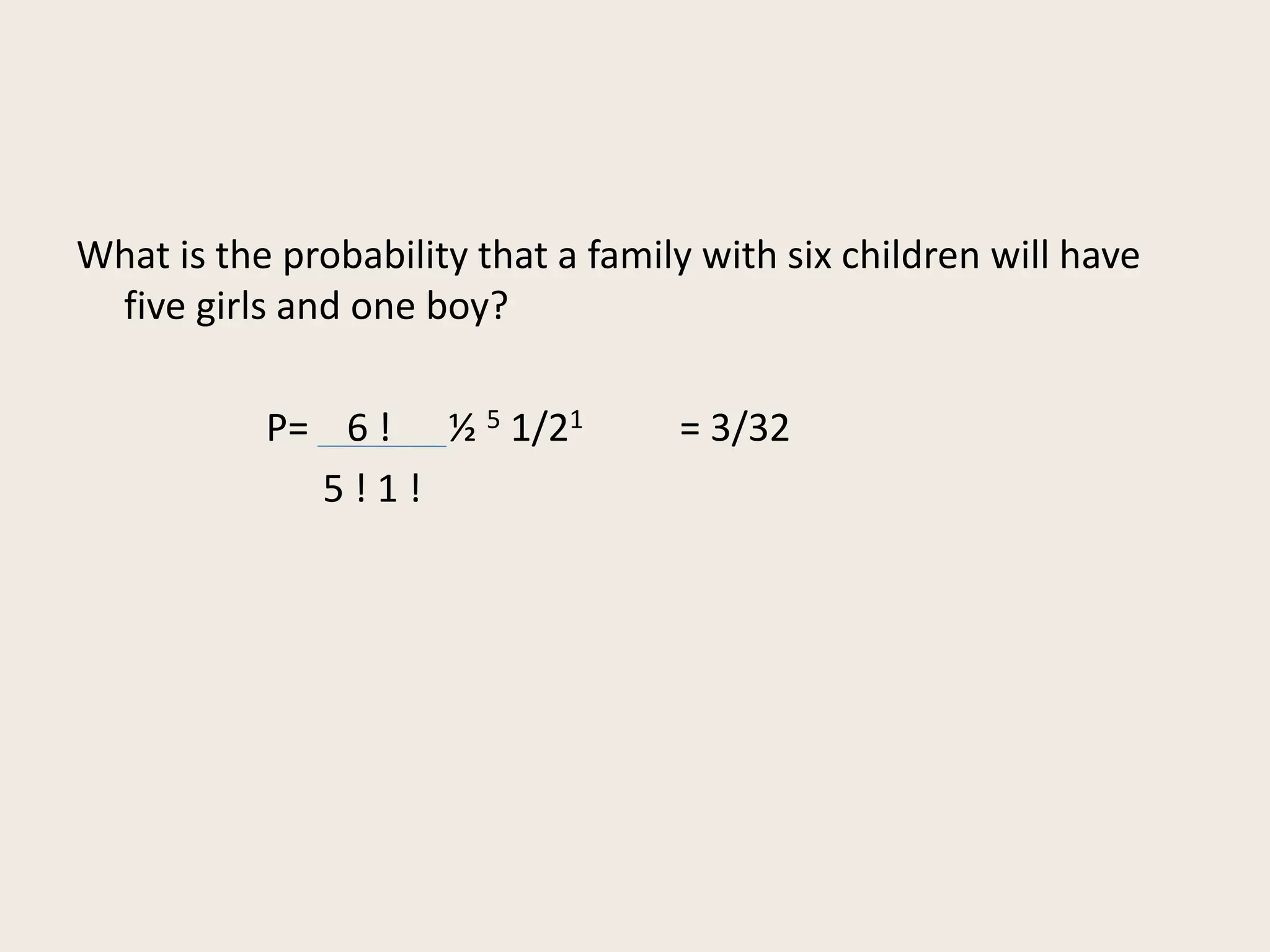This document discusses probability and provides examples of calculating probability using different rules:
1) The sum rule states that for mutually exclusive events, the probability of one of the events occurring is the sum of their individual probabilities.
2) The product rule states that for independent events, the probability they both occur is the product of their individual probabilities.
3) The binomial theorem provides a shorthand method for calculating the probability of unordered events using the sum and product rules.