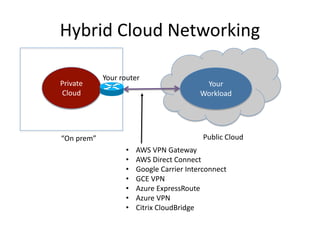
The document discusses private cloud networking in Apache CloudStack, highlighting the differences between basic and advanced zone configurations. It emphasizes the importance of simplifying network setups while addressing various networking issues such as security, automation, and integration with legacy systems. The presentation outlines features related to security groups, service offerings, and networking design principles to facilitate efficient private cloud deployment.




















![Multi-‐tier virtual networking
VLAN2724
DB
VM 1
Web
VM 1
Web
VM 3
Web
VM 2
VLAN101
App
VM 1
App
VM 2
VLAN398Virtual Router
Internet /
Rest of DC
Remote DC
IPSec VPN
Integration VLANLoadbalancer
(HW or
Virtual)
Network Services
• IPAM
• DNS
• LB [intra]
• S-2-S VPN
• Static Routes
• ACLs
• NAT, PF
• FW [ingress & egress]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/privatecloudnetworkingcloudstackdaysaustin-150416170046-conversion-gate01/85/Private-cloud-networking_cloudstack_days_austin-23-320.jpg)
![Virtual networking with overlays
GREKEY2724
DB
VM 1
Web
VM 1
Web
VM 3
Web
VM 2
GREKEY101
App
VM 1
App
VM 2
GREKEY398VR + vSwitches
Internet /
Rest of DC
Remote DC
IPSec VPN
Private GatewayLoadbalancer
(Virtual)
Network Services
• IPAM
• DNS
• LB [intra]
• S-2-S VPN
• Static Routes
• ACLs
• NAT, PF
• FW [ingress & egress]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/privatecloudnetworkingcloudstackdaysaustin-150416170046-conversion-gate01/85/Private-cloud-networking_cloudstack_days_austin-24-320.jpg)