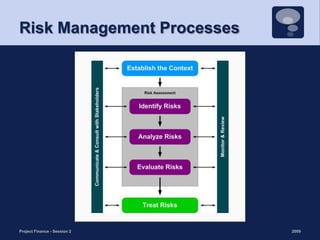
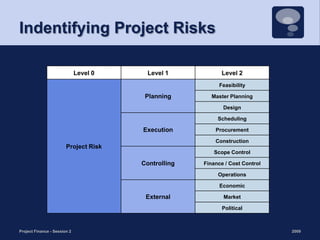
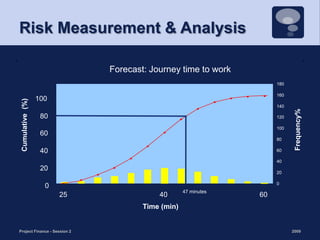
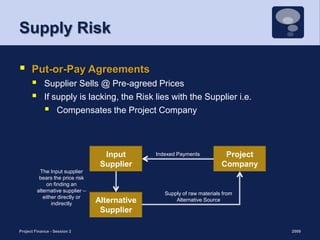
This document discusses project risk management and the role of advisors in project finance. It covers identifying and allocating project risks, common risk management processes, and the functions of legal, independent engineering, and insurance advisors. Proper risk management is important for ensuring consistent cash flows to reduce the likelihood of default, while advisors play a crucial role in risk mitigation through due diligence, project structuring, and monitoring.