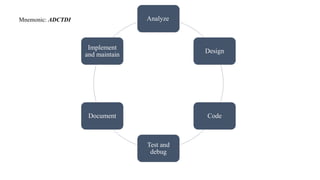
The document outlines the Program Development Cycle (PDC), which consists of steps such as analyzing the problem, designing a solution, coding, testing, debugging, documenting, and implementing the program. It emphasizes the importance of clear instructions and proper planning to successfully develop a program, highlighting tools such as algorithms and flowcharts. Additionally, it discusses types of errors, the need for documentation, and the significance of program maintenance.







![Code
• Choose a programming language based on the design and suitablity for
the program development.
• Keep the program simple and avoid complex logic.
• Program must be so simple that it can be communicated and easily
understood by other programmers.
• Comments are helpful in understanding the program.
[Most codes are either compiled or translated based on the programming
language.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programdevelopmentcycle-240624162010-eaae300e/85/computer-science-presentation-on-program-development-cycle-9-320.jpg)




