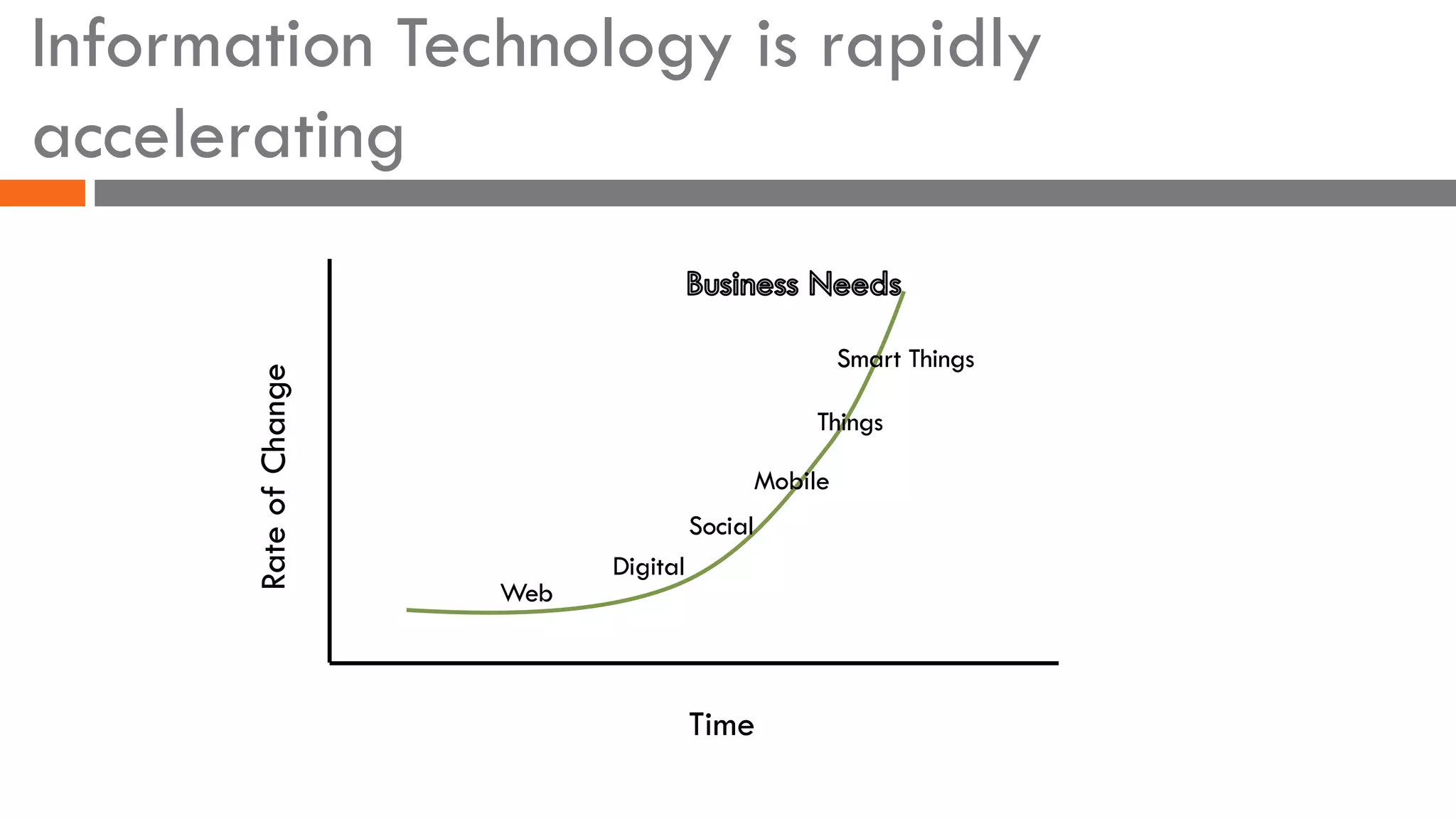
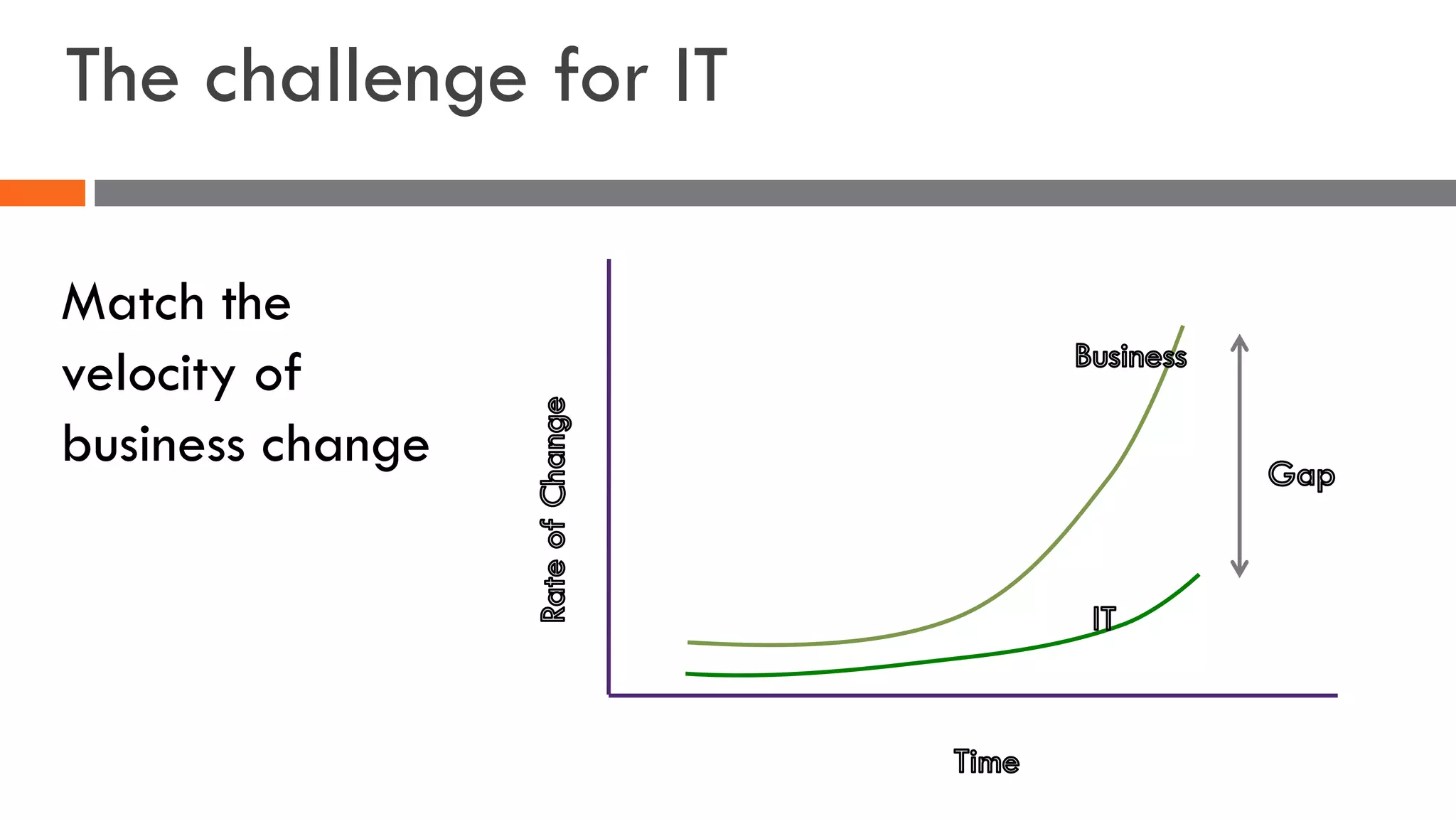
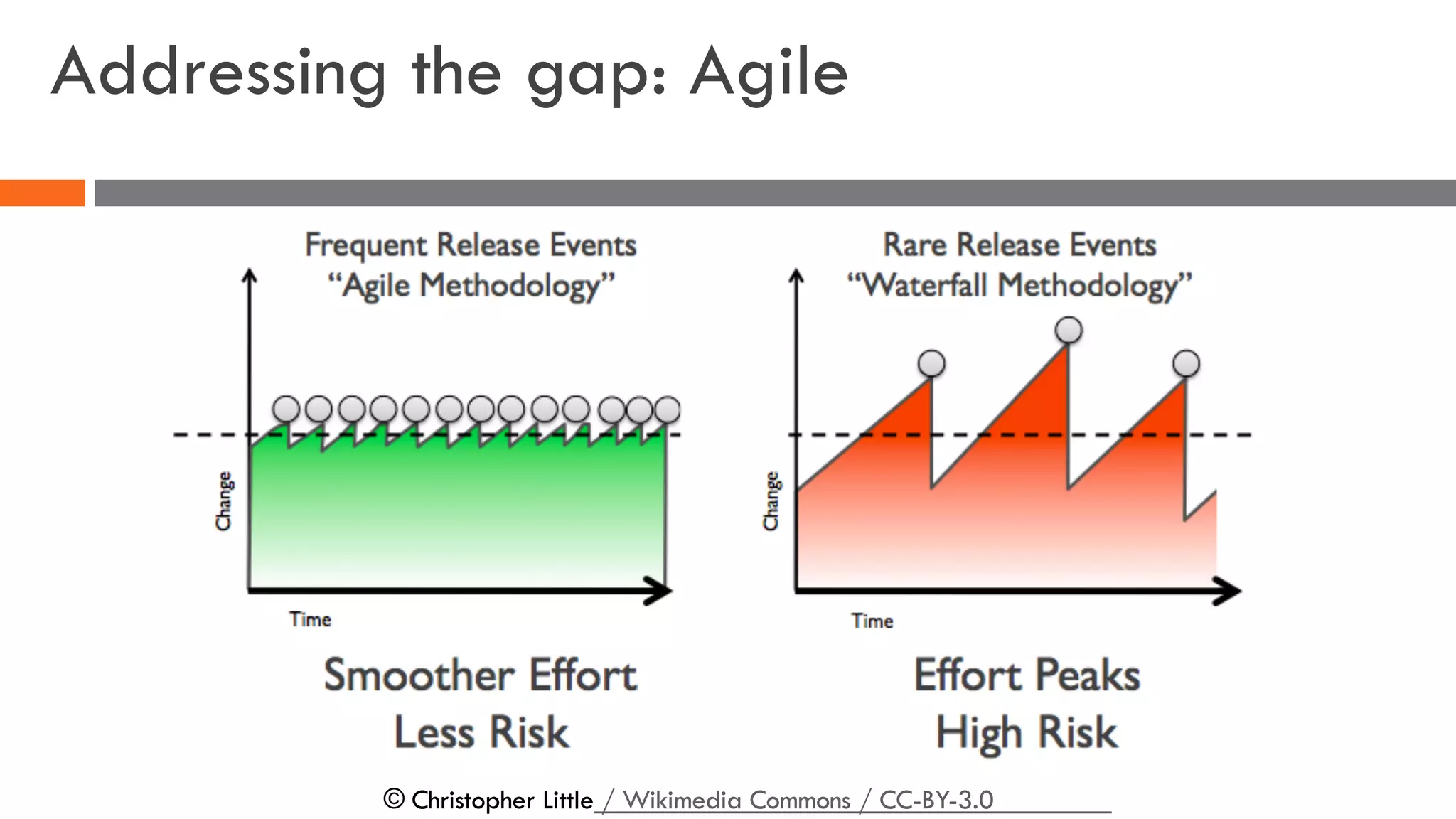
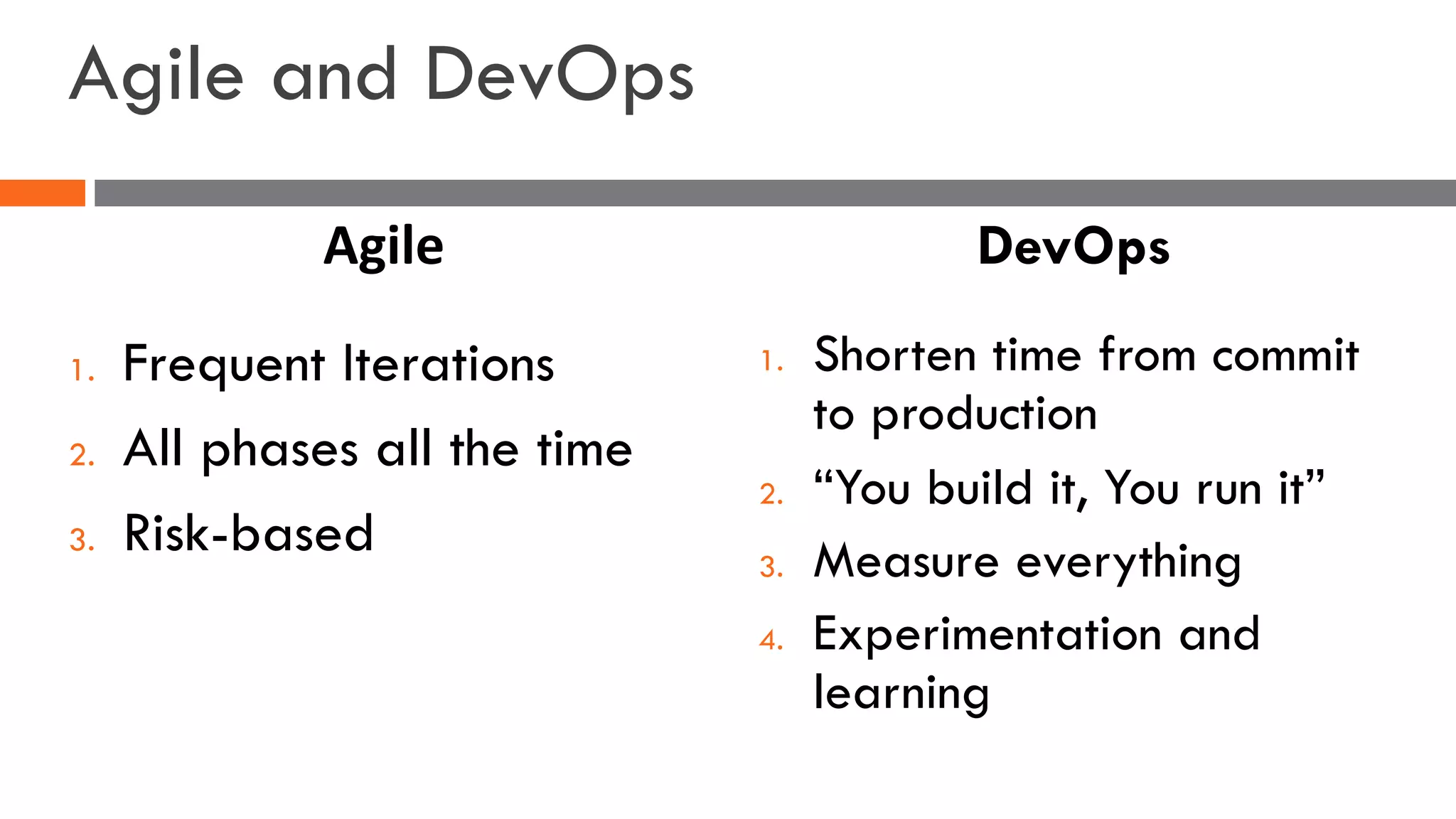
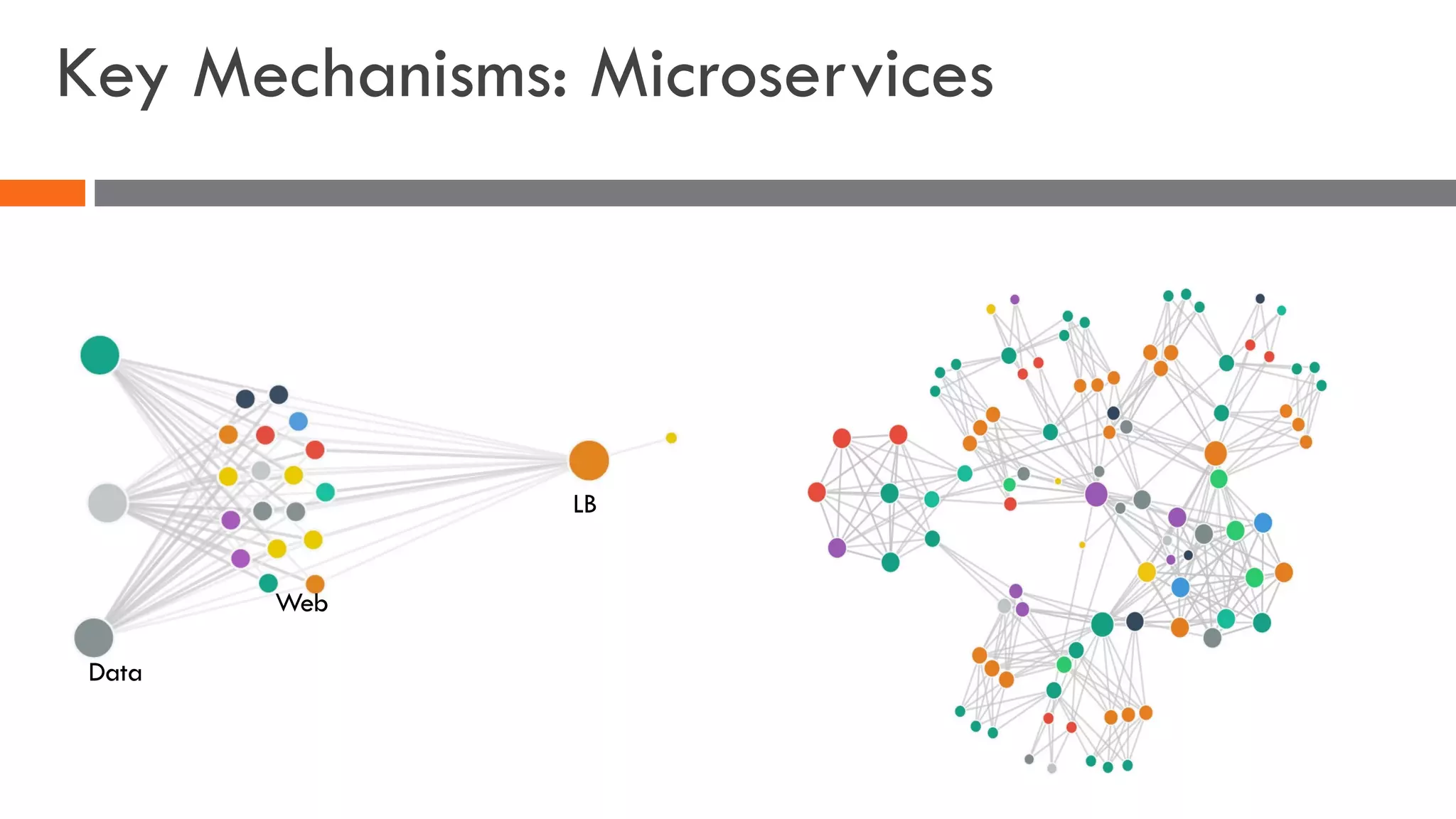
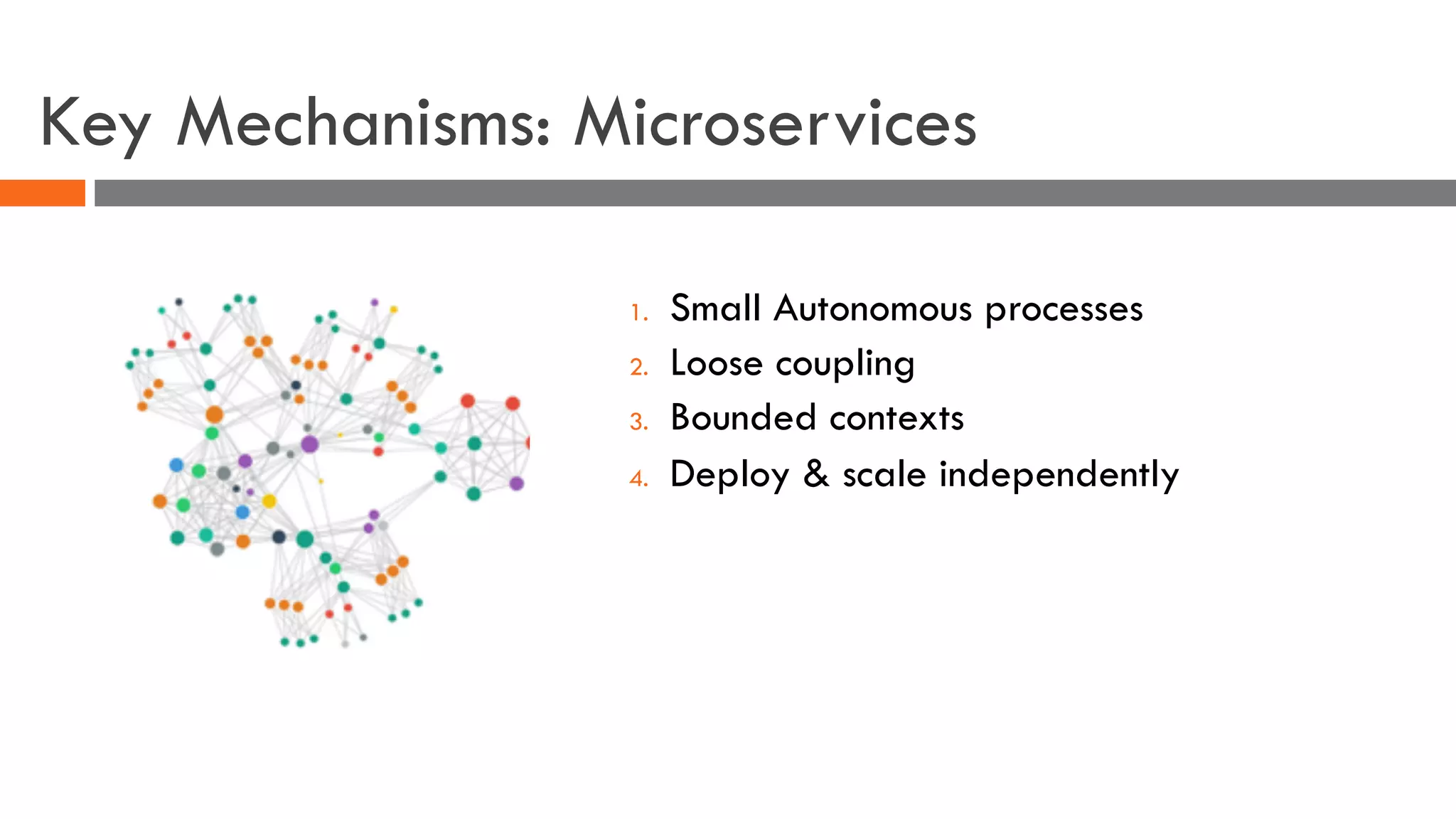
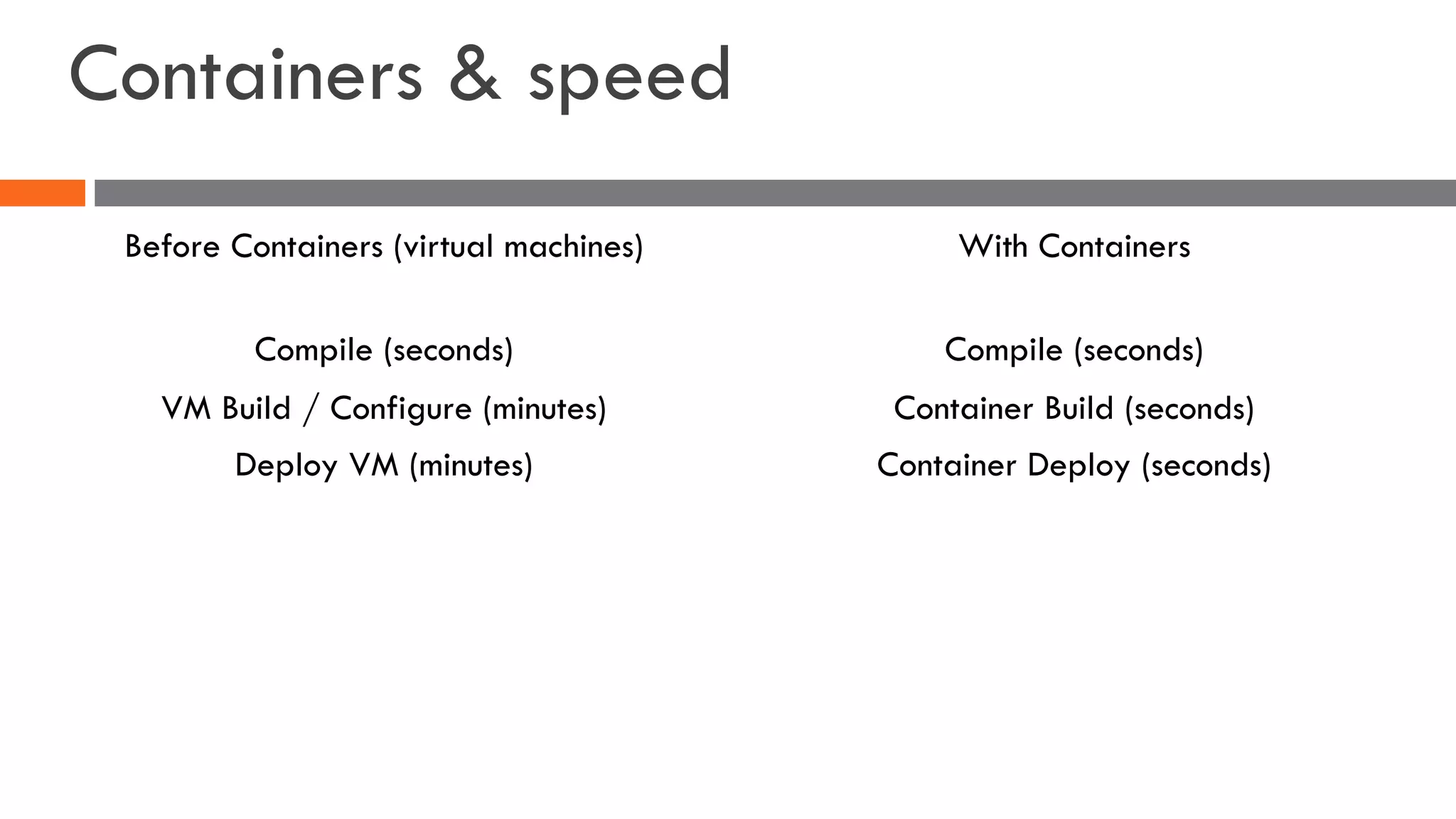
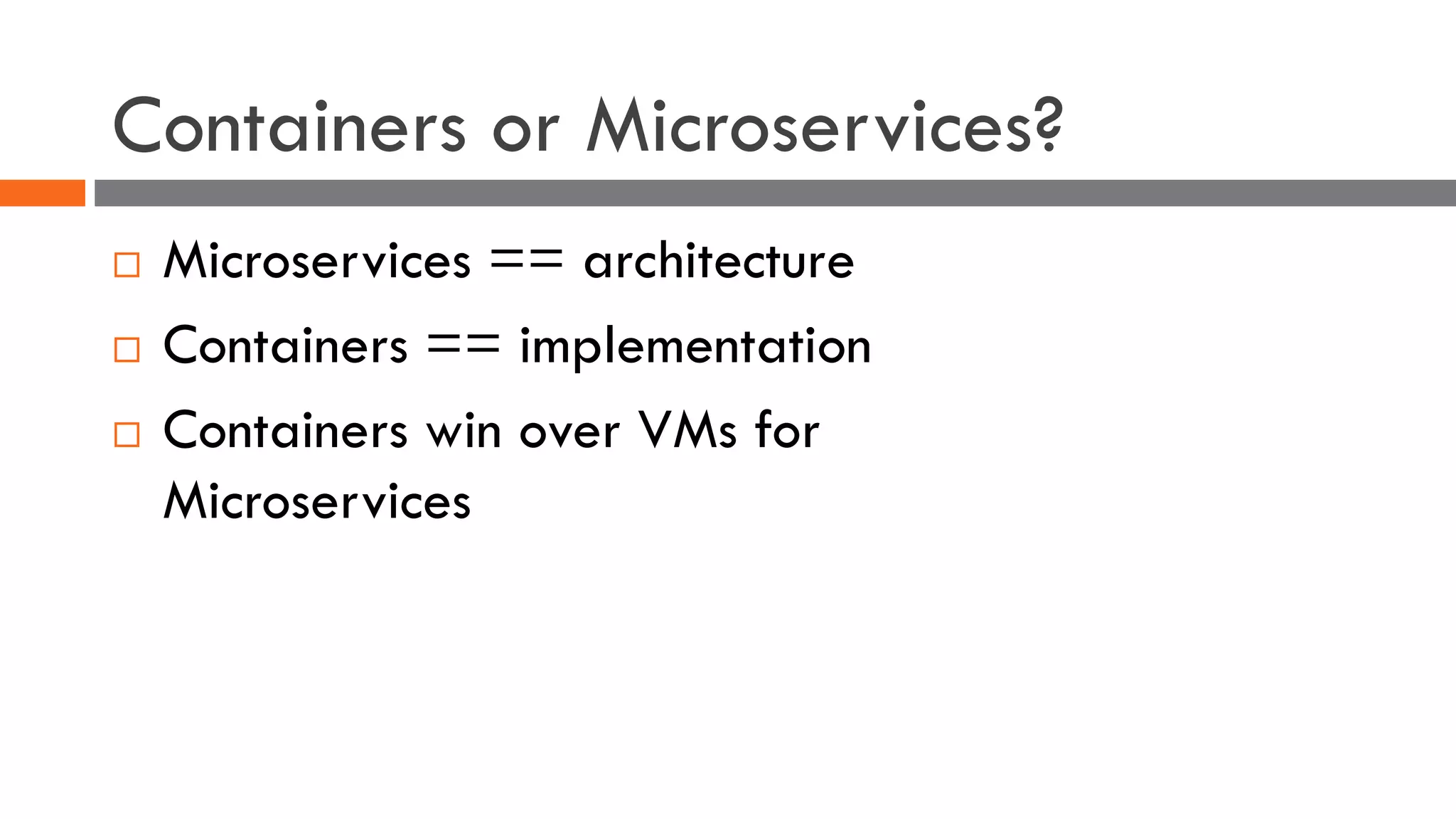
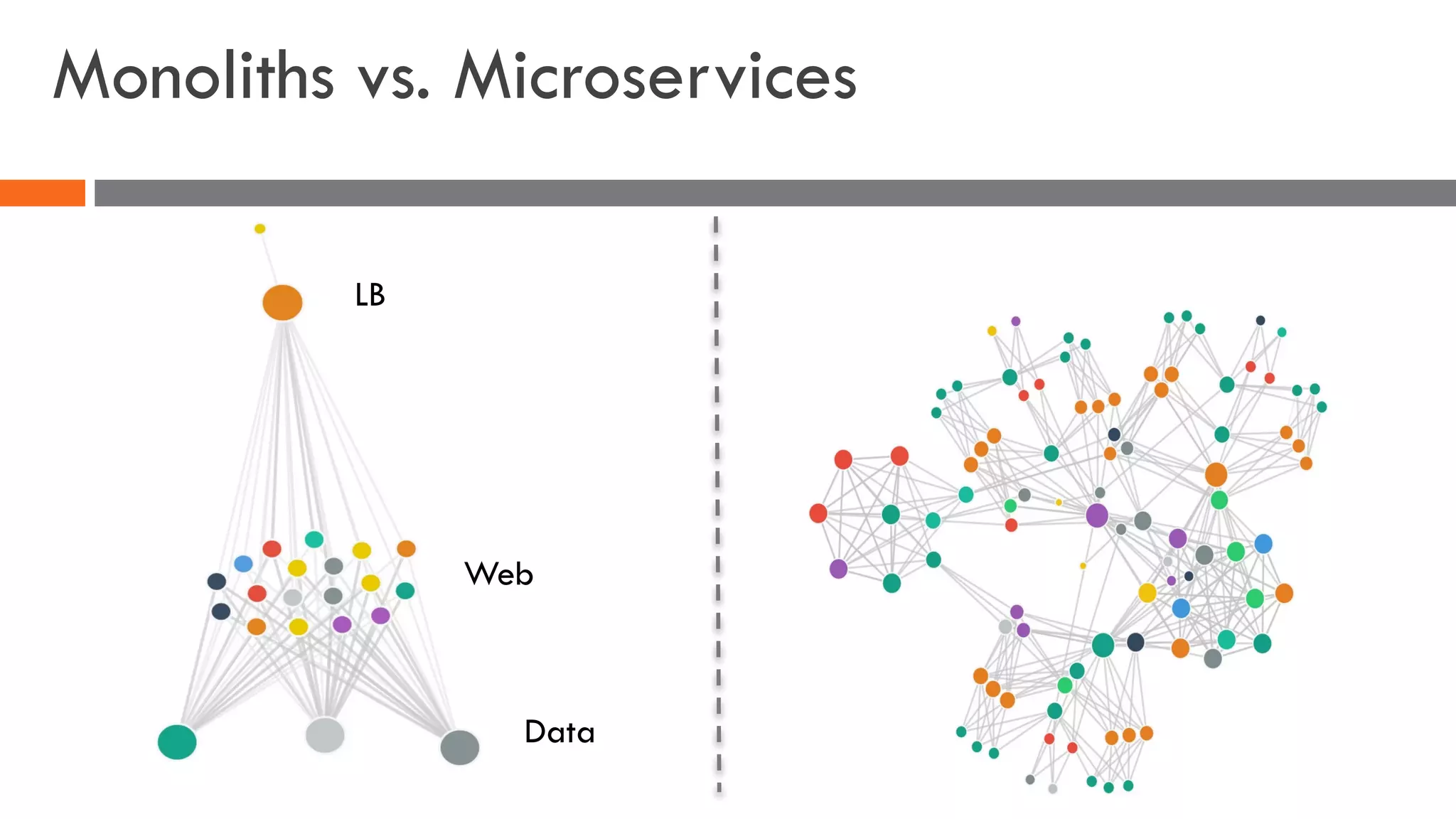
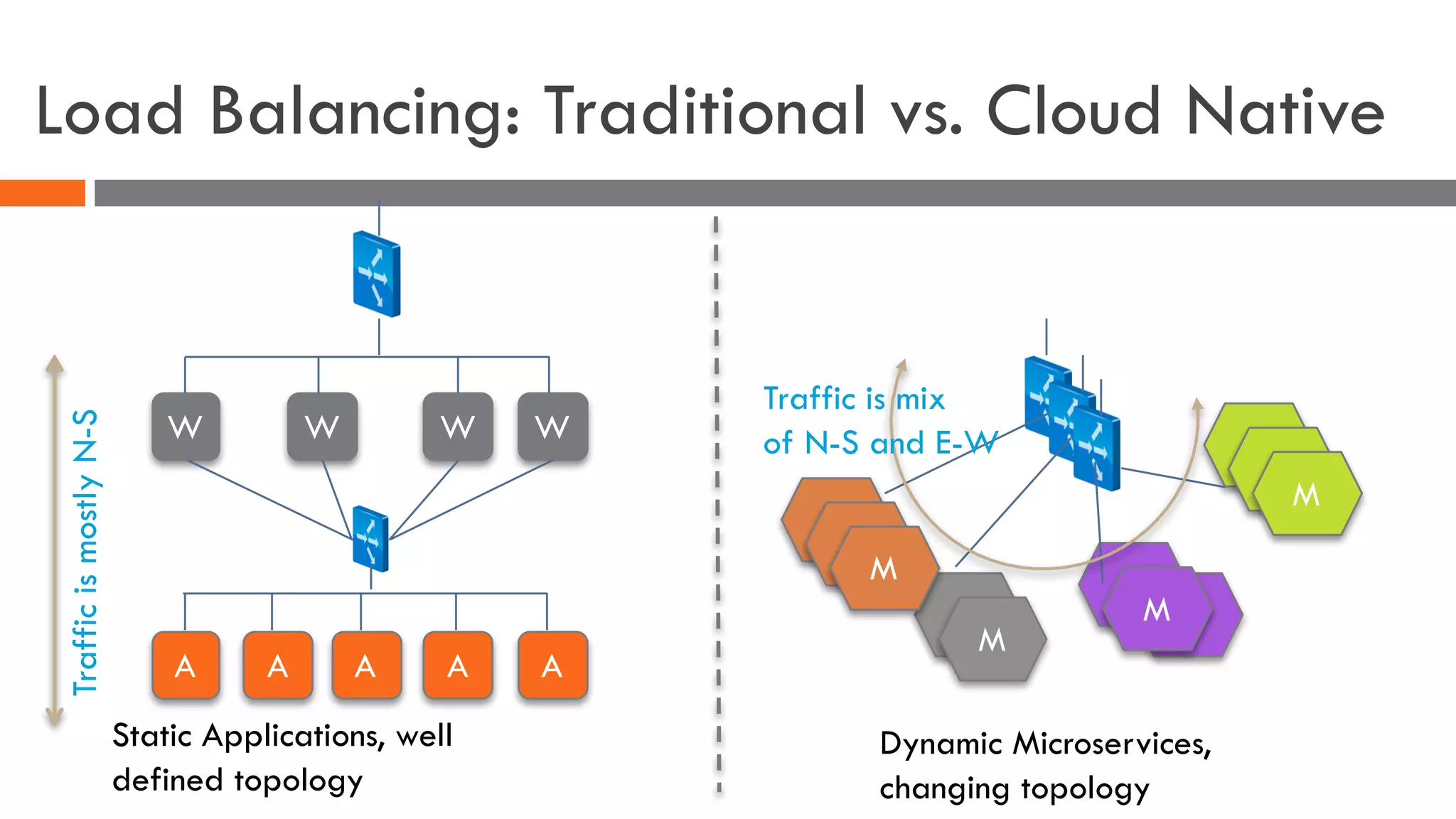
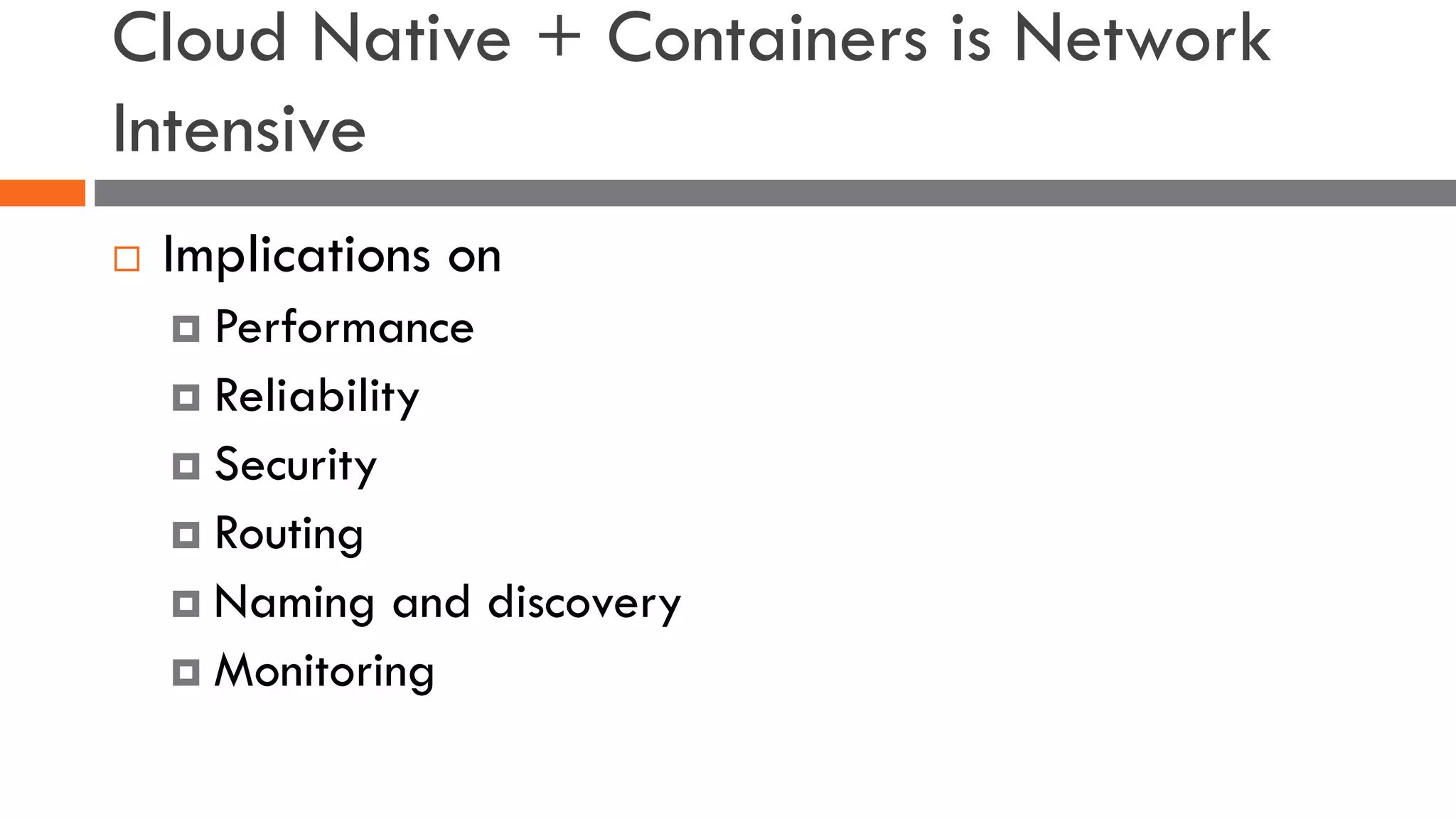
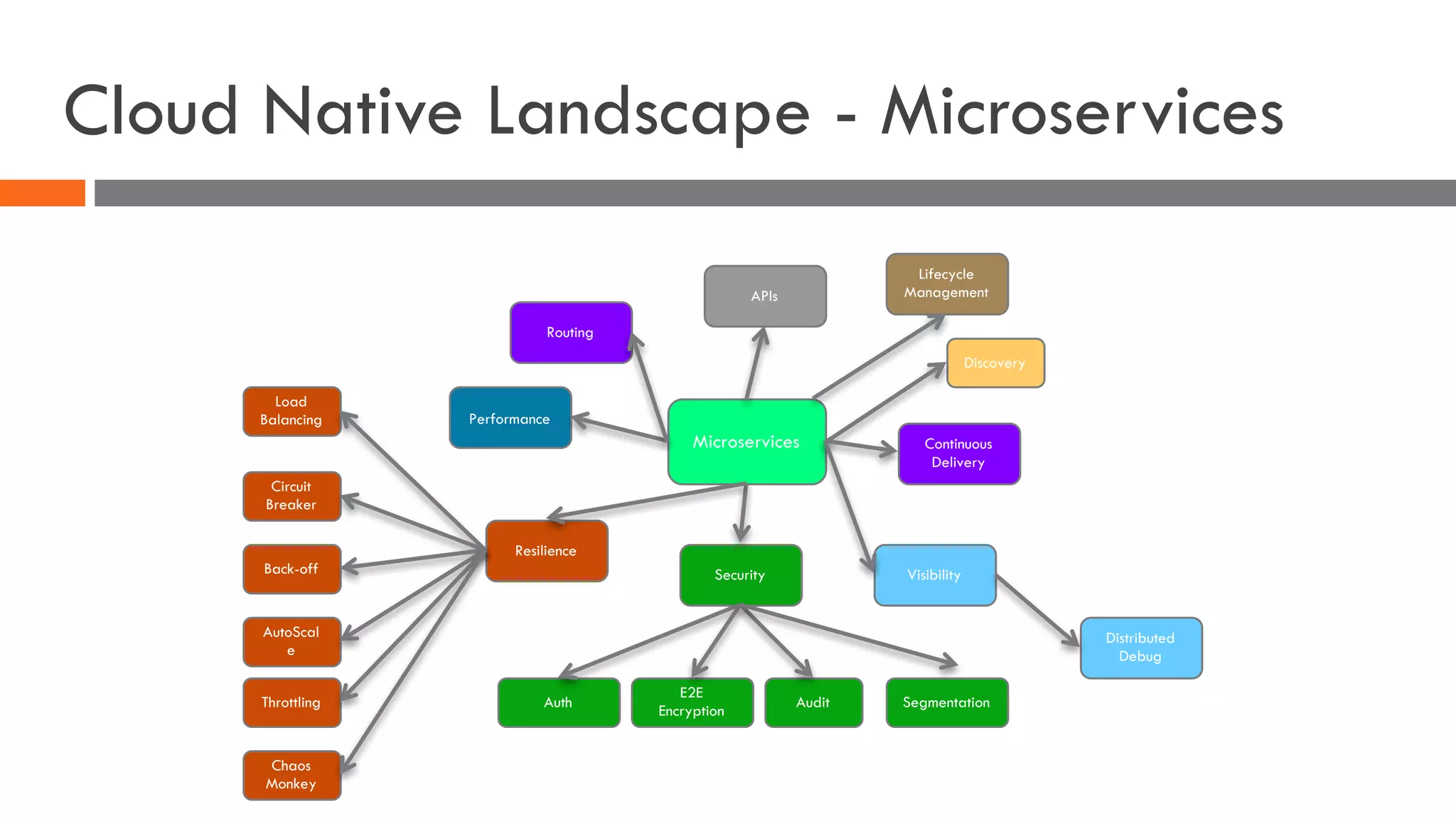
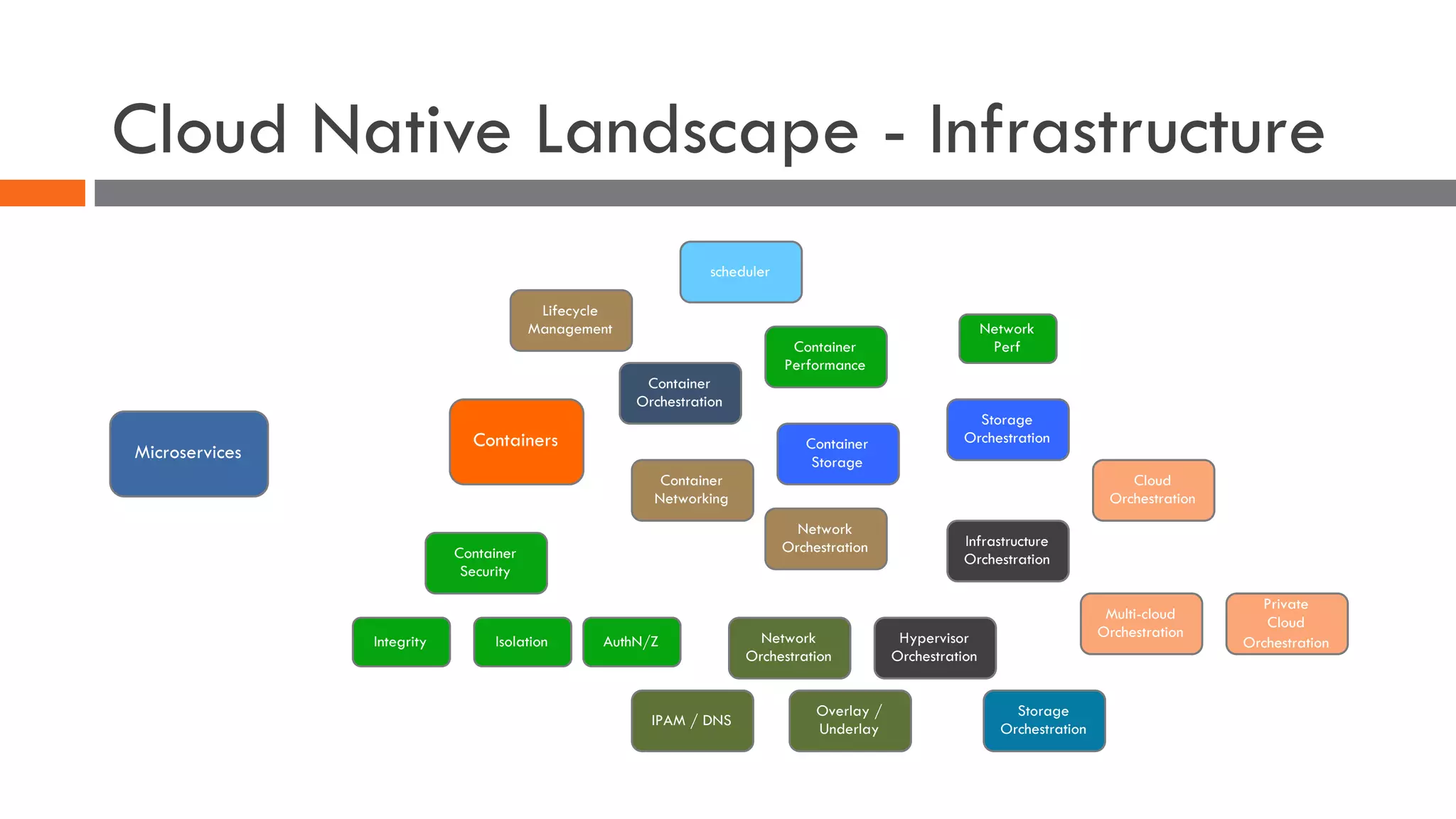
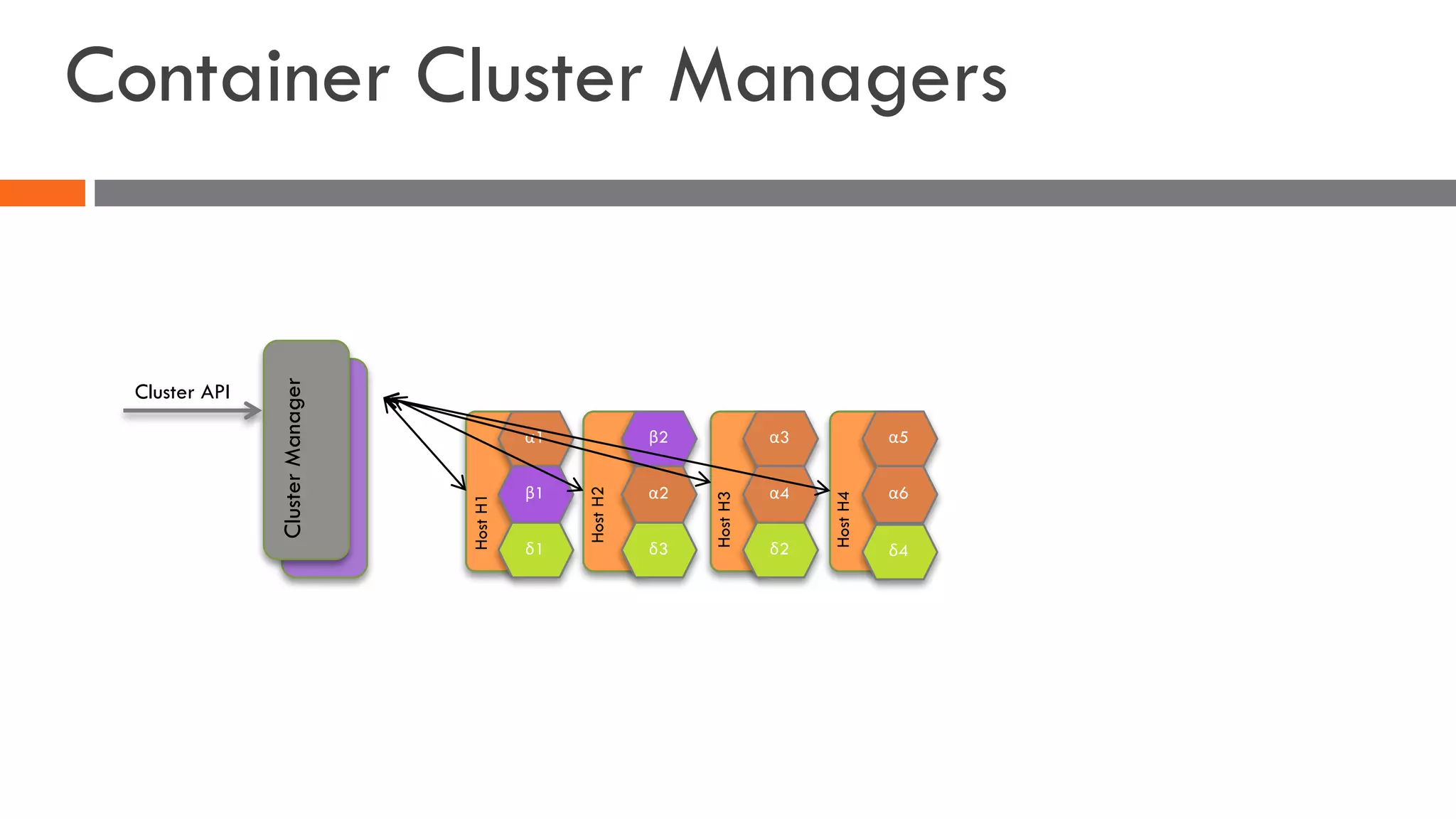
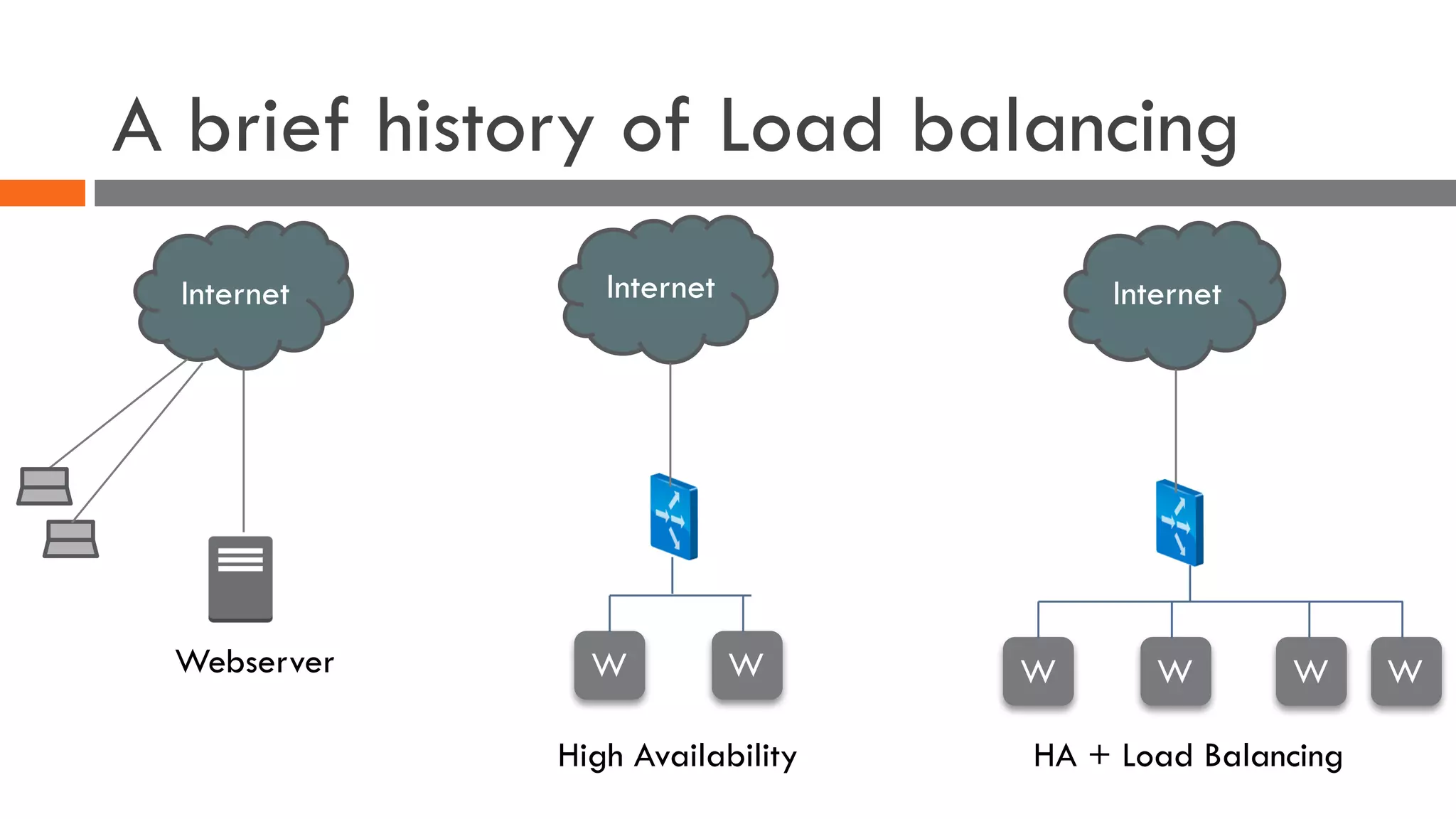
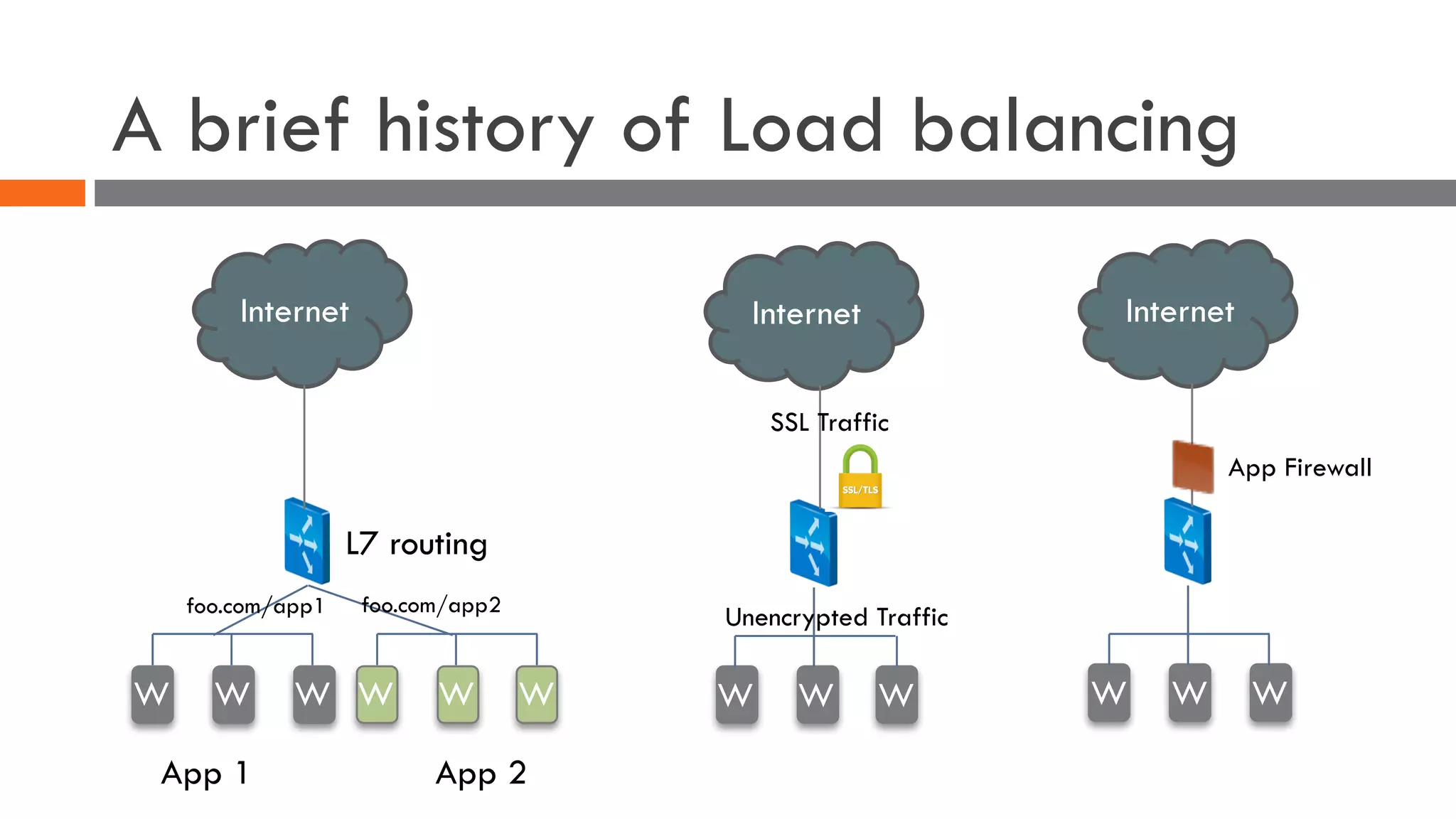
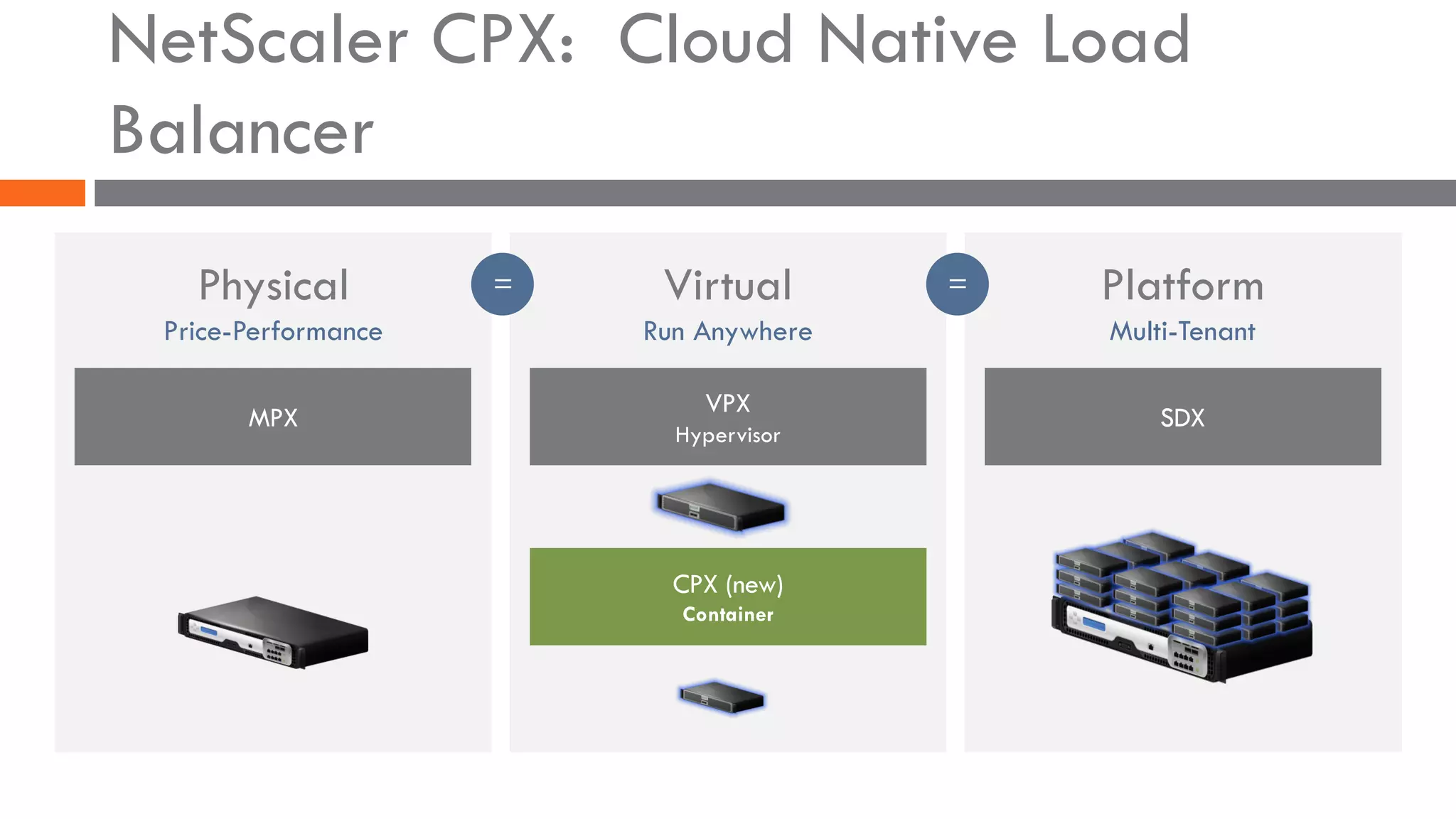
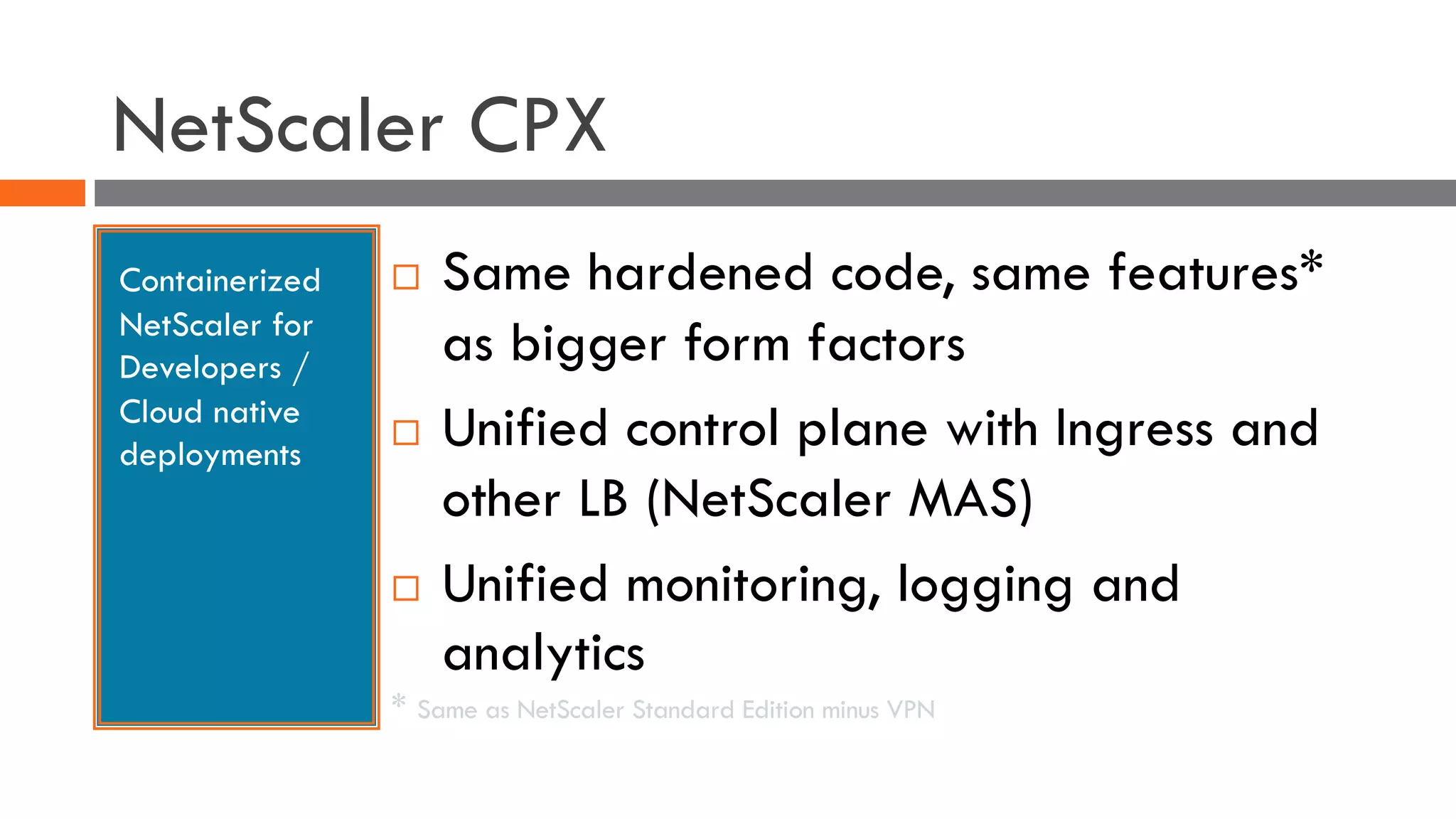
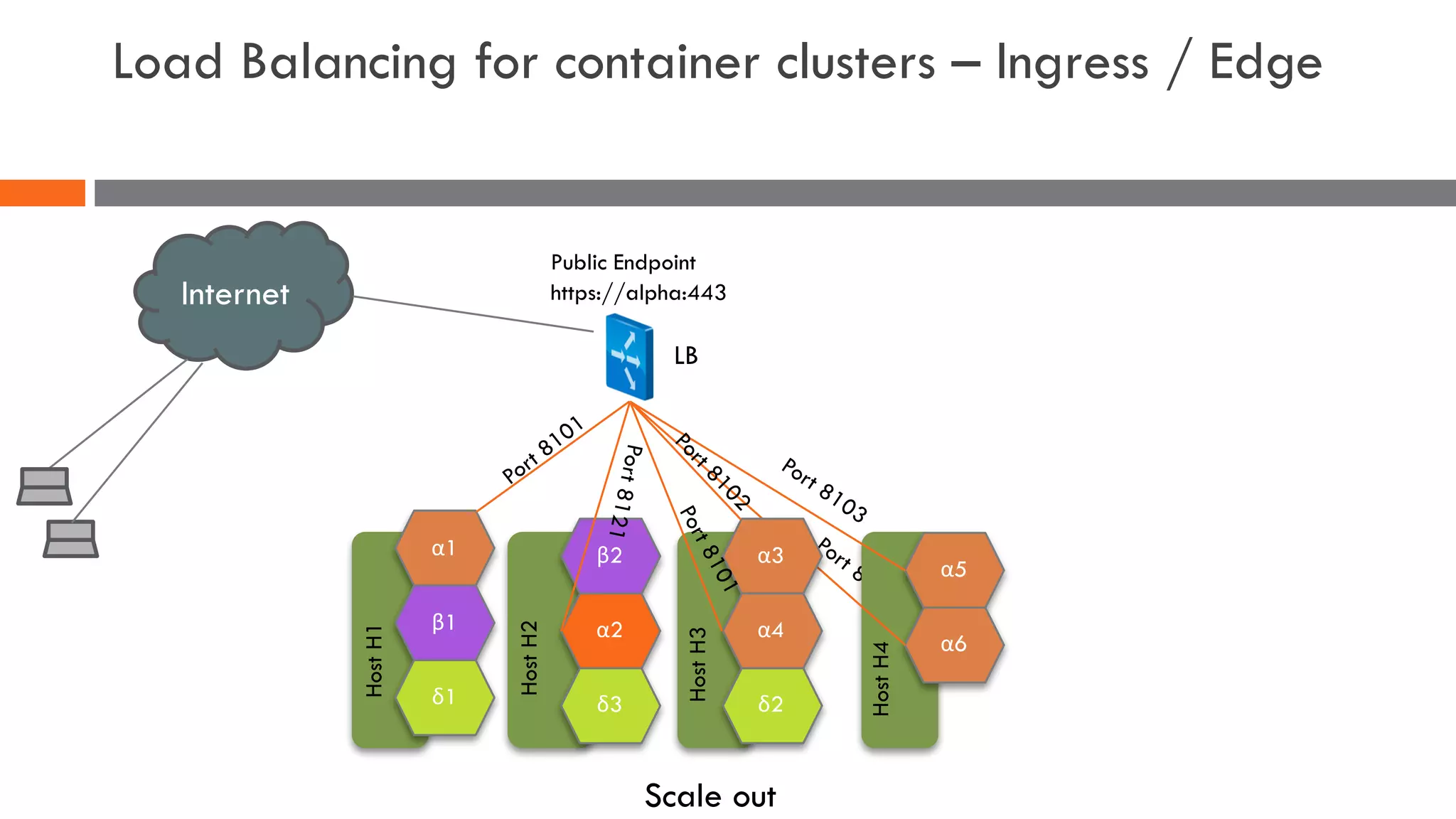
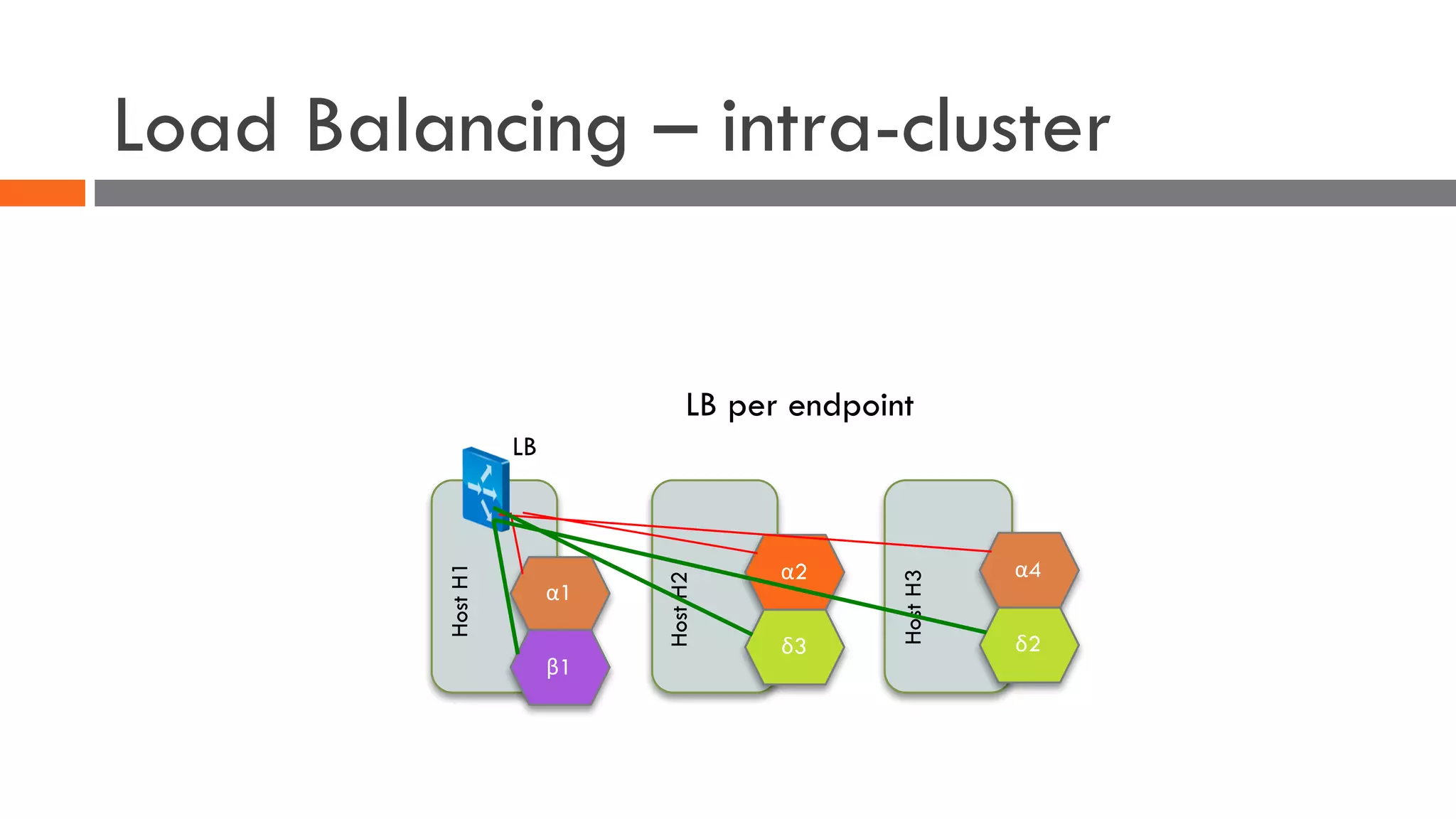
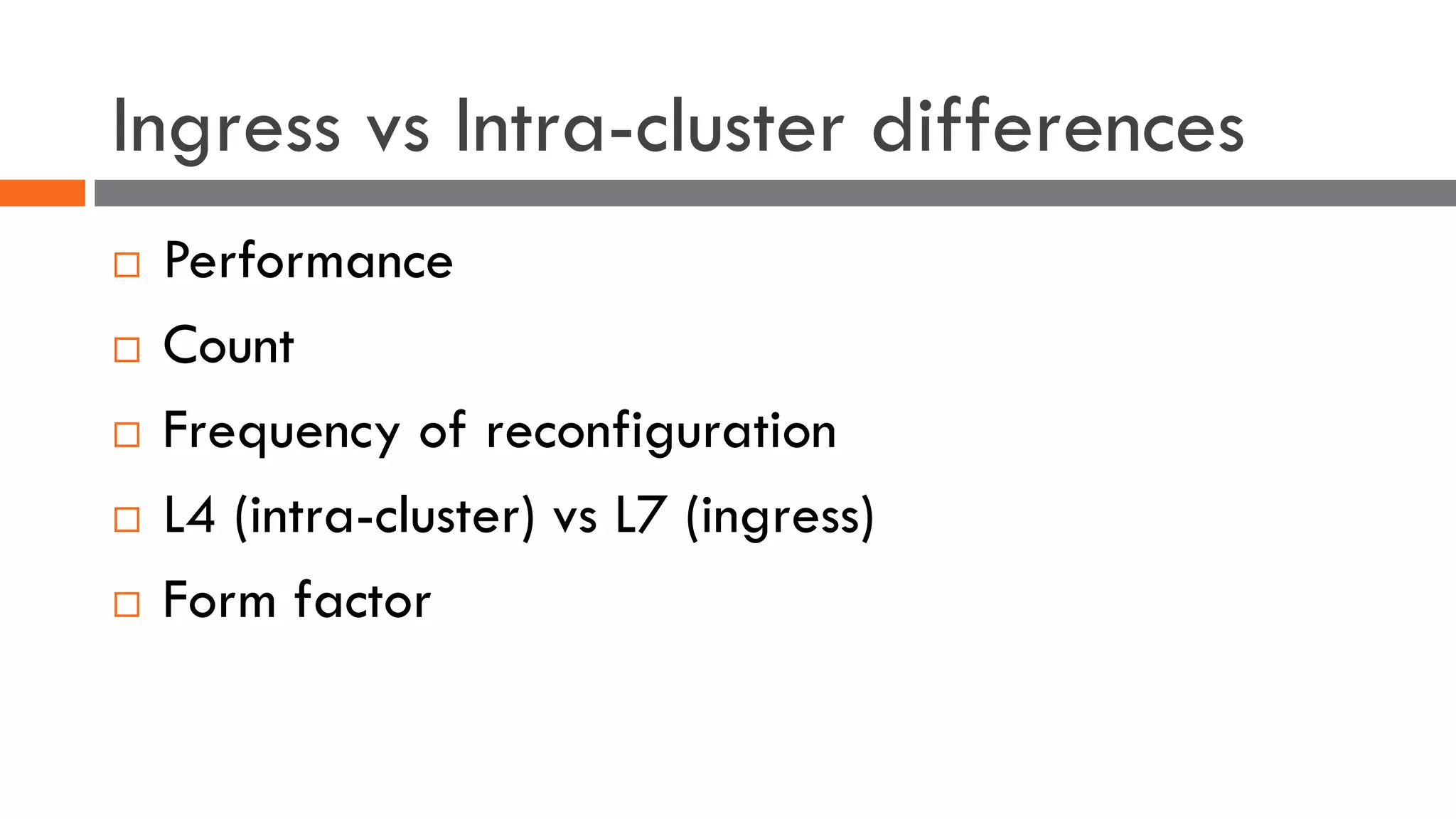
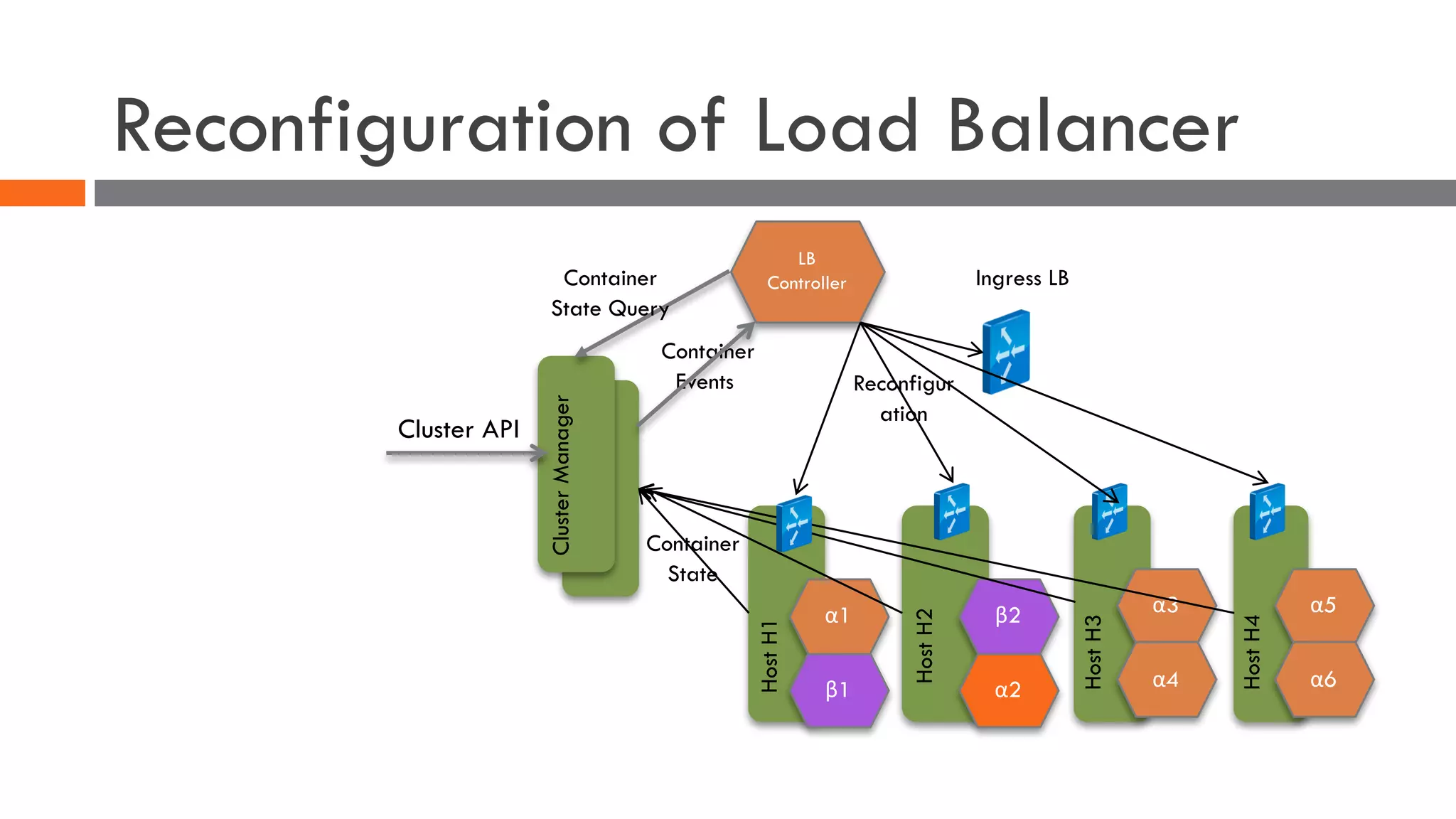
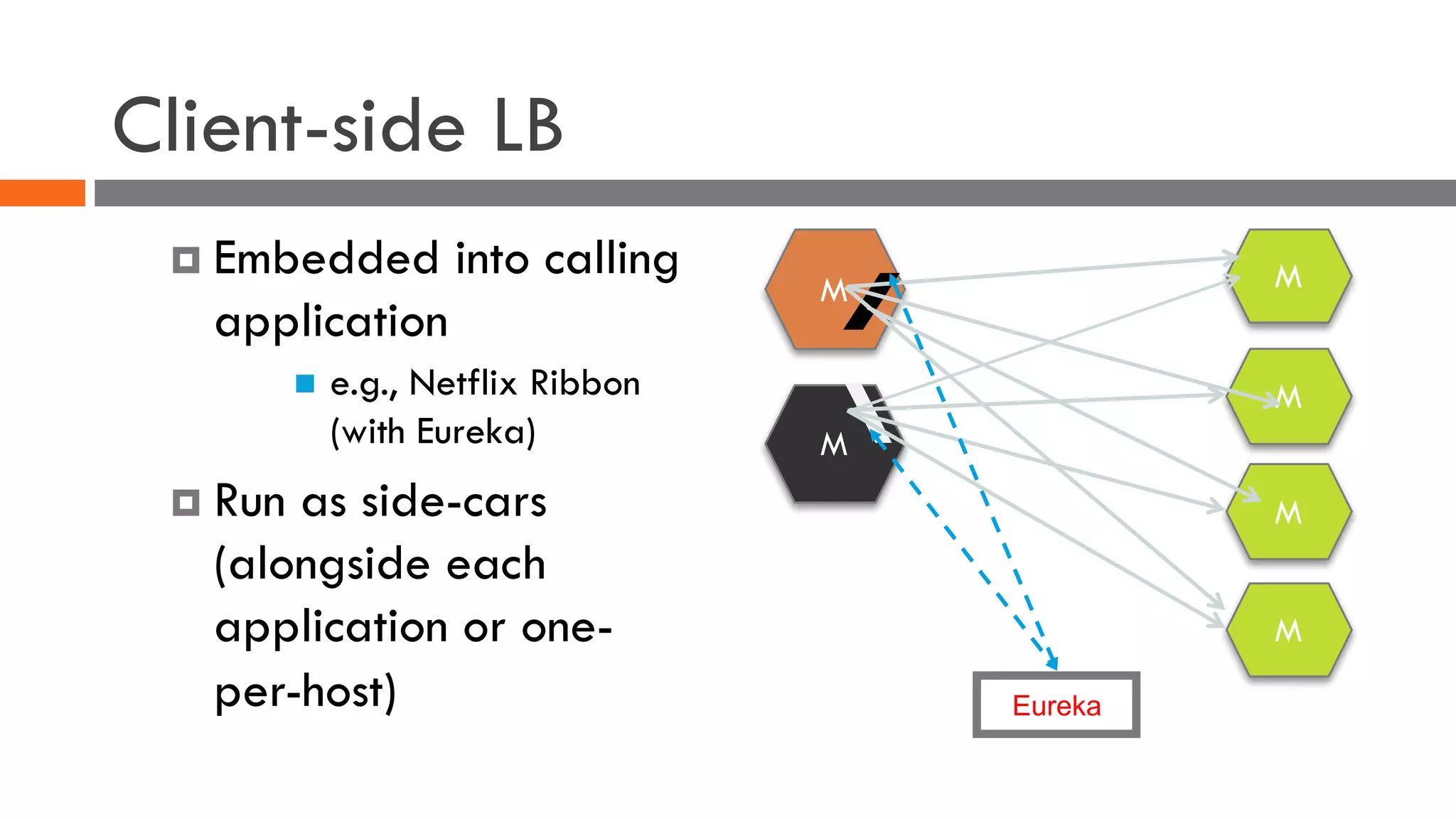
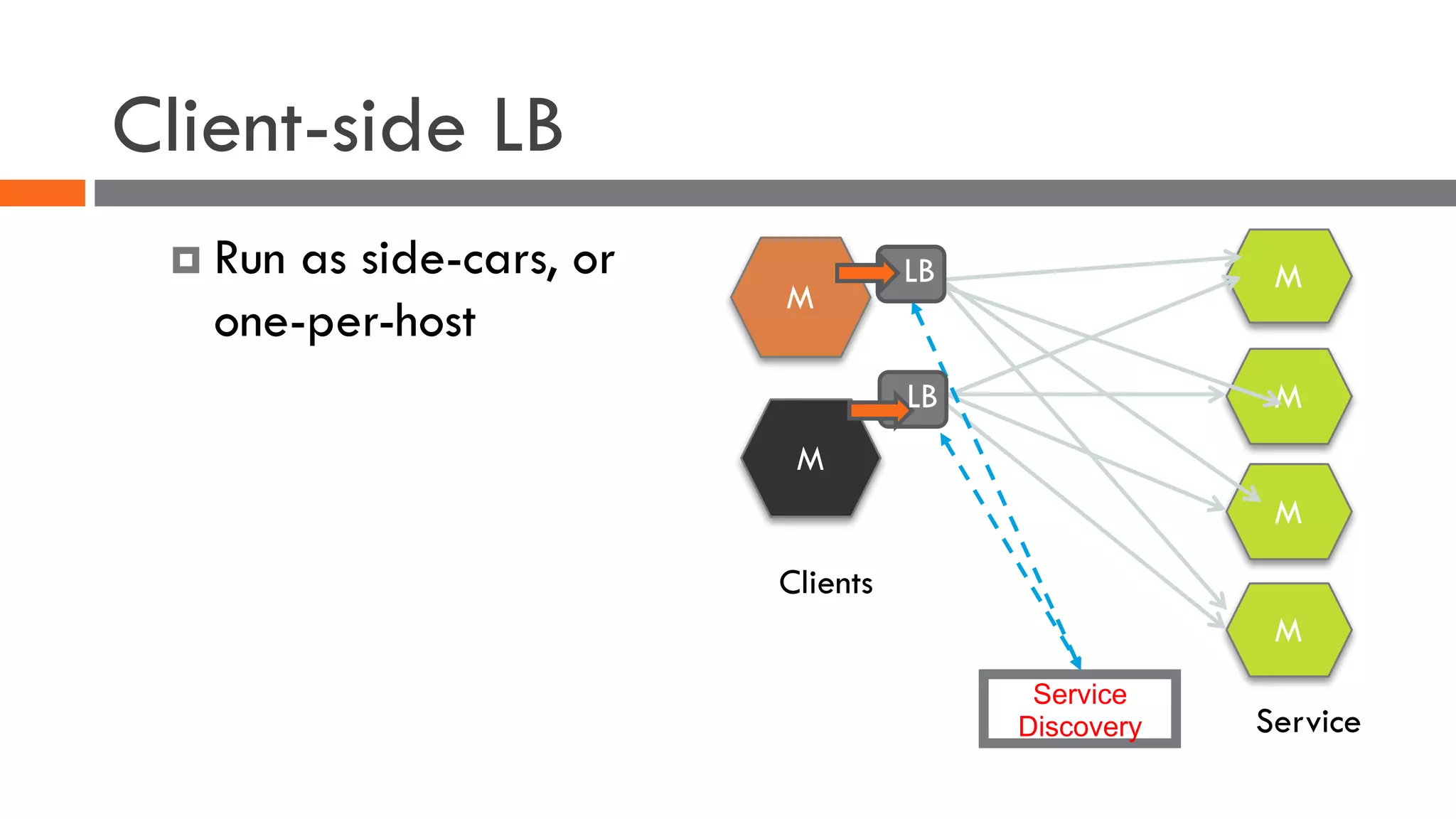
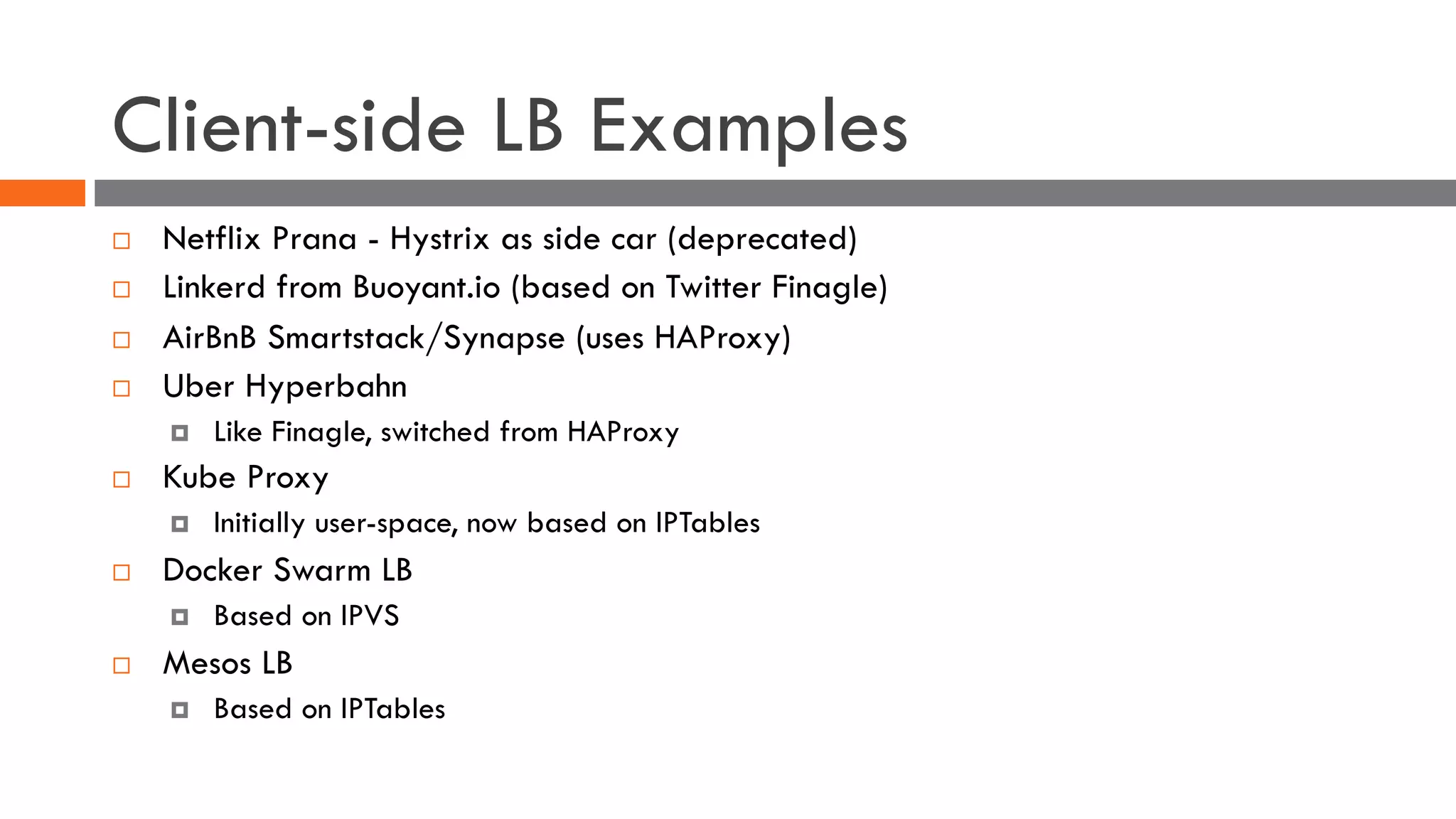
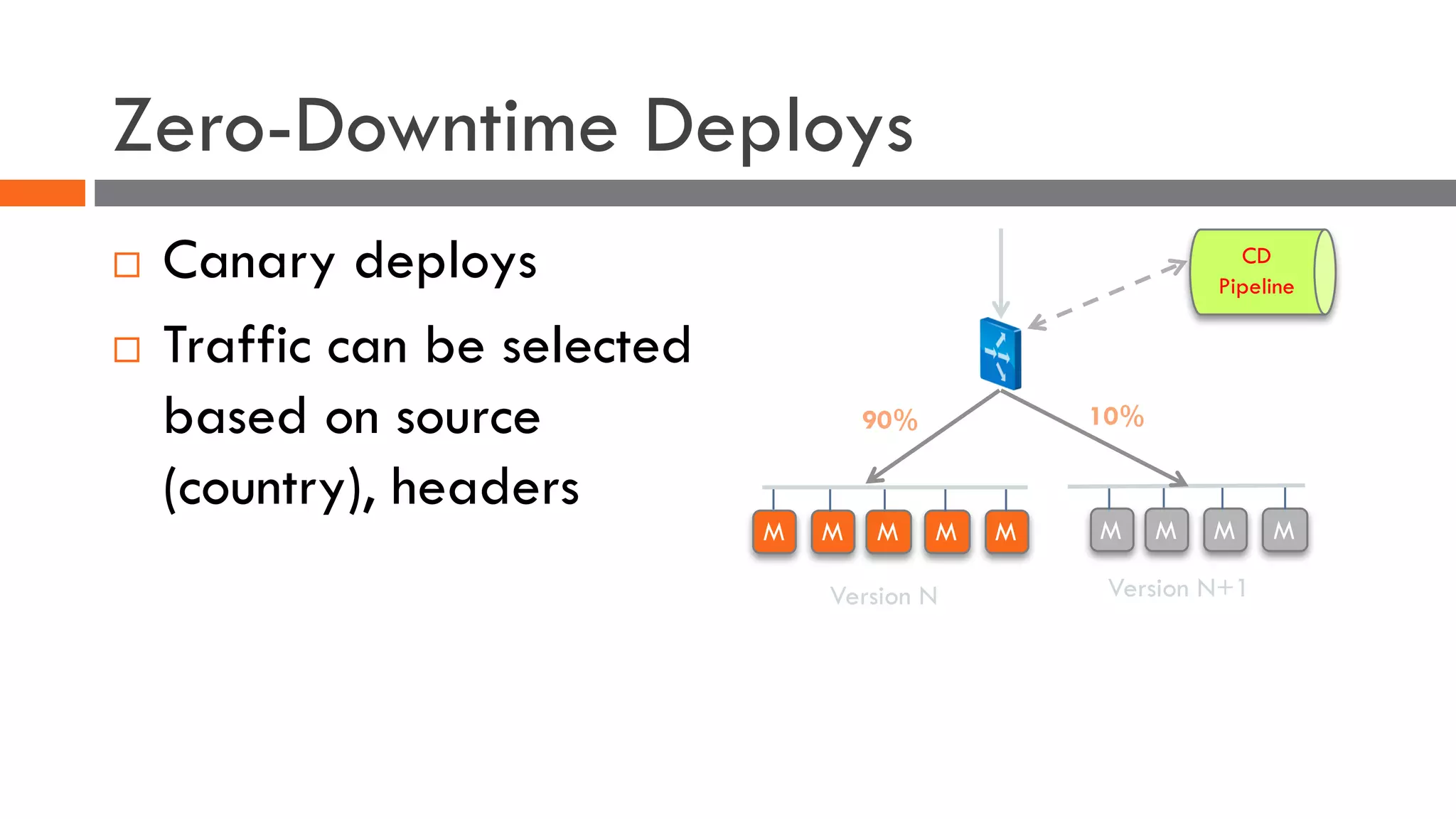
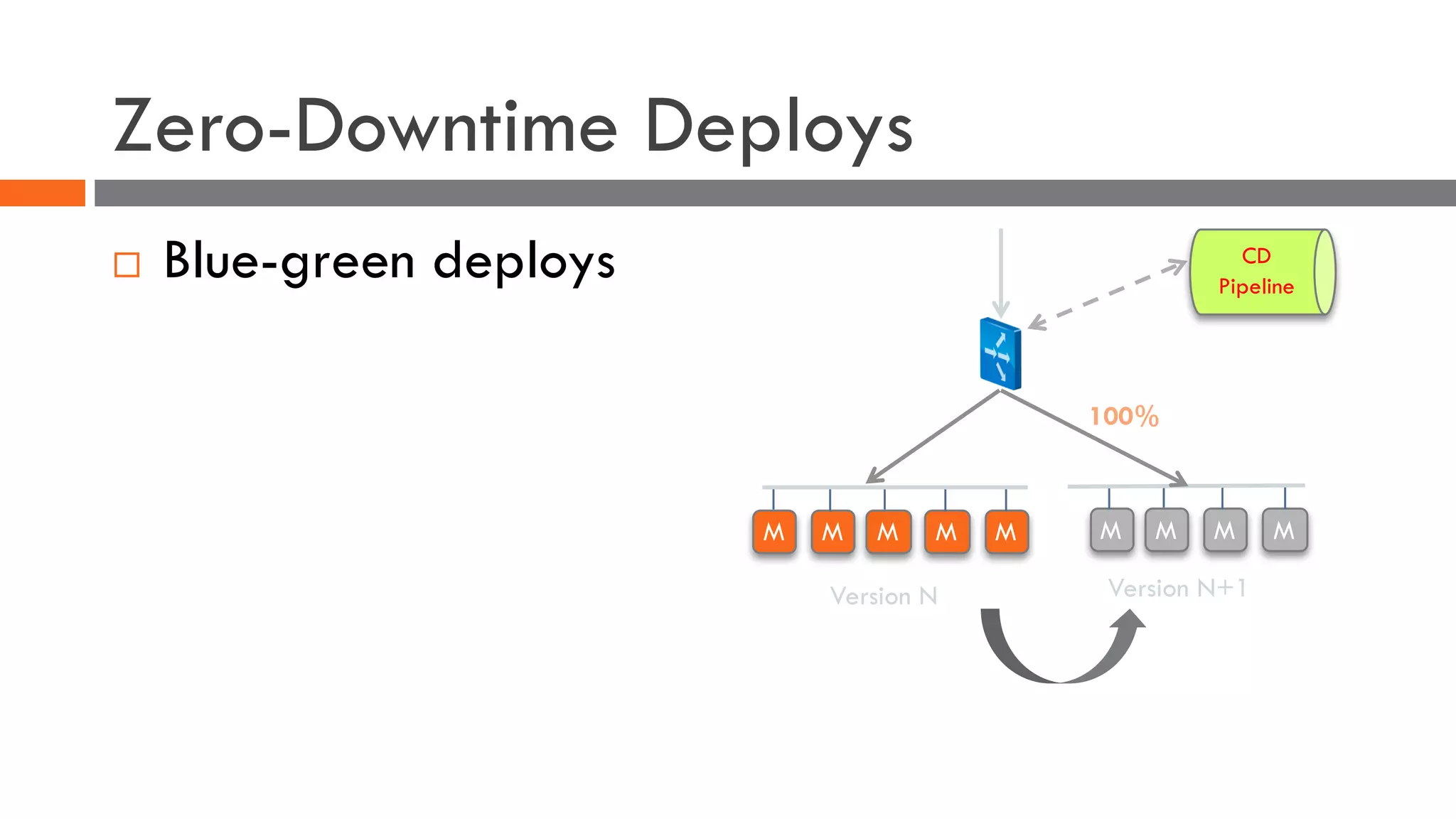
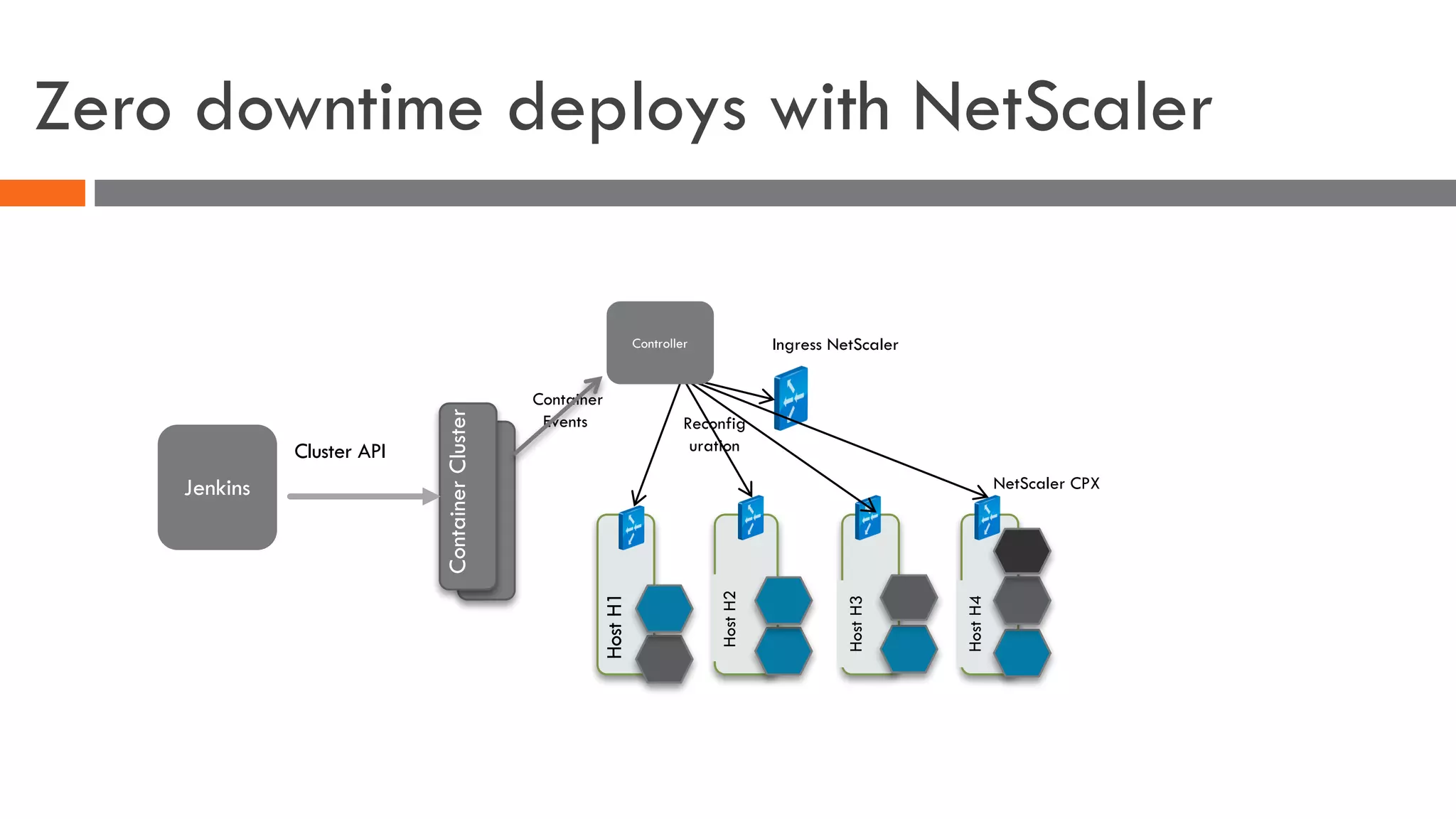
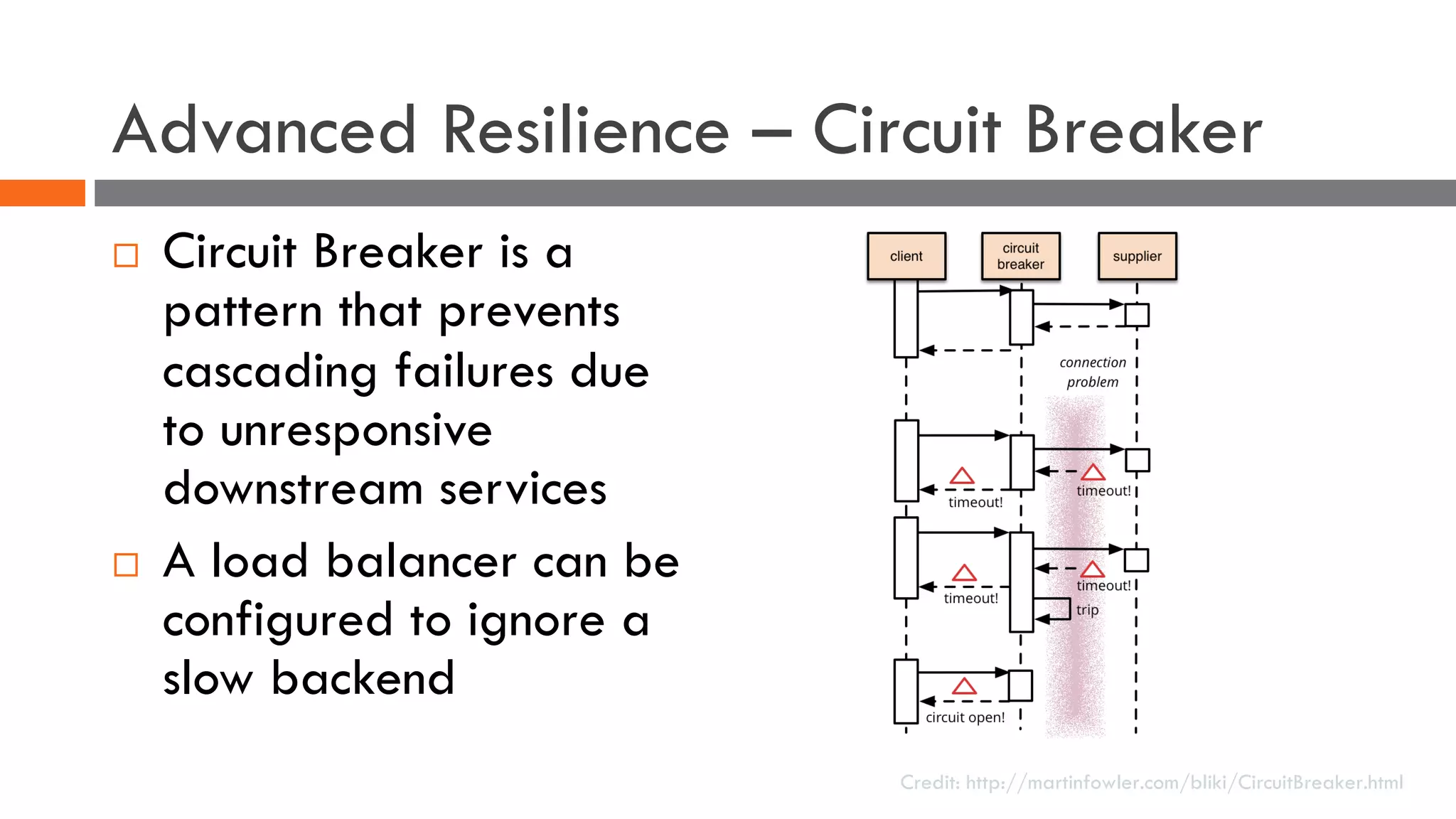
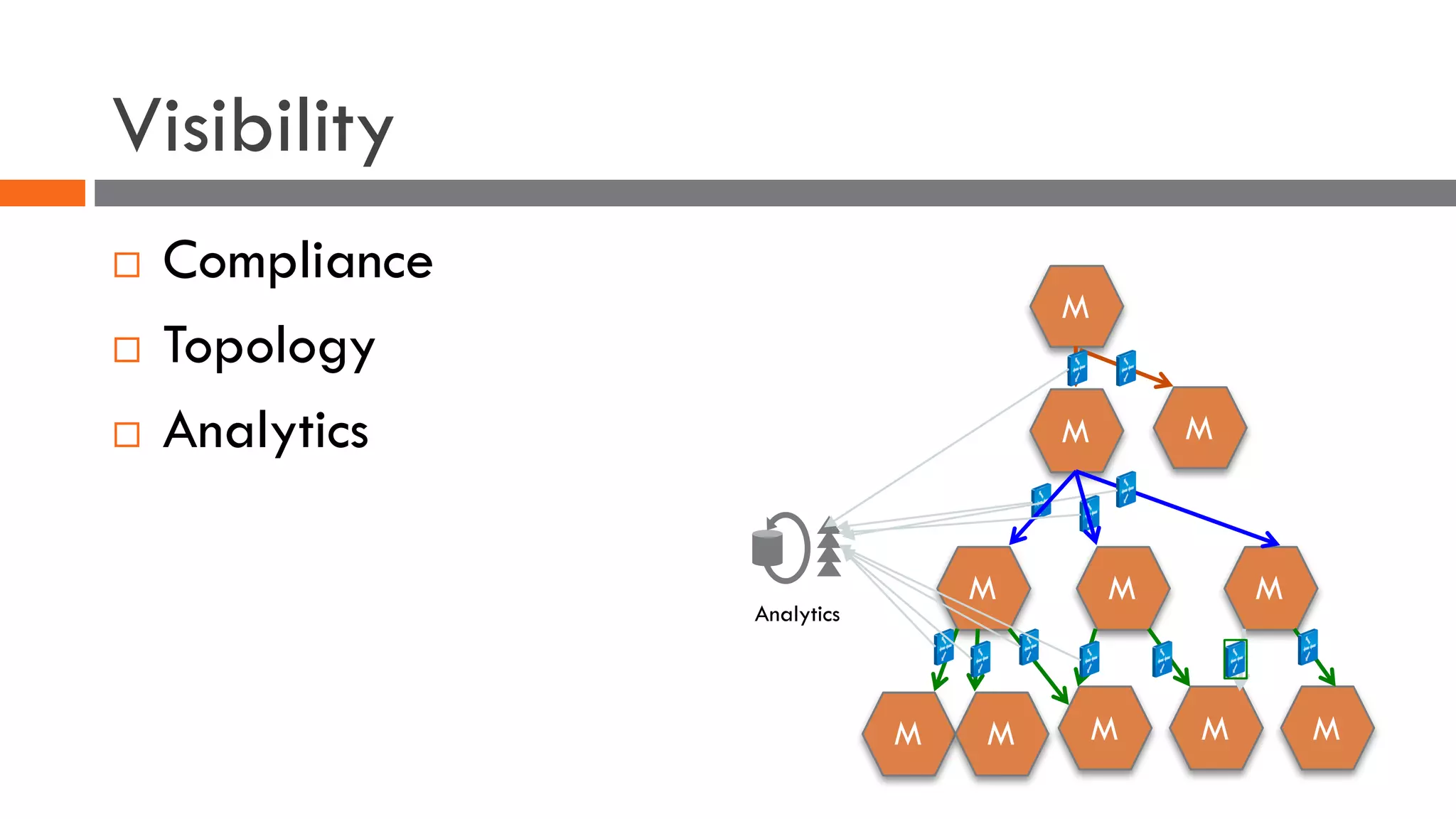
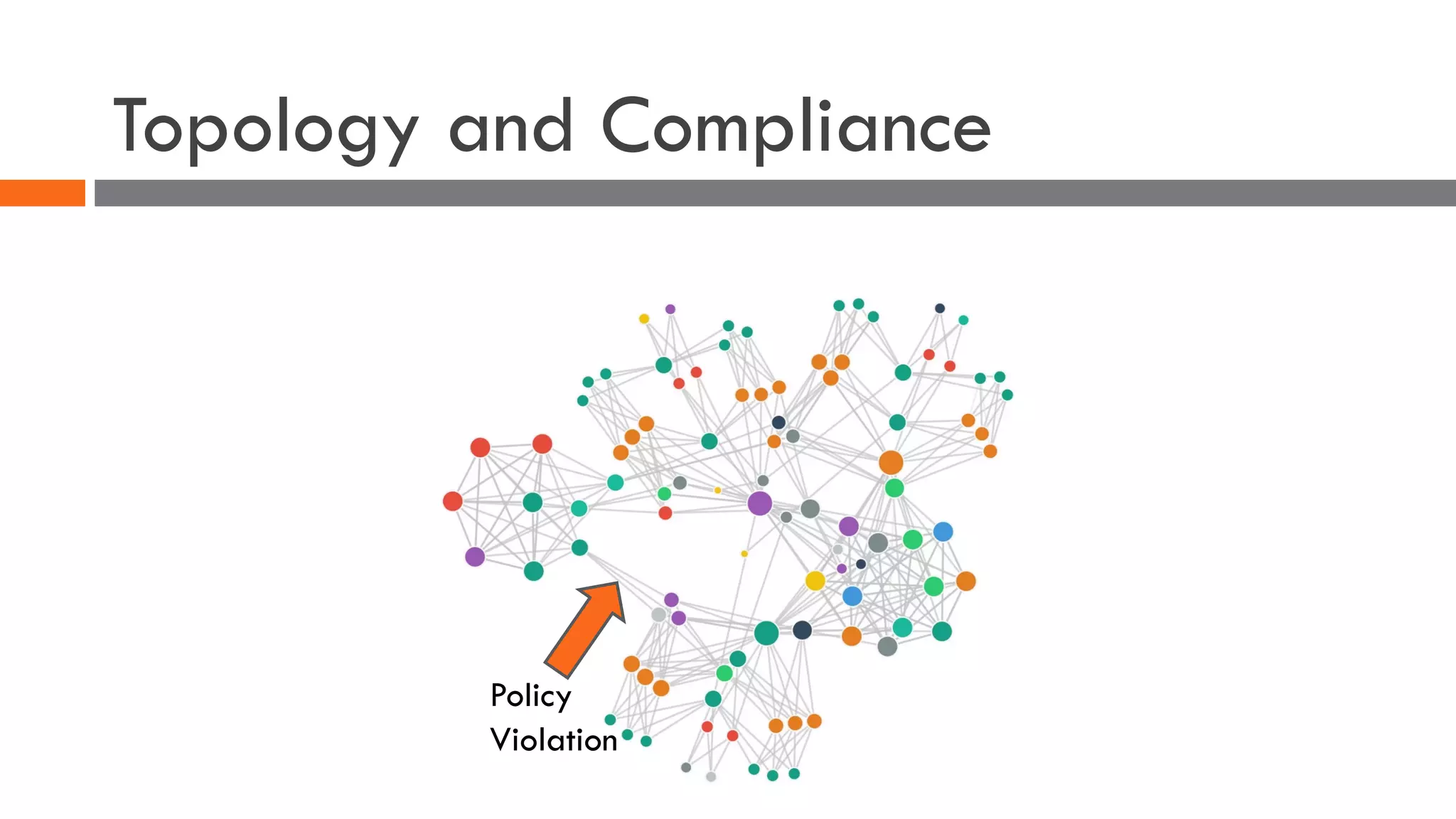
The document discusses the importance of load balancers for microservices and container-based architectures. It covers how load balancing needs have evolved from traditional monolithic applications to modern approaches that support dynamic microservices topologies, zero-downtime deployments, client-side load balancing, and advanced patterns like circuit breakers. It also introduces NetScaler CPX as a cloud-native load balancer solution for container environments.