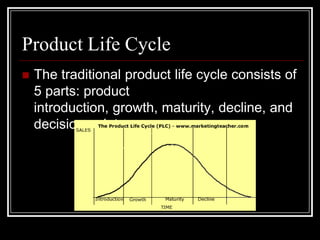
This document discusses the traditional product life cycle model which consists of 5 stages: introduction, growth, maturity, decline, and decision point. It provides examples for each stage. The introduction stage involves low sales and high promotion costs to build awareness. The growth stage sees rapid sales increases as more people learn about the product. The maturity stage is when sales level off and competition increases, driving down prices. The decline stage is when sales begin to fall as new products replace the old. At the decision point, companies must decide whether to reformulate, discontinue, or find new uses for the product.