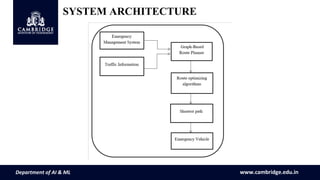
This document proposes an emergency vehicle route optimization system using graph theory and Dijkstra's algorithm. The system converts road network data into a graph with nodes representing areas and edges representing travel time. Dijkstra's algorithm is then used to determine the shortest path for emergency vehicles by calculating the total travel time along routes using weights assigned to edges. The aim is to reduce emergency vehicle travel time and enhance effectiveness of routes through congested traffic situations.