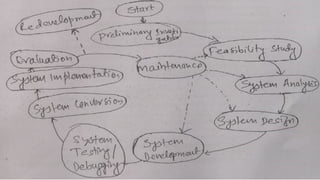
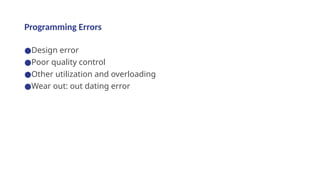
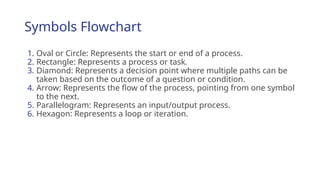
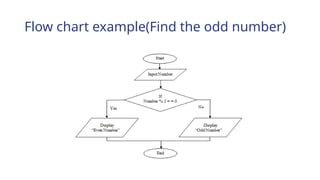
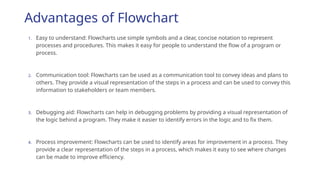
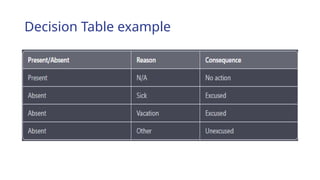
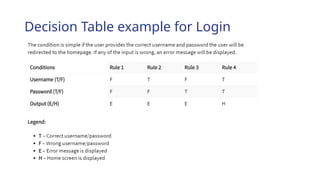
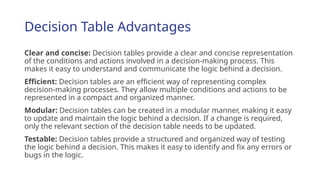
The document outlines the process of software development, detailing the program development life cycle, the importance of initial investigation, feasibility studies, system analysis, design, coding, testing, and implementation phases. It emphasizes the structured approach needed for effective program development, including the need for clear objectives, thorough documentation, and rigorous testing. Key factors in successful software include program efficiency, reliability, maintainability, and strong user design considerations.