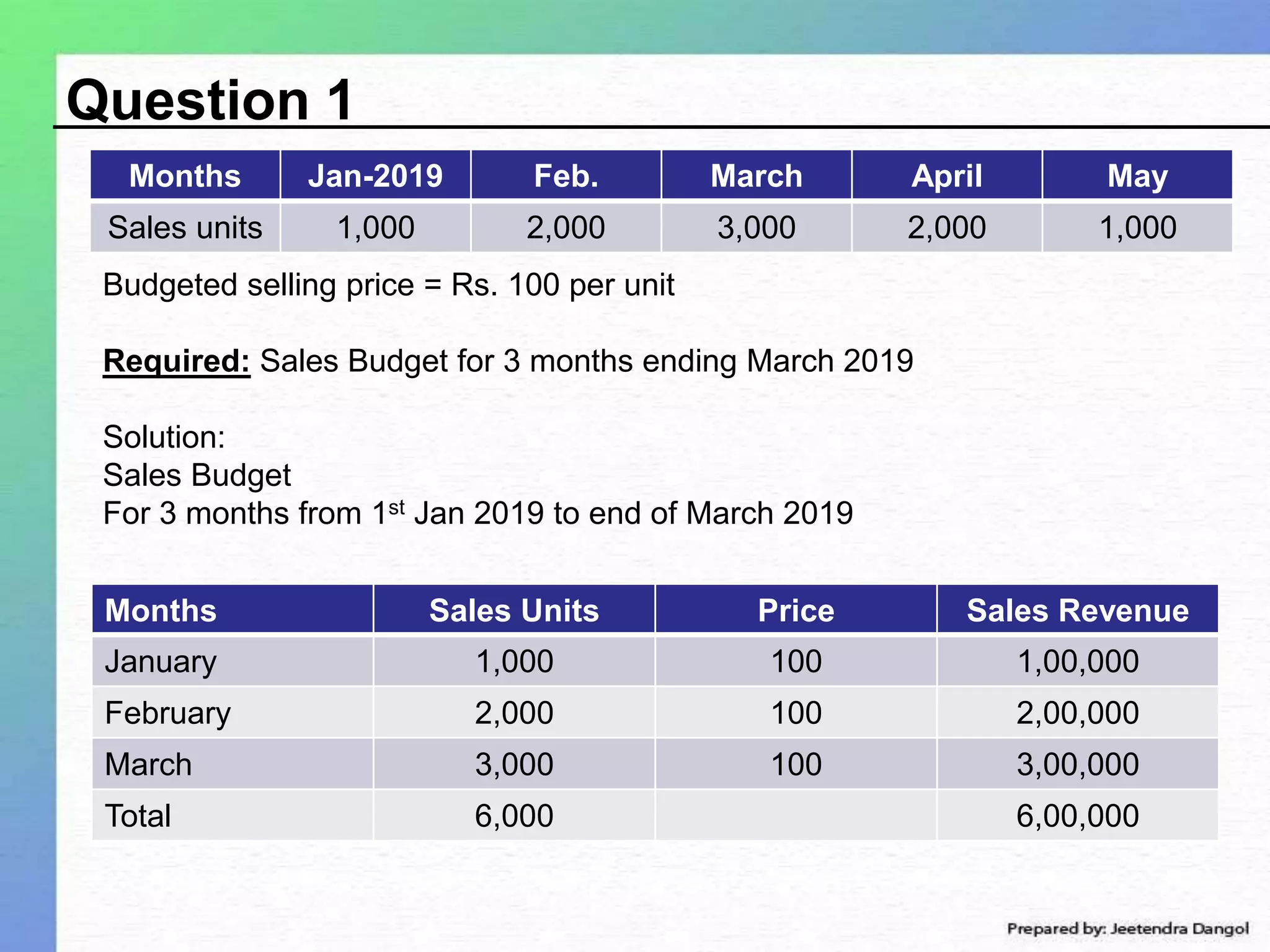
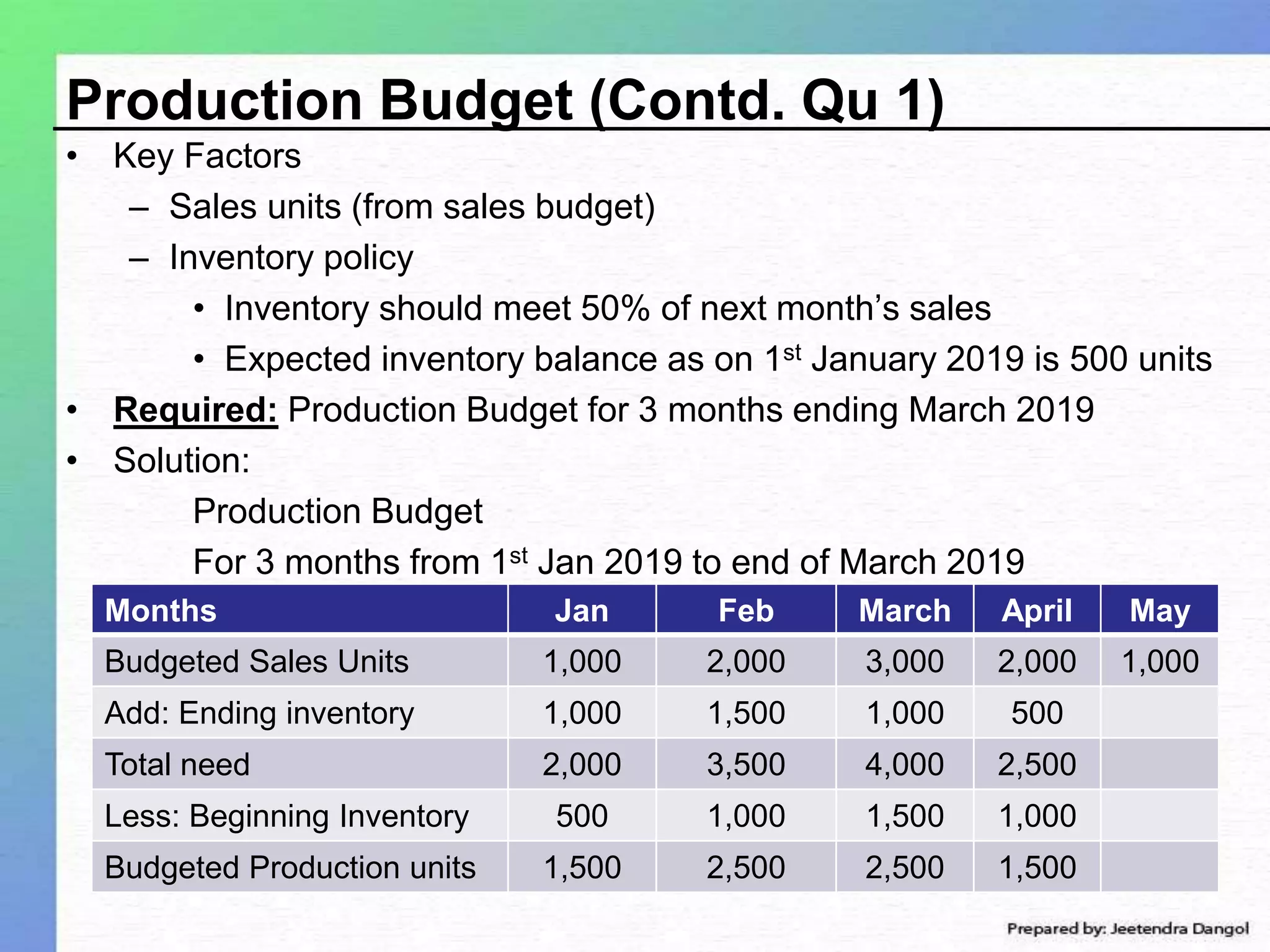
The document discusses profit planning and budgeting. It provides examples of budgets such as sales budget, production budget, raw material consumption budget, and cash budget. The key elements included in budgets are sales units, production units, raw material requirements, expenses, and cash inflows and outflows. The example shows how to create a 3 month sales, production, raw material, and cash budget by setting assumptions and linking the different elements between budgets.