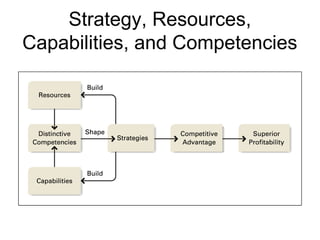
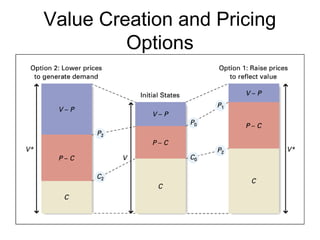
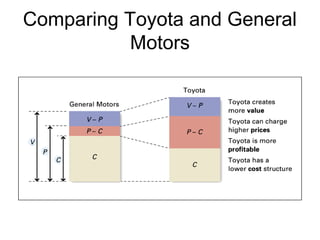
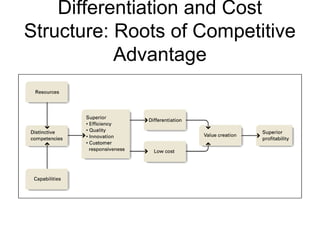
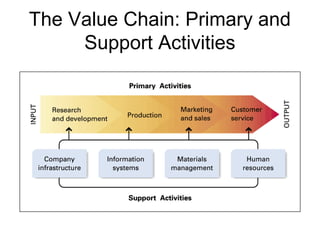
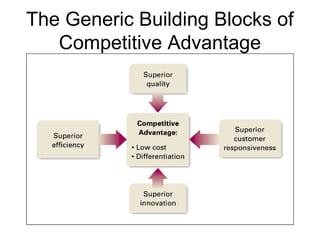
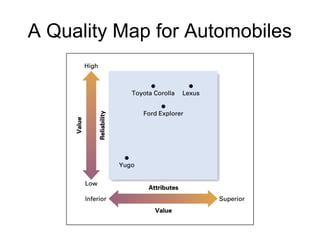
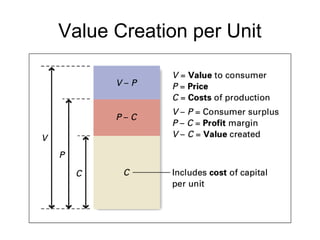
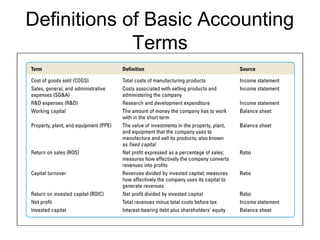
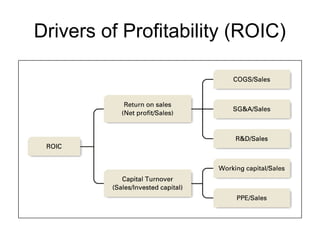
This document discusses internal analysis and identifying a company's strengths and weaknesses. It defines distinctive competencies as firm-specific strengths that allow a company to gain competitive advantages through differentiation or lower costs. Resources and capabilities are the basis for distinctive competencies. Competitive advantages lead to greater value creation, pricing power, and profitability. Key aspects that drive competitive advantages are efficiency, quality, innovation, and responsiveness to customers.