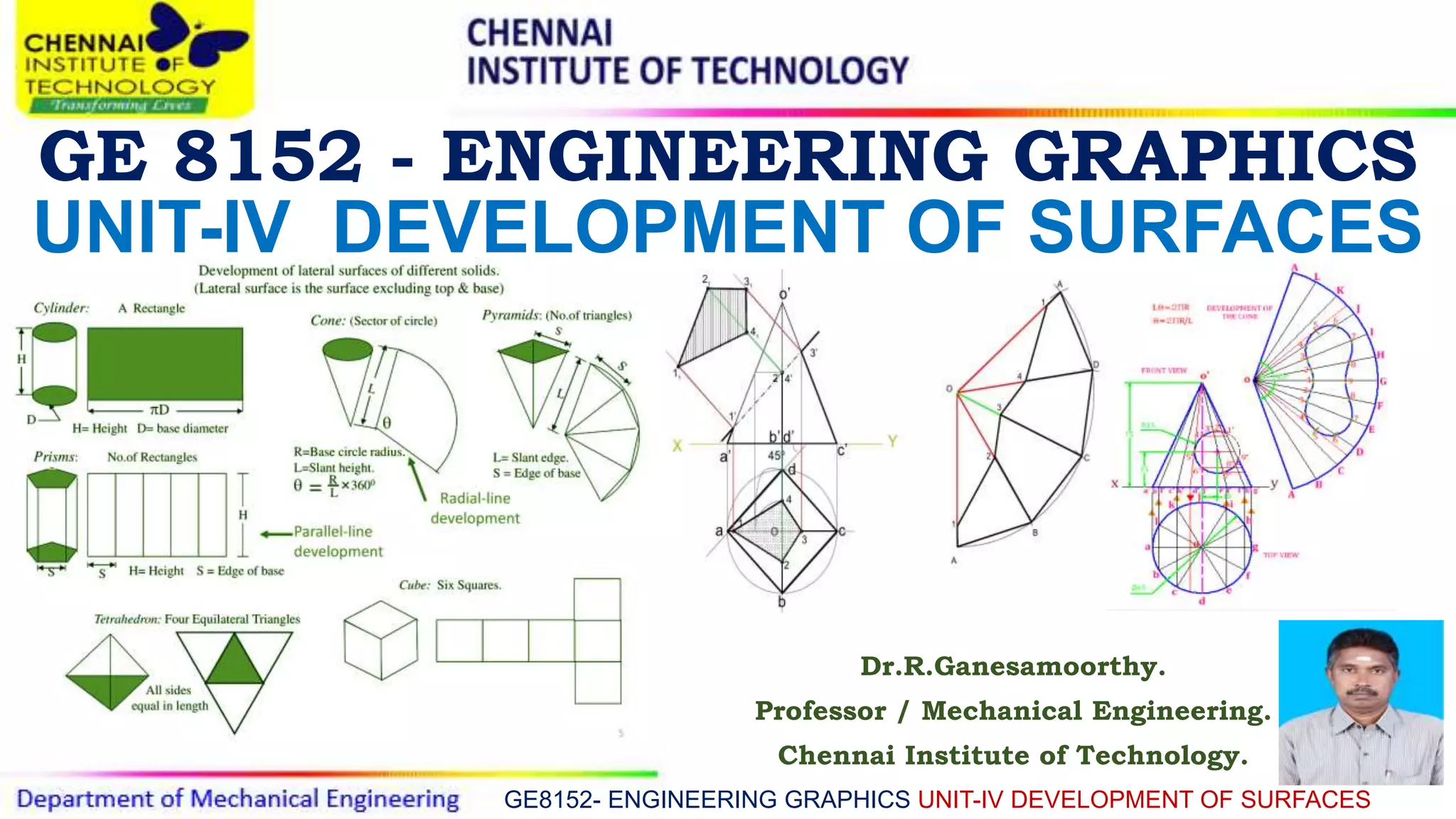
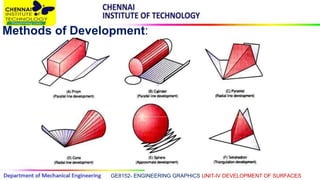
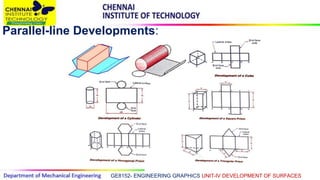
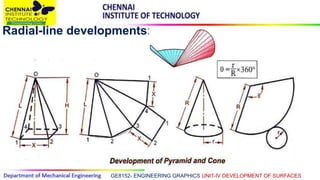
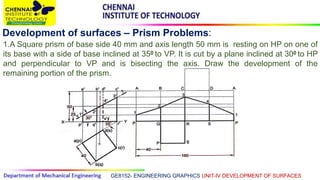
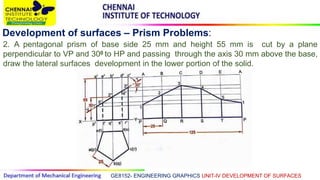
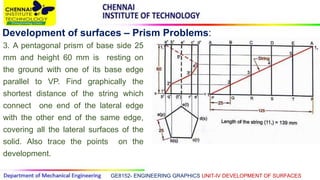
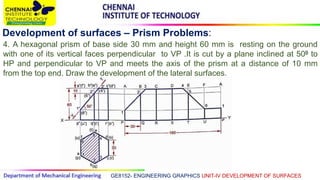
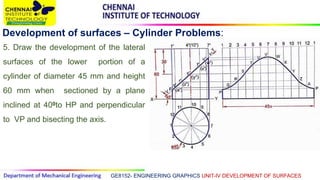
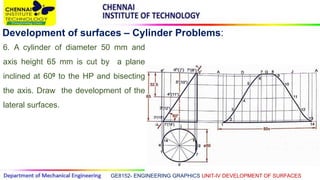
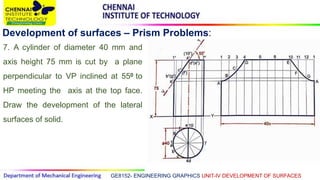
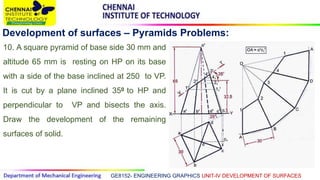
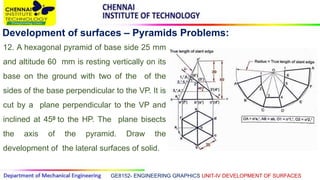
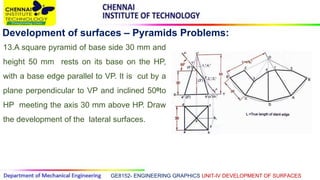
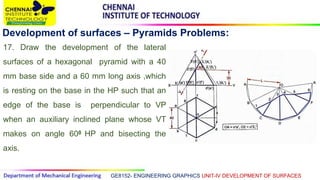
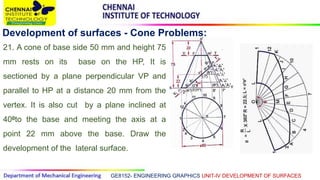
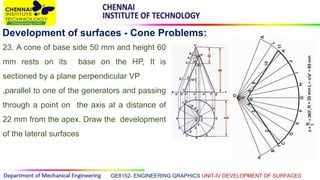
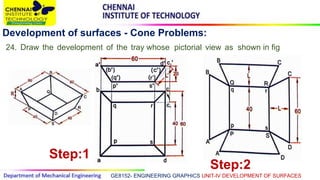
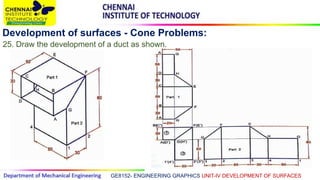
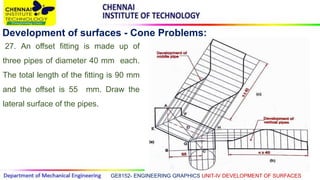
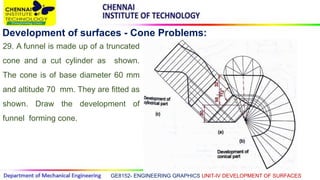
This document discusses the development of surfaces, which is the process of unfolding 3D objects into 2D patterns. It covers key concepts like parallel-line development for prisms and cylinders, radial-line development for cones and pyramids, and triangulation development for complex surfaces. The document then provides examples of developing various prisms, cylinders, cones and pyramids that are cut or intersected by different planes. Solutions are presented for 14 problems involving developing these different types of objects.