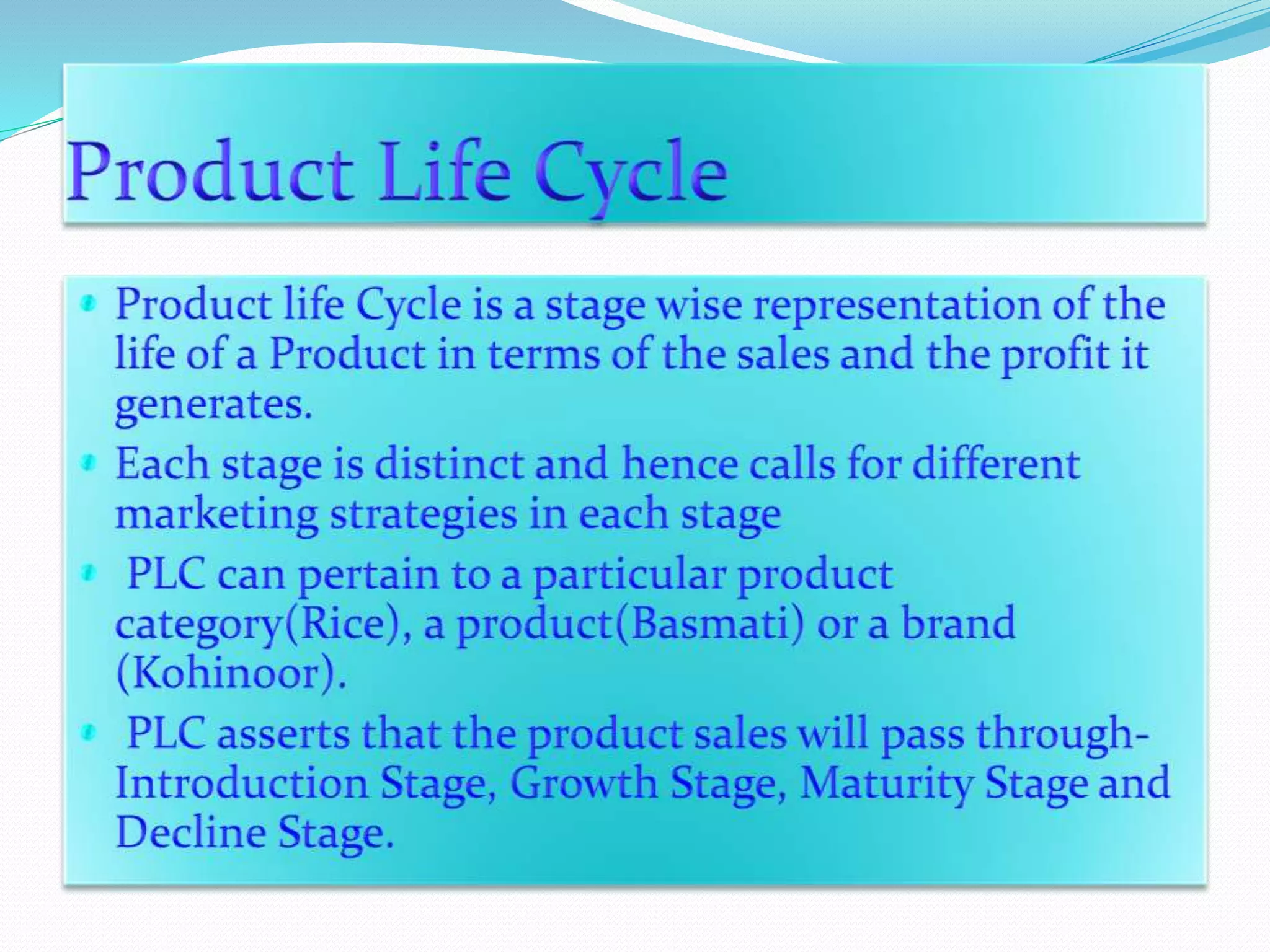
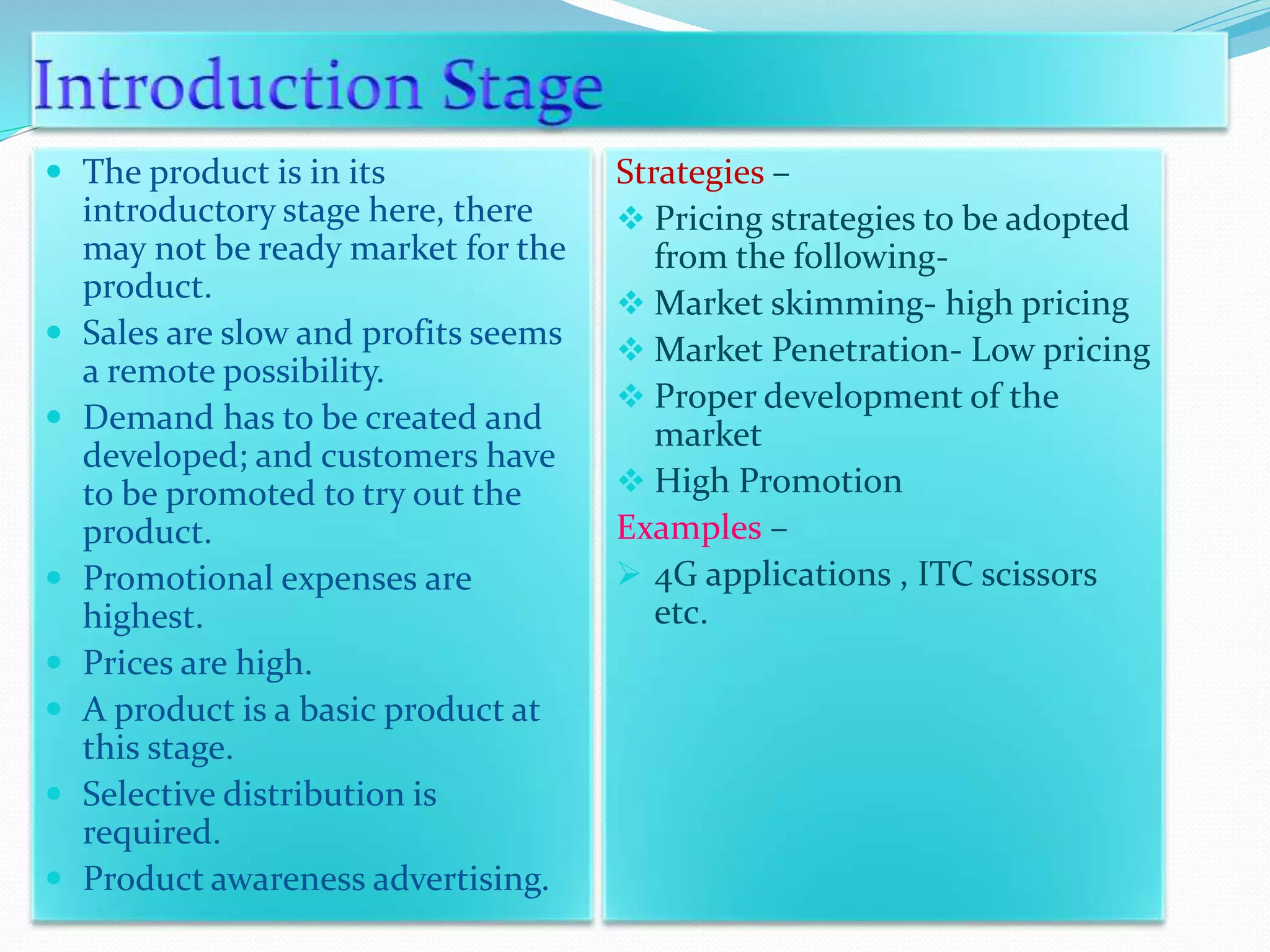
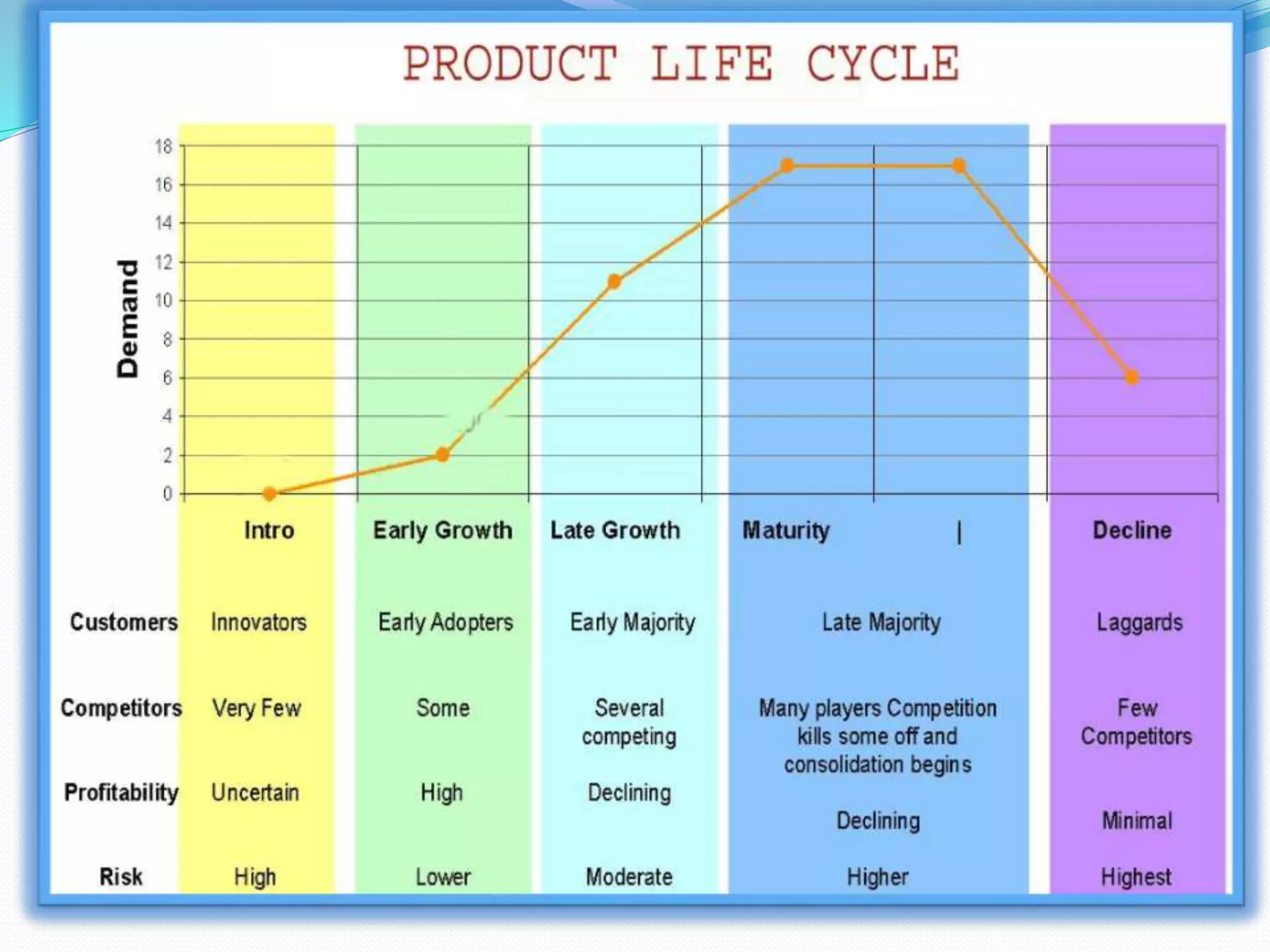
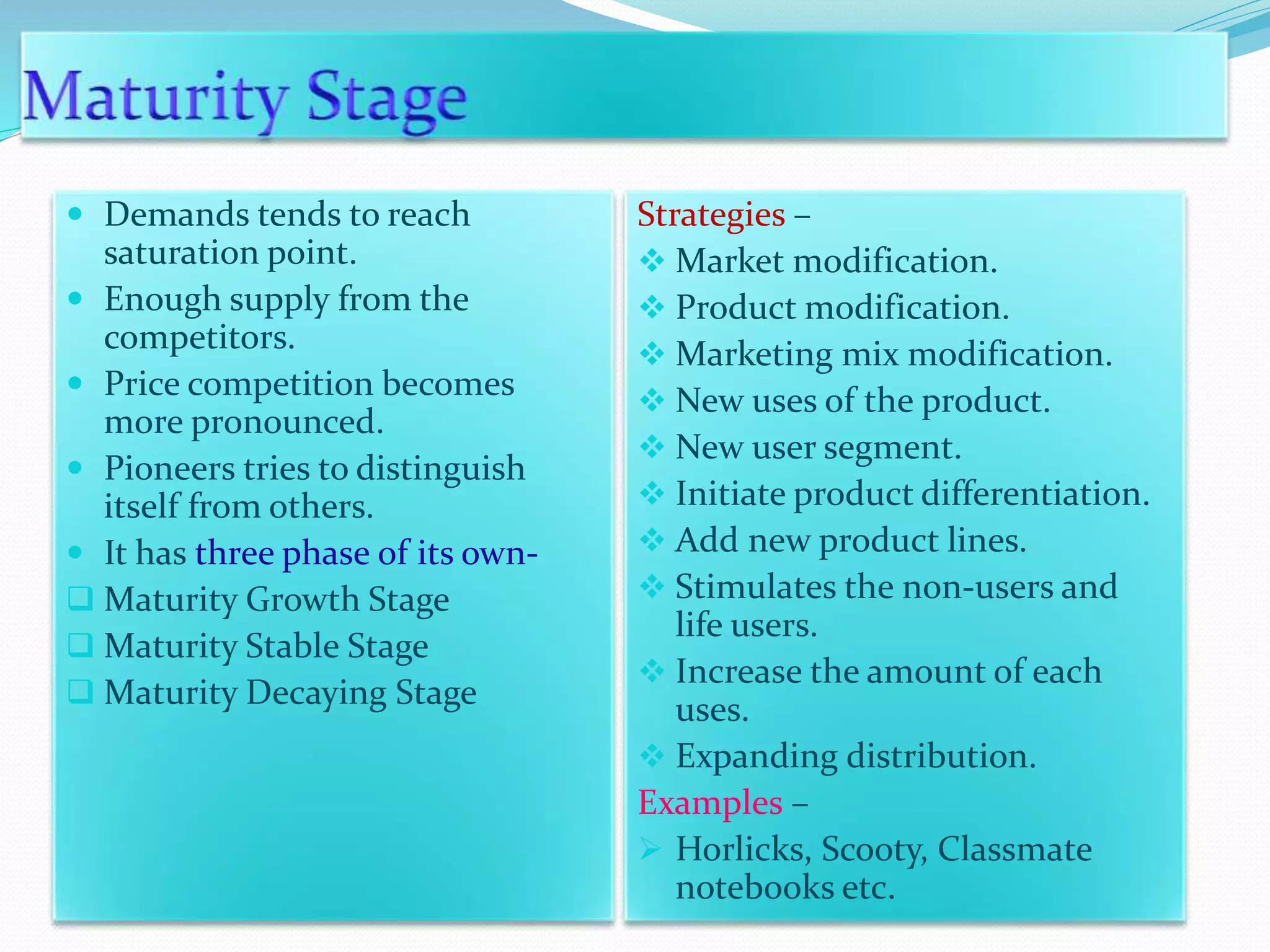
The document outlines the marketing strategies of a product throughout its lifecycle, from its introductory stage with slow sales and high promotional expenses to eventual growth and increasing competition. As demand reaches saturation, firms adapt by modifying products and marketing strategies, but may face declining demand and reduced margins in the maturity phase. Strategies for declining products include maintaining or selectively decreasing investments and linking to premium products to extend market life.