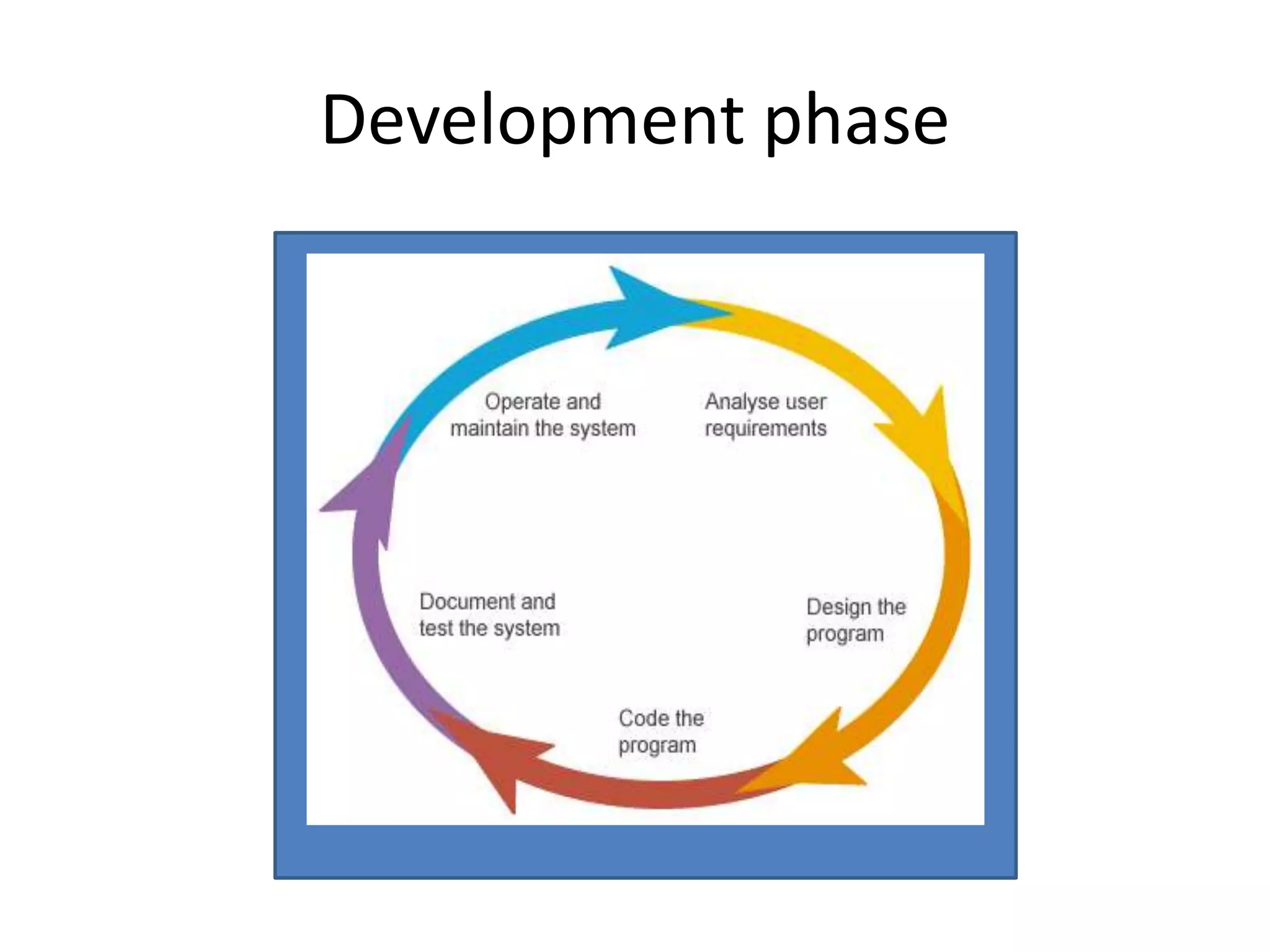
This document outlines the phases of program development: problem analysis, design, coding, testing, and documentation. Problem analysis involves completely defining the problem in writing, understanding the definition, and identifying inputs and desired outputs. Design breaks the project into smaller pieces and describes desired features. Coding translates the design into a programming language. Testing examines outputs for errors and runs the program with different test data. Documentation includes user manuals and materials to help future programmers understand the program.