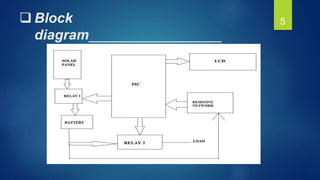
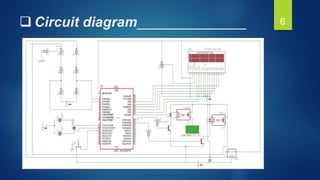
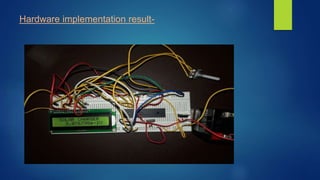
This document outlines a final year project that involves designing a microcontroller-based solar charger. The project aims to maximize the use of solar energy by using a microcontroller to charge a 12V lead-acid battery from a 10W solar panel. The system provides overcharge and overload protection for the battery. It uses a PIC16F877A microcontroller to control an LCD display, relays, and voltage regulation circuitry to safely charge and monitor the battery status. The project implements the design in hardware and simulates the microcontroller code. It demonstrates charging, overcharge protection, overload protection, and voltage regulation functionality.