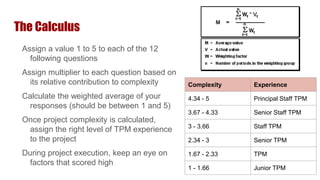
The presentation aims to provide a framework for calculating project complexity rather than offering a comprehensive strategy. It identifies six compound factors contributing to complexity: team member count, project challenges, technical challenges, perceived value, distributed resources, and visibility. A scoring system is provided to assess these factors, enabling project managers to align their experience with the project's complexity and manage it more effectively.