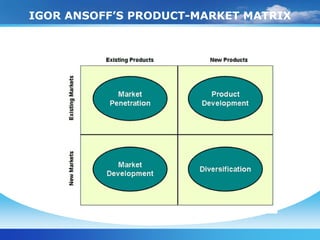
The document discusses various expansion strategies for organizations, including concentration, integration, and diversification. Concentration strategies focus on intensifying the core business through market penetration, market development, and product development. Integration involves combining related activities, such as horizontal integration through mergers and acquisitions, or vertical integration along the supply chain. Diversification can be related, known as concentric diversification, or unrelated through conglomerate diversification into new industries.