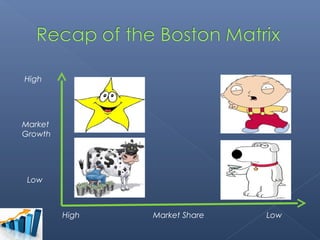
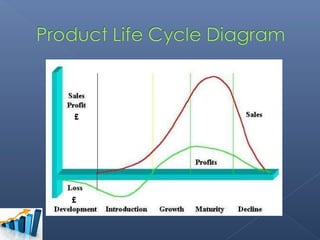
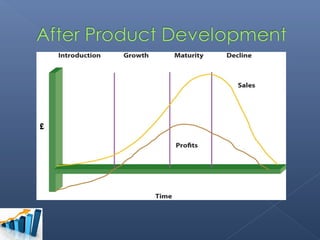
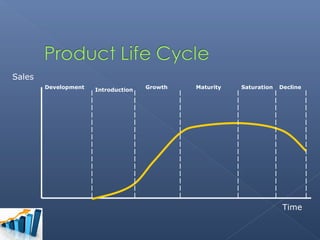
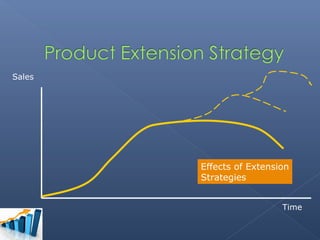
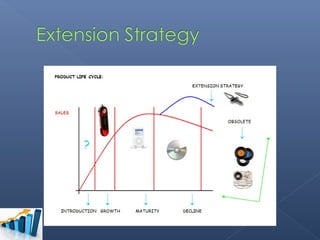
- The group chose the Sony Walkman as their product in the maturity stage of its life cycle.
- Their extension strategies included redesigning it to be smaller and add more colors/styles to appeal to younger customers.
- They also proposed adding Bluetooth connectivity and memory storage to give it new functionality to transition to a new market segment.
- The group argued these changes would make the Walkman relevant to new users while retaining loyal customers.