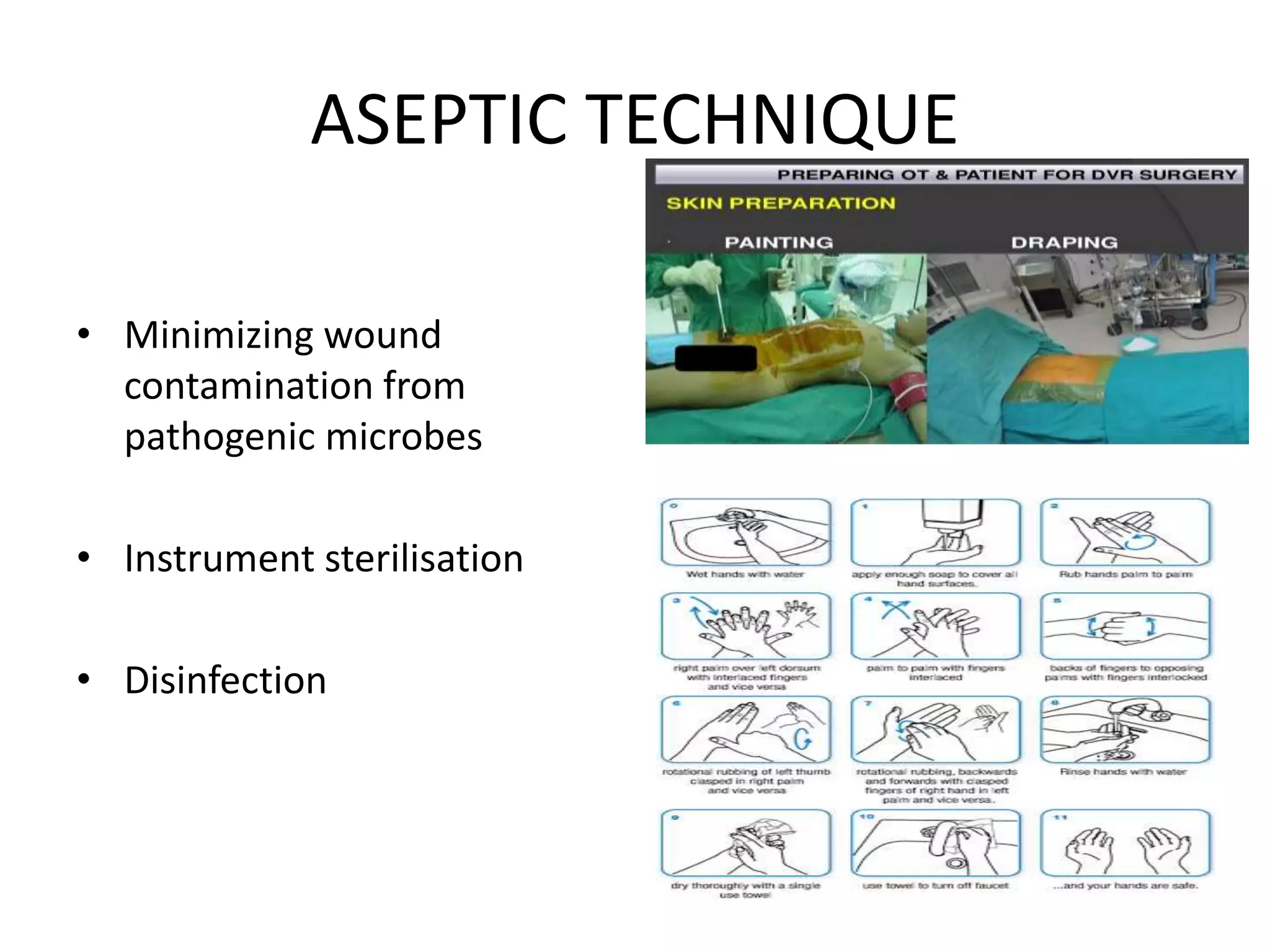
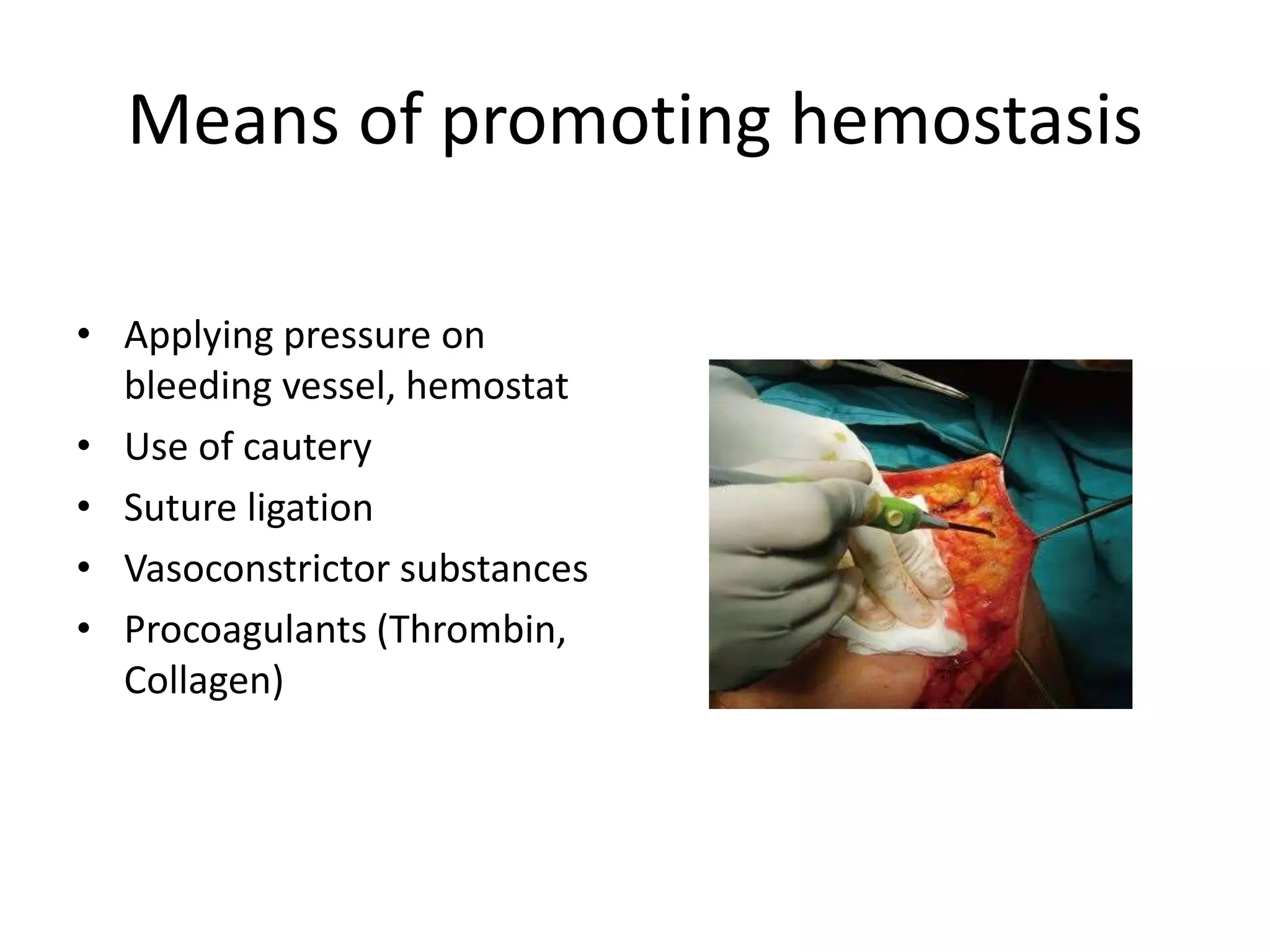
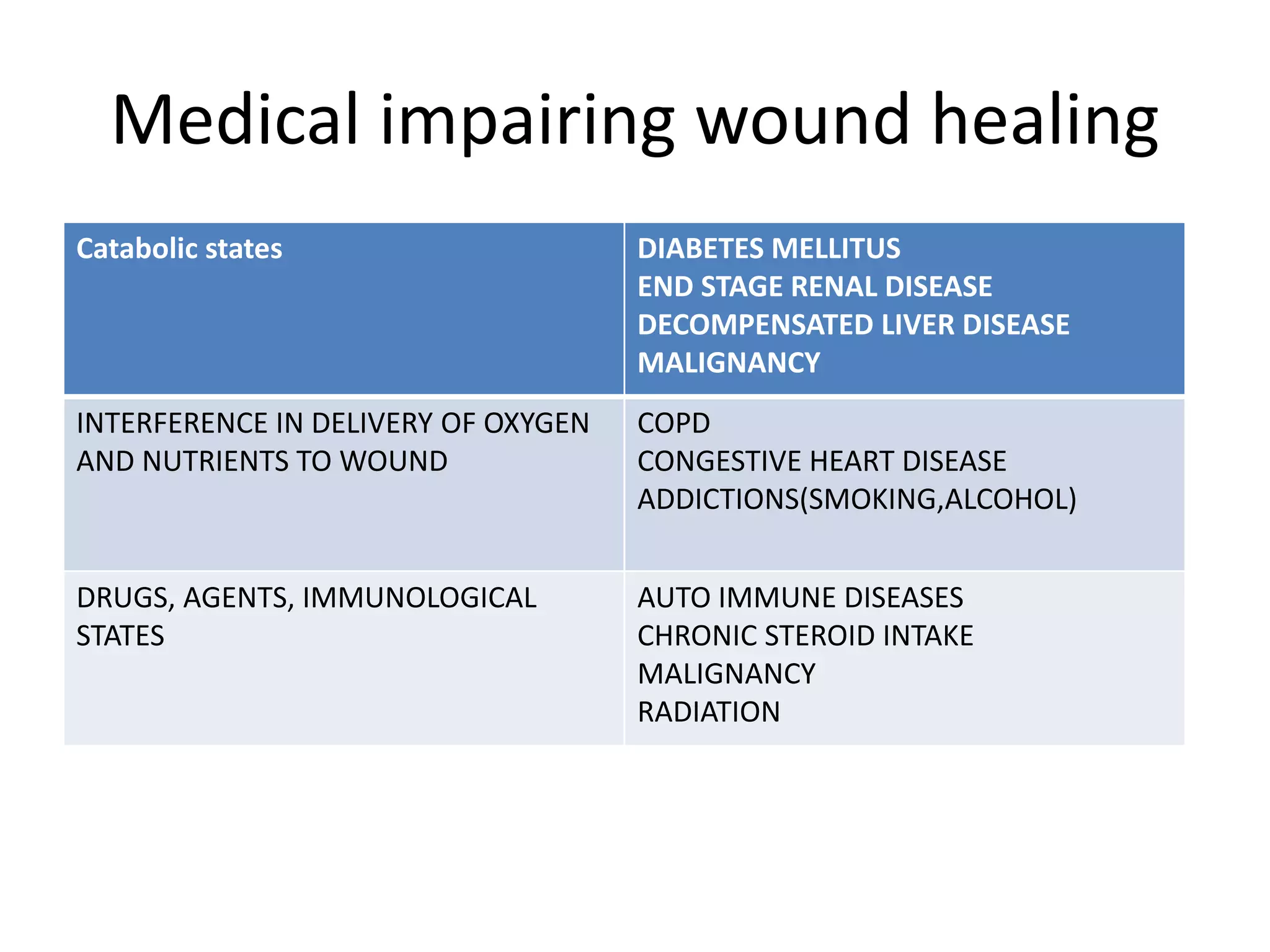
This document outlines the basic principles of general surgery, which are developed from experience to optimize healing. It discusses developing a surgical diagnosis through identifying signs, symptoms, history, and tests. The basic necessities for surgery are listed as consent, access, anesthesia, visibility, hemostasis, and assistance. Aseptic technique, incisions, tissue handling, hemostasis, wound healing, decontamination, edema control, and nutrition are also covered. Principles like gentle tissue handling, hemostasis, and patient optimization are emphasized for proper healing.